|
Southside Railroad (Virginia)
The Southside Railroad was formed in Virginia in 1846. Construction was begun in 1849 and completed in 1854. The track gauge, gauge railroad connected City Point, Virginia, City Point, a port on the James River (Virginia), James River with the farm country south and west of Petersburg, Virginia, to Lynchburg, Virginia, a distance of about . The Southside Railroad was important to the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War (1861–1865). Ravaged by the war, it was rebuilt and later became an important part of Norfolk and Western and Norfolk Southern's coal route from the mountains to port at Hampton Roads. In addition to coal, most of the route is in active use in the 20th century for intermodal freight transport, intermodal container and automobile parts and completed vehicle shipments. Charter, construction, City Point Railroad The State of Virginia issued the charter for the new Southside Railroad in 1846, with a capital of $1 million. directed toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the transverse distance be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Tie
A railroad tie, crosstie (American English), railway tie (Canadian English) or railway sleeper ( Australian and British English) is a rectangular support for the rails in railroad tracks. Generally laid perpendicular to the rails, ties transfer loads to the track ballast and subgrade, hold the rails upright and keep them spaced to the correct gauge. Railroad ties are traditionally made of wood, but prestressed concrete is now also widely used, especially in Europe and Asia. Steel ties are common on secondary lines in the UK; plastic composite ties are also employed, although far less than wood or concrete. As of January 2008, the approximate market share in North America for traditional and wood ties was 91.5%, the remainder being concrete, steel, azobé (red ironwood) and plastic composite. Tie spacing may depend on the type of tie, traffic loads and other requirements, for example on North American mainline railroads to on London, Midland and Scottish Railway joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
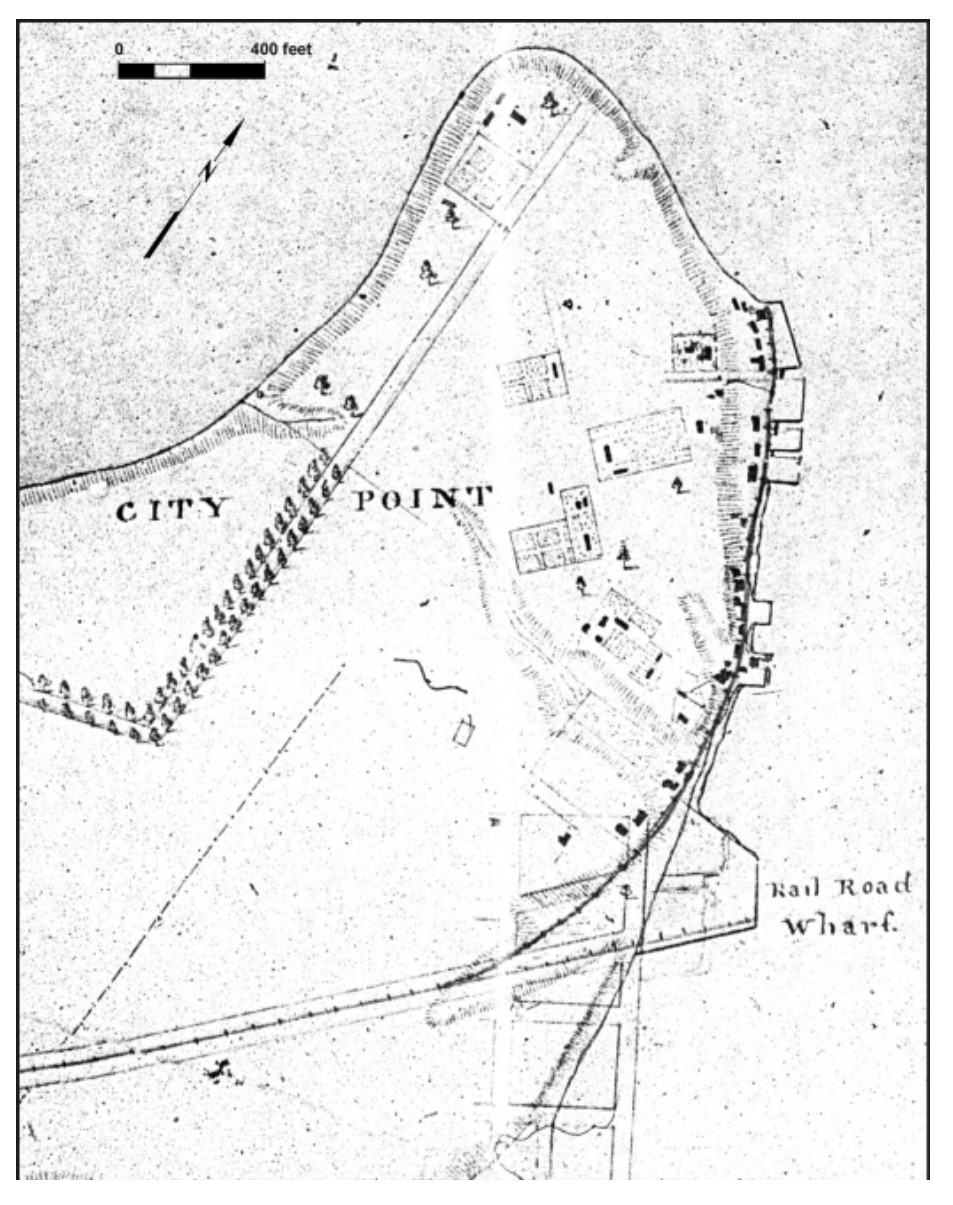
Map Of The Proposed Line Of Rail Road Connection Between Tide Water Virginia And The Ohio River At Guyandotte, Parkersburg And Wheeling - Cropped To Show The Southside Railroad
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Point Railroad
In 1836, the Virginia House of Delegates approved a charter for the City Point Railroad. City Point, Virginia, was just ten years old. The Lower Appomattox Company ran boats of cargo from Petersburg, Virginia, to the large port at City Point. The company knew that the port needed a rail road to be competitive in the 1830s even though this would only be the second rail road in Virginia. Large ships that were too large for Port Walthall or Petersburg had to load and unload at City Point. Goods for export arrived in Petersburg from farms and plantations by way of the Upper Appomattox Canal Navigation System. The Richmond and Petersburg Railroad bringing coal and goods to port was also chartered in 1836. Coal arriving by boat from the Clover Hill Pits in 1837 and goods would soon be taken on the Clover Hill Railroad to connect with the Richmond and Petersburg Railroad to export from the area ports. History The City Point Railroad was an eight plus mile railroad in eastern Virginia es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percival Island
Perceval (, also written Percival, Parzival, Parsifal), alternatively called Peredur (), is a figure in the legend of King Arthur, often appearing as one of the Knights of the Round Table. First mentioned by the French author Chrétien de Troyes in the tale ''Perceval, the Story of the Grail'', he is best known for being the original hero in the quest for the Grail before being replaced in later literature by Galahad. Etymology and origin The earliest reference to Perceval is found in Chrétien de Troyes's first Arthurian romance ''Erec et Enide'', where, as "Percevaus li Galois" (Percevaus of Wales), he appears in a list of Arthur's knights. In another of Chrétien's romances, '' Cligés'', Perceval is a "renowned vassal" who is defeated by the knight Cligés in a tournament. He then becomes the eponymous protagonist of Chrétien's final romance, ''Perceval, the Story of the Grail''. In the Welsh romance '' Peredur son of Efrawg'', the corresponding figure goes by the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appomattox River
The Appomattox River is a tributary of the James River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 in central and eastern Virginia, named for the Appomattocs Indian tribe who lived along its lower banks in the 17th century. It drains a cotton and tobacco-growing region of the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont and coastal plain southwest of Richmond, Virginia, Richmond. Course The Appomattox River rises in the middle of a field near State Route 656 (Horseshoe Road) in the Piedmont of northeastern Appomattox County, Virginia, Appomattox County, approximately northeast of the town of Appomattox, Virginia, Appomattox. It flows generally southeast through the Appomattox-Buckingham State Forest to Farmville, Virginia, Farmville. From Farmville it flows in a large arc northeast then southeast across the coastal plain, passing southwest of Richmond and passing through the Lake Chesdin re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Bridge (Appomattox River)
High Bridge is a historic former railroad bridge across the Appomattox River valley about east, or downstream, of the town of Farmville, Virginia, Farmville in Prince Edward County, Virginia. The remains of the bridge and its adjacent rail line are now a rail trail park, High Bridge Trail State Park. Originally constructed in the 1850s, the bridge was integral to the Southside Railroad (Virginia), Southside Railroad between Petersburg, Virginia, Petersburg and Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg. As the site of the Battle of High Bridge in April 1865, the bridge played a pivotal role in Lee's retreat in the final days of the American Civil War – and ultimately the war's outcome. Rebuilt after the Civil War to its former dimensions, the 21-span structure was long at a maximum height of above the Appomattox River Valley. The bridge was completely rebuilt in 1914, leaving many of the original masonry piers adjacent to the new structure. By 2005 its then-owner, Norfolk Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Virginia. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city (United States), independent city since 1871. The city's population in the 2020 United States census was 226,610, up from 204,214 in 2010, making it Virginia's List of cities and counties in Virginia#Largest cities, fourth-most populous city. The Greater Richmond Region, Richmond metropolitan area, with over 1.3 million residents, is the Commonwealth's Virginia statistical areas, third-most populous. Richmond is located at the Atlantic Seaboard fall line, James River's fall line, west of Williamsburg, Virginia, Williamsburg, east of Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, east of Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg and south of Washington, D.C. Surrounded by Henrico County, Virginia, Henrico and Chesterfield County, Virginia, Chesterfield counties, Richmond is at the intersection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkeville, Virginia
Burkeville is an incorporated town in Nottoway County, Virginia, Nottoway County, Virginia, United States. The population was 432 at the 2010 census. The source of the town name is disputed. The town is located at the crossroads of U.S. routes U.S. Route 360, 360 and U.S. Route 460 in Virginia, 460. Major employers * Luck Stone, Burkeville Plant, is the nation’s largest family-owned and -operated producer of crushed stone, sand, and gravel. In 1935 Luck Stone purchased the Burkeville Plant, located on the Route 360/460 bypass in Nottoway County, Virginia. The Burkeville plant is the recipient of the National Stone, Sand & Gravel Association’s 1997 About Face Award for Outstanding Achievement. * A Southern States Cooperative store provides a full range of services and growing solutions for large commercial farming, tending backyard gardens, and trying to keep home yards looking green and lush. * James River Equipment operates a John Deere dealership here. * The Nottoway Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farmville, Virginia
Farmville is a town in Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward and Cumberland County, Virginia, Cumberland counties in the U.S. state, Commonwealth of Virginia. It is the county seat of Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward County. The population was 7,473 at the United States Census 2020, 2020 census. It was in a major tobacco growing area. Coal mining and brick making also occurred in the area. Farmville developed near the headwaters of the Appomattox River in central Virginia; the waterway was long its main transportation access to other markets. In the 19th century, a railroad was constructed here. Since the late 20th century, the former railway has been converted to the High Bridge Trail State Park, a more than rail trail park. U.S. Route 15 in Virginia, US 15, Virginia State Route 45, VA 45 and U.S. Route 460 in Virginia, US 460 now intersect at Farmville. The town is the home of Longwood University and is the town nearest to Hampden–Sydney College. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enslaved Africans
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the Ancient history, ancient and Post-classical history, medieval world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Red Sea slave trade, Indian Ocean slave trade, and Atlantic slave trade (which started in the 16th century) began, many of the pre-existing local African slave systems began supplying captives for slave markets outside Africa. Slavery in contemporary Africa still exists in some regions despite being illegal. In the relevant literature African slavery is categorized into indigenous slavery and export slavery, depending on whether or not slaves were traded beyond the continent. Slavery in historical Africa was practised in many different forms: Debt slavery, enslavement of war captives, military slavery, slavery for prostitution, and enslavement of criminals were all practised in various parts of Africa. Slavery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Stellata
''Quercus stellata'', the post oak or iron oak, is a North American species of oak in the white oak section. It is a slow-growing oak that lives in dry areas on the edges of fields, tops of ridges, and also grows in poor soils, and is resistant to rot, fire, and drought. Interbreeding occurs among white oaks, thus many hybrid species combinations occur. It is identifiable by the rounded cross-like shape formed by the leaf lobes and hairy underside of the leaves. Taxonomy The specific epithet ''stellata'' is Latin for "star"; it is named this because the trichome hairs on the bottom of the leaves are stellate or star-shaped. Several variants of ''Q. stellata'' were named by American botanist Charles Sprague Sargent. The variety most recognised by the United States Forest Service is ''Q. stellata'' var. ''paludosa'' Sarg (delta post oak).Stransky, John J. "Quercus stellata Wangenh.--post oak.''Silvics of North America'' 2(1990): 738–743. Varieties Varieties inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |