|
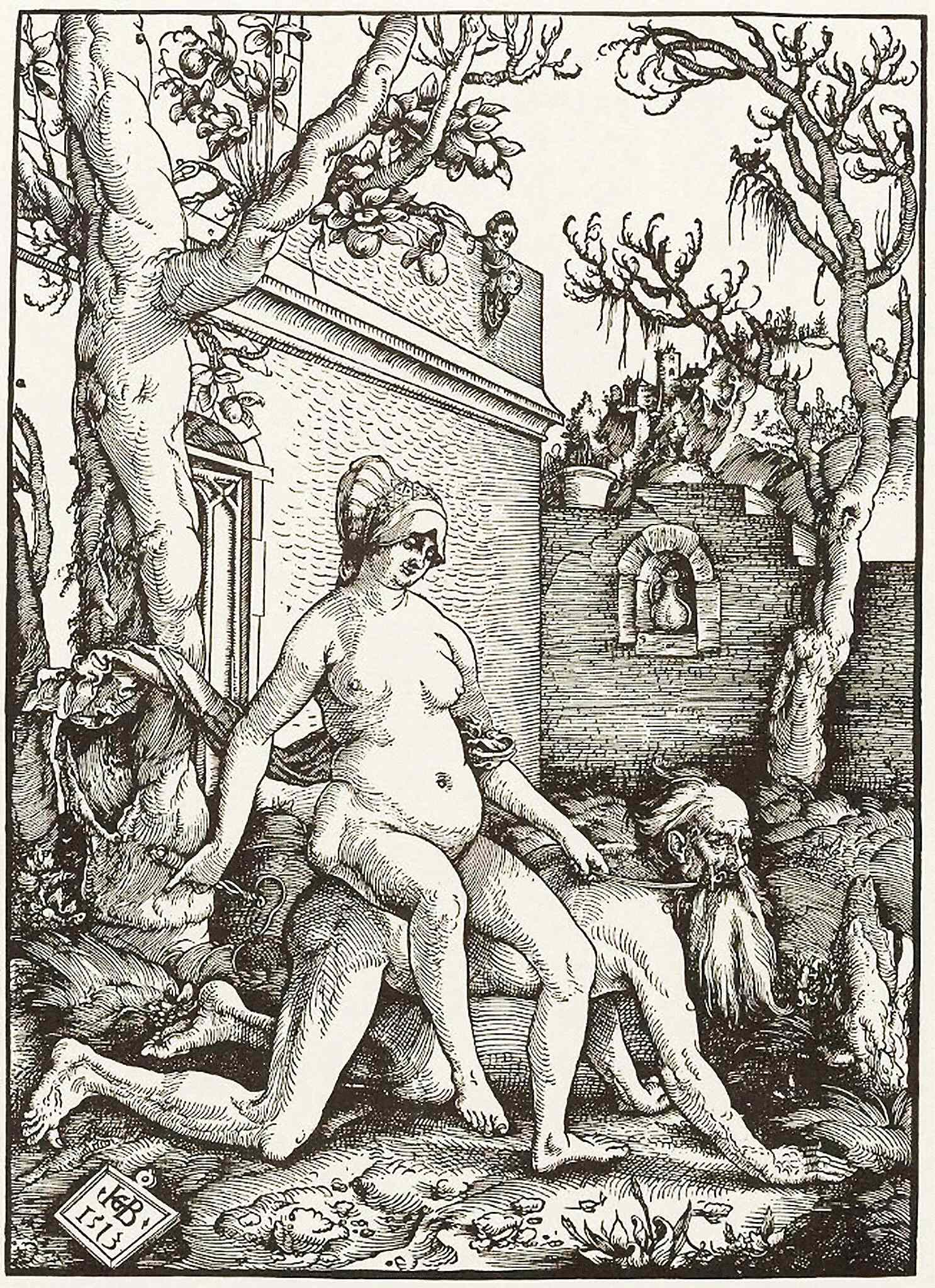
Tale Of Phyllis And Aristotle
The tale of Phyllis and Aristotle is a medieval cautionary tale about the triumph of a seductive woman, Phyllis, over the greatest male intellect, the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle. It is one of several Power of Women stories from that time. Among early versions is the French ''Lai d'Aristote'' from 1220. The story of the dominatrix and the famous intellectual was taken up by artists from the 12th century onwards, in media from stone sculpture in churches to panels of wood or ivory, textiles such as carpets and tapestries, engravings, oil paintings, brass jugs ( aquamanile), and stained glass. Artists attracted to the theme include Hans Baldung, Albrecht Dürer, Lucas Cranach the Elder, and Alessandro Turchi. Story The tale varies in the telling, but the core of it is as follows: Aristotle advises his pupil Alexander to avoid Phyllis, the seductive mistress of his father, the king, but is himself captivated by her. She agrees to ride him, on condition that she play th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gower
John Gower (; c. 1330 – October 1408) was an English poet, a contemporary of William Langland and the Pearl Poet, and a personal friend of Geoffrey Chaucer. He is remembered primarily for three major works—the ''Mirour de l'Omme'', ''Vox Clamantis'', and ''Confessio Amantis—''three long poems written in French, Latin, and English respectively, which are united by common moral and political themes. Life Few details are known of Gower's early life. He was probably born into a family which held properties in Kent and Kentwell Hall, Suffolk.Lee, Sidney (1890). "wikisource:Dictionary of National Biography, 1885-1900/Gower, John, Gower, John". In ''Dictionary of National Biography''. 22. London. pp. 299-304. Stanley and Smith use a Confessio Amantis#Language, linguistic argument to conclude that "Gower’s formative years were spent partly in Kent and partly in Suffolk". Southern and Nicolas conclude that the Gower family of Kent and Suffolk cannot be related to the Yorkshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casket With Scenes Of Romances (Walters 71264)
The object called by the museum Casket with Scenes of Romances (catalogued as Walters 71264) is a French Gothic ivory casket made in Paris between 1330 and 1350, and now in the Walters Art Museum, Baltimore, Maryland. The casket is 4 5/8 inches high, 9 15/16 inches wide and 5 1/16 inches deep (11.8 × 25.2 × 12.9 cm).Walters The casket is one of the relatively few surviving Gothic ivory caskets decorated with a variety of themes from courtly literature, called composite caskets for that reason. There are at least eight known surviving examples (and numerous fragments), of which two more are also discussed in this article: firstly a casket in the British Museum with an almost identical set of scenes, and one in the Cluny Museum in Paris, which shares many scenes, but diverges in others.Carns p.69. Both Carns and the Victoria and Albert Museum cite "eight", others "at least eight". By this period, Paris was the main European centre of ivory carving, producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadouin Abbey
Cadouin Abbey ( or ''Abbaye Notre-Dame de la Nativité de Cadouin'') was a Cistercian monastery founded as a hermitage in 1115 by Gerald of Salles, in the name of Robert of Arbrissel, in what is now the commune of Le Buisson-de-Cadouin in the Dordogne, south-west France. In 1119 Cadouin was made an abbey under its first abbot, Henri, a monk of Pontigny Abbey, the second daughter house of Cîteaux Abbey, but seems to have remained independent of the Cistercian Order until around 1199. Cadouin founded daughter houses of its own ( Grandselve Abbey, Gondon Abbey, Bonnevaux Abbey, Ardorel Abbey, La Faise Abbey and Saint-Marcel Abbey) which also became Cistercian, not necessarily at the same time as Cadouin itself. At an uncertain date the monastery came into possession of what was believed to be the facecloth from the tomb of Christ (), said to have been brought from Antioch by a priest of Périgord. In some traditional accounts the cloth is linked to the Bishop of Le Puy, Adhé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapestry
Tapestry is a form of Textile arts, textile art which was traditionally Weaving, woven by hand on a loom. Normally it is used to create images rather than patterns. Tapestry is relatively fragile, and difficult to make, so most historical pieces are intended to hang vertically on a wall (or sometimes in tents), or sometimes horizontally over a piece of furniture such as a table or bed. Some periods made smaller pieces, often long and narrow and used as borders for other textiles. Most weavers use a natural warp thread, such as wool, linen, or cotton. The warp and weft, weft threads are usually wool or cotton but may include silk, gold, silver, or other alternatives. In Late Middle Ages, late medieval Europe, tapestry was the grandest and most expensive medium for figurative images in two dimensions, and despite the rapid rise in importance of painting it retained this position in the eyes of many Renaissance patrons until at least the end of the 16th century, if not beyond. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seduction
In sexuality, seduction means enticing someone else into sexual intercourse or Human sexual activity, other sexual activity. Strategies of seduction include conversation and Sexual script theory, sexual scripts, paralanguage, paralingual features, non-verbal communication, and short-term behavioural strategies. The word ''seduction'' stems from Latin and means, literally, 'leading astray'. As a result, the term may have a negative connotation. Seen negatively, seduction involves temptation and wikt:enticement, enticement, often sexual in nature, to coerce someone into a behavioural choice they would not have made if they were not in a state of sexual arousal. Seen positively, seduction is synonymous for the act of charming someone—male or female—by an appeal to the senses, often with the goal of reducing unfounded Fear, fears and leading to "sexual emancipation". Some sides in contemporary academic debate state that the morality of seduction depends on the long-term impacts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers (, abbreviated OP), commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic Church, Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilians, Castilian priest named Saint Dominic, Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for , meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, Religious sister (Catholic), active sisters, and Laity, lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as Third Order of Saint Dominic, tertiaries). More recently, there have been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the The gospel, gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed it at the forefront of the intellectual life of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forgetting
Forgetting or disremembering is the apparent loss or modification of information already encoded and stored in an individual's short or long-term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which old memories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. Problems with remembering, learning and retaining new information are a few of the most common complaints of older adults. Studies show that retention improves with increased rehearsal. This improvement occurs because rehearsal helps to transfer information into long-term memory. Forgetting curves (amount remembered as a function of time since an event was first experienced) have been extensively analyzed. The most recent evidence suggests that a power function provides the closest mathematical fit to the forgetting function. Overview Failing to retrieve an event does not mean that this specific event has been forever forgotten. Research has shown that there are a few health behaviors that to some extent can prevent forg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllogism
A syllogism (, ''syllogismos'', 'conclusion, inference') is a kind of logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion based on two propositions that are asserted or assumed to be true. In its earliest form (defined by Aristotle in his 350 BC book '' Prior Analytics''), a deductive syllogism arises when two true premises (propositions or statements) validly imply a conclusion, or the main point that the argument aims to get across. For example, knowing that all men are mortal (major premise), and that Socrates is a man (minor premise), we may validly conclude that Socrates is mortal. Syllogistic arguments are usually represented in a three-line form: All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.In antiquity, two rival syllogistic theories existed: Aristotelian syllogism and Stoic syllogism. From the Middle Ages onwards, ''categorical syllogism'' and ''syllogism'' were usually used interchangeably. This article is concern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridle
A bridle is a piece of equipment used to direct a horse. As defined in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the "bridle" includes both the that holds a bit that goes in the mouth of a horse, and the reins that are attached to the bit. It provides additional control and communication through rein pressure (Oxford English Dictionary, n.d., para. 1). Headgear without a bit that uses a noseband to control a horse is called a hackamore, or, in some areas, a bitless bridle. There are many different designs with many different name variations, but all use a noseband that is designed to exert pressure on sensitive areas of the animal's face to provide direction and control. The bridle was devised by Indo-European herders of the Pontic-Caspian steppes to control horses between 3000 BC and 2000 BC. Parts The bridle consists of the following elements: * Crownpiece: The crownpiece, headstall (US) or headpiece (UK) goes over the horse's head just behind the animal's ears, at the pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllogism
A syllogism (, ''syllogismos'', 'conclusion, inference') is a kind of logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion based on two propositions that are asserted or assumed to be true. In its earliest form (defined by Aristotle in his 350 BC book '' Prior Analytics''), a deductive syllogism arises when two true premises (propositions or statements) validly imply a conclusion, or the main point that the argument aims to get across. For example, knowing that all men are mortal (major premise), and that Socrates is a man (minor premise), we may validly conclude that Socrates is mortal. Syllogistic arguments are usually represented in a three-line form: All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.In antiquity, two rival syllogistic theories existed: Aristotelian syllogism and Stoic syllogism. From the Middle Ages onwards, ''categorical syllogism'' and ''syllogism'' were usually used interchangeably. This article is concern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |