|
Zirid Dynasty
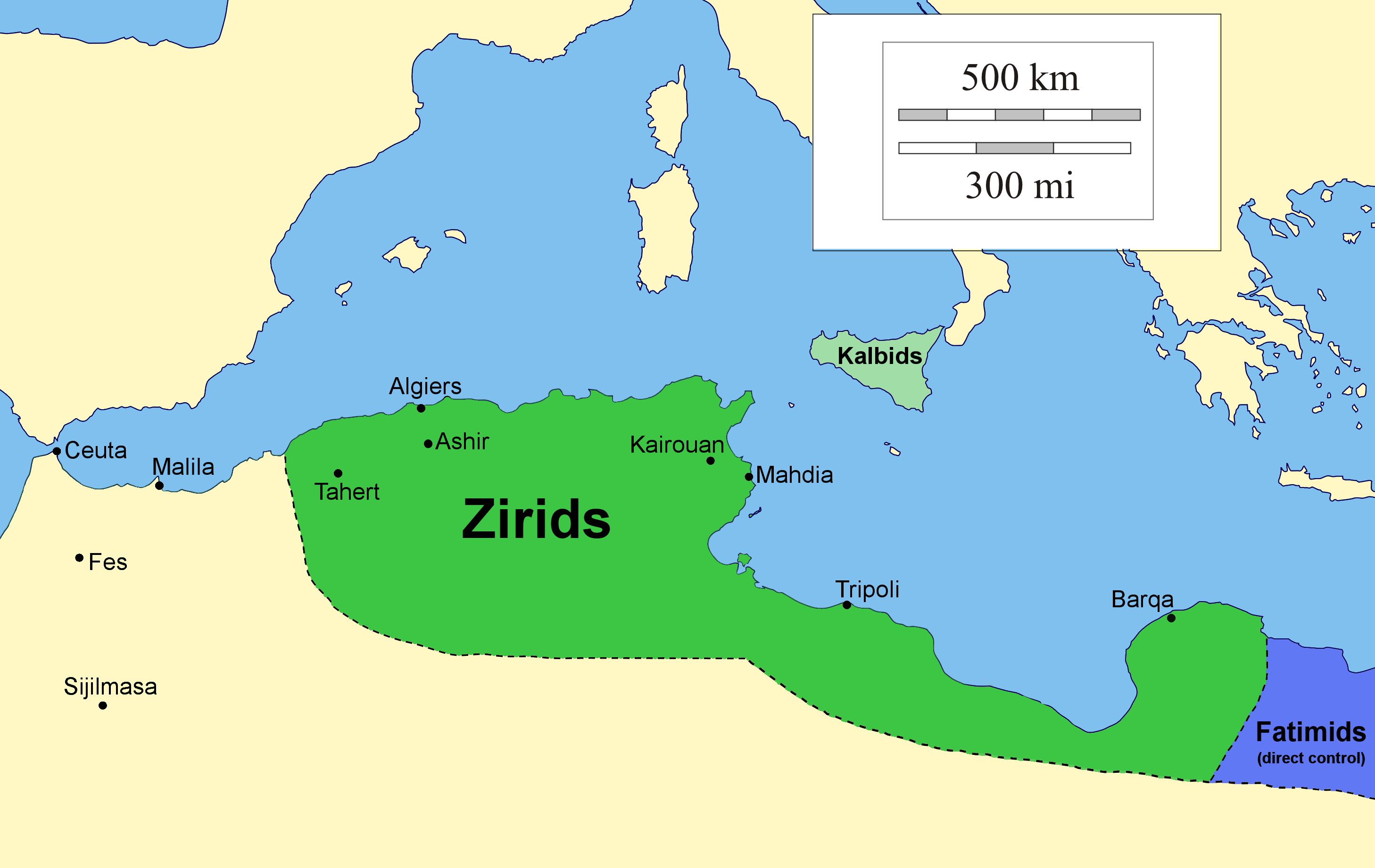
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148. Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of the Fatimid Caliphate and the eponymous founder of the dynasty, the Zirids were emirs who ruled in the name of the Fatimids. The Zirids gradually established their autonomy in Ifriqiya through military conquest until officially breaking with the Fatimids in the mid-11th century. The rule of the Zirid emirs opened the way to a period in North African history where political power was held by Berber dynasties such as the Almoravid dynasty, Almohad Caliphate, Zayyanid dynasty, Marinid Sultanate and Hafsid dynasty. Under Buluggin ibn Ziri the Zirids extended their control westwards and briefly occupied Fez and much of present-day Morocco after 980, but encountered resistance from the local Zenata Berbers who gave their allegiance to the Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanhaja
The Sanhaja (, or زناگة ''Znāga''; , pl. Iẓnagen, and also Aẓnaj, pl. Iẓnajen) were once one of the largest Berbers, Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zenata, Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Tunisia and Western Sahara bore and still carry this ethnonym, especially in its Berber languages, Berber form. Other names for the population include ''Zenaga'', ''Znaga'', ''Sanhája'', ''Sanhâdja'' and ''Senhaja''. Triad Ibn Khaldun and others defined the Sanhaja as a grouping made up of three separate confederations, not as a single confederation. The distinction is usually made with a diacritical point placed above or below that is present in the Arabic text and often lost in English. # Danhāǧa/Sanhaja [Sanhaja of the first type] is a confederation of: Kutama, Kutāma-Igawawen, Zawāwa of the Kabyle people, Kabyle mountains, including some areas like Algiers and Constantine, Algeria, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Atlas
The Tell Atlas (, Latn, ar, al-ʾaṭlas al-tlī) is a mountain chain over in length, belonging to the Atlas mountain ranges in North Africa, stretching mainly across northern Algeria, ending in north-eastern Morocco and north-western Tunisia. The ranges of this system have an average elevations of about and form a natural barrier between the Mediterranean and the Sahara. Its highest summit is the high Lalla Khedidja in the Djurdjura Range. Several large cities such as the Algerian capital, Algiers, with ~1,500,000 residents (2005) and Oran with ~770,000 residents (2005) lie at the base of the Tell Atlas. The Algerian city Constantine with approximately 505,000 residents (2005) lies 80 km inland and directly in the mountains at 650 meters in elevation. A number of smaller towns and villages are situated within the Tell; for example, Chiffa is nestled within the Chiffa gorge. Geography The Tell Atlas runs parallel to the Mediterranean coast. Together with the Sahar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids traced their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband Ali, the first Shi'a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids initially conquered Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia and north-eastern Algeria). They extended their rule across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelif River
Chelif River () (also spelled Chéliff, or Sheliff) is a river in Algeria, the longest in the country. It rises in the Saharan Atlas near the city of Aflou, flows through the Tell Atlas and empties into the Mediterranean Sea north of the city of Mostaganem. The water level in the river often fluctuates. The river is being used for irrigation Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ... (mainly on its lower course). The river was formerly called the Mekerra and the Sig River. Notes References * Rivers of Algeria {{Algeria-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igawawen
Igawawen or Gawawa, mostly known as Zwawa (in Kabyle: Igawawen, in Arabic: زواوة, and in Latin: Jubaleni''Revue archéologique, Société française d'archéologie classique'' (in French), p. 28) were a group of Kabyle tribes inhabiting the Djurdjura mountains, Greater Kabylia, in Algeria. The Zouaoua are a branch of the Kutama tribe of the Baranis Berbers.Ibn Khaldun, ''Histoire des Berbères et des dynasties musulmanes de l'Afrique septentrionale'' (in French), Volume 1, Paris, Imprimerie du gouvernement, 1852, 447 p.read online, p. 255 In the most restricted sense, the Igawawen were a confederation ( kabyle: ''taqbilt'', derived from arabic "قبيلة" meaning tribe) of 8 tribes split into two groups: * Ait Betrun: Ait Yenni, At Wasif, Ait Budrar, Ait Bu Akkash. * Ait Mengellet: Ait Mengellet ''proper'', Ait Aqbil, Ait Attaf, Ait Bu Yusef. Etymology "Zwawa" was the Arabic name of medieval Muslim historians for the tribes who inhabited the region between Bej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achir
Achir or Ashir () is a medieval city in Algeria, first capital of the Muslim dynasty of the Zirids, which ruled under Fatimid suzerainty in the 10th–11th centuries. It is located at an altitude of 4,593 feet in the Titteri Mountains, in the current Algerian commune of Kef Lakhdar ( Wilaya of Médéa). The city is mentioned by Ibn Khaldun, who indicates that Mount Tetri is the kingdom of the Zirids, in which the ruins of Achir are located. Archaeological excavations have determined the existence of two Zirid sites in this area. History The eponymous of the Berber Sanhaja dynasty, Ziri ibn Menad, who inherited the domination over Ifriqya, had been the Fatimid faithful and active lieutenant. In their struggles against Abu Yazid's soldiers and against the Zenetas, who dominated west of Tiaret, his interventions had been decisive. Thus, the Fatimid Caliph al-Qaim had authorized him to affirm his young power by the construction, in 935–36, of a capital that served as a stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenata
The Zenata (; ) are a group of Berber tribes, historically one of the largest Berber confederations along with the Sanhaja and Masmuda. Their lifestyle was either nomadic or semi-nomadic. Society The 14th-century historiographer Ibn Khaldun reports that the Zenata were divided into three large tribes: Jarawa, Maghrawa, and Banu Ifran. Formerly occupying a large portion of the Maghreb, they were displaced to the south and west in conflicts with the more powerful Kutama and Houara. The Zenata adopted Islam early, in the 7th century. While other Berber tribes continued to resist the Umayyad Caliphate conquest well into the 8th century, they were quickly Islamized. They also formed a substantial contingent in the subsequent Muslim conquest of Iberia. Language As Berbers, the Zenata spoke one of the Berber languages. Ibn Khaldun wrote that their dialect was distinct from other Berber dialects. French linguist Edmond Destaing in 1915 proposed " Zenati" as a loose subgrouping wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliana
Miliana (in Berber: ⵎⵉⵍⵉⴰⵏⴰ, in Darija: مليانة) is an Algerian commune in the Aïn Defla province, serving as the capital of Miliana district approximately southwest of the Algerian capital, Algiers.r/sup>, which covers its entire northern border and reaches . There is also a smaller ridge to the south that reaches , separating Miliana from Khemis Miliana. The area around the town is well forested. To the east and south is the Chélif River Valley, and to the west is a large plateau that stretches to the Ouarsenis range. Climate Miliana has a Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Toponymy Miliana correspondsMiliana ville historique to the town of |
Bouïra
Bouïra is the capital of Bouïra Province, Algeria Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger .... The city is also called "Garanda" by the locals. Demographics It has 75,086 inhabitants as of the 1998 census, which gives it 15 seats in the PMA. Geography It is located in the geographical heart of the province. It borders the municipality of Ait Laziz in the north, Aïn Turk in the north-east (home to the largest aqueduct in Africa), Aïn El Hadjar in the east, El Hachimia in the south-east, Oued El Berdi in the south, El Asnam in the south-west, Haizer in the west, and Taghzourt in the north-west. Climate Transportation The Autoroute A2 passes through the city. References See also * Souk Hamza External links Kabylia Populated places in Bouï ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béjaïa
Béjaïa ( ; , , ), formerly known as Bougie and Bugia, is a Mediterranean seaport, port city and communes of Algeria, commune on the Gulf of Béjaïa in Algeria; it is the capital of Béjaïa Province. Geography Location Béjaïa owes its existence to its port, which also makes it prosperous. It is located in a sickle-shaped bay protected from the swell of offshore winds (northwest facing) by the advance of Cape Carbon (to the west of the city). The city is backed by :fr:Yemma Gouraya, Mount Gouraya located in a northwest position. This port site, in one of the most beautiful bays of the Maghreb and Mediterranean coast, is dominated in the background by the Babor Mountains, Babors mountain range. Another advantage is that the city is the outlet of the Soummam River, Soummam valley, a geographical corridor facing southwest. However, since the time when the city was a capital, there has been a divorce between the city and the region (Kabylia) linked to the difficulty of secur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |