|
Short Singapore
The Short Singapore was a British multi-engined biplane flying boat built after the First World War. The design was developed into two four-engined versions: the prototype Singapore II and production Singapore III. The latter became the Royal Air Force's main long-range maritime patrol flying boat of the 1930s and saw service against the Japanese with the Royal New Zealand Air Force during the Second World War. Design and development The first prototype of the Short Singapore, also known as the Short S.5 ( military designation Singapore I), was a metal hull version of the wooden-hulled Short Cromarty. The biplane design included a single fin and rudder, and was originally powered by two Rolls-Royce Condor IIIA engines. Its maiden flight was made from Rochester on 17 August 1926, piloted by Short's Chief Test Pilot John Lankester Parker. The type did not enter production, but was used by Sir Alan Cobham for a survey flight around Africa. Registered ''G-EBUP'', it left Rochest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Singapore I
The Short Singapore was a British multi-engined biplane flying boat built after the First World War. The design was developed into two four-engined versions: the prototype Singapore II and production Singapore III. The latter became the Royal Air Force's main long-range maritime patrol flying boat of the 1930s and saw service against the Japanese with the Royal New Zealand Air Force during the Second World War. Design and development The first prototype of the Short Singapore, also known as the Short S.5 ( military designation Singapore I), was a metal hull version of the wooden-hulled Short Cromarty. The biplane design included a single fin and rudder, and was originally powered by two Rolls-Royce Condor IIIA engines. Its maiden flight was made from Rochester on 17 August 1926, piloted by Short's Chief Test Pilot John Lankester Parker. The type did not enter production, but was used by Sir Alan Cobham for a survey flight around Africa. Registered ''G-EBUP'', it le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Cobham
Sir Alan John Cobham, KBE, AFC (6 May 1894 – 21 October 1973) was an English aviation pioneer. Early life and family As a child he attended Wilson's School, then in Camberwell, London. The school relocated to the former site of Croydon Airport in 1975. In the summer of 1922 he married Gladys Lloyd, and subsequently they had two sons, Geoffrey (b.1925) and Michael (b.1927). After National Service and a short career at the Bar, Michael Cobham followed him into the Flight Refuelling business, and for many years was in charge of it. Lady Cobham died in 1961 aged 63. Career Alan Cobham began work as a teenage commercial apprentice in the City of London. He enjoyed the outdoors, and after completing his apprenticeship spent a year working on his uncle's farm, hoping to make a career in estate management. After a brief return to London commercial work, in August 1914 he joined the British Army, being directed to the Royal Army Veterinary Corps due to his farming experience. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
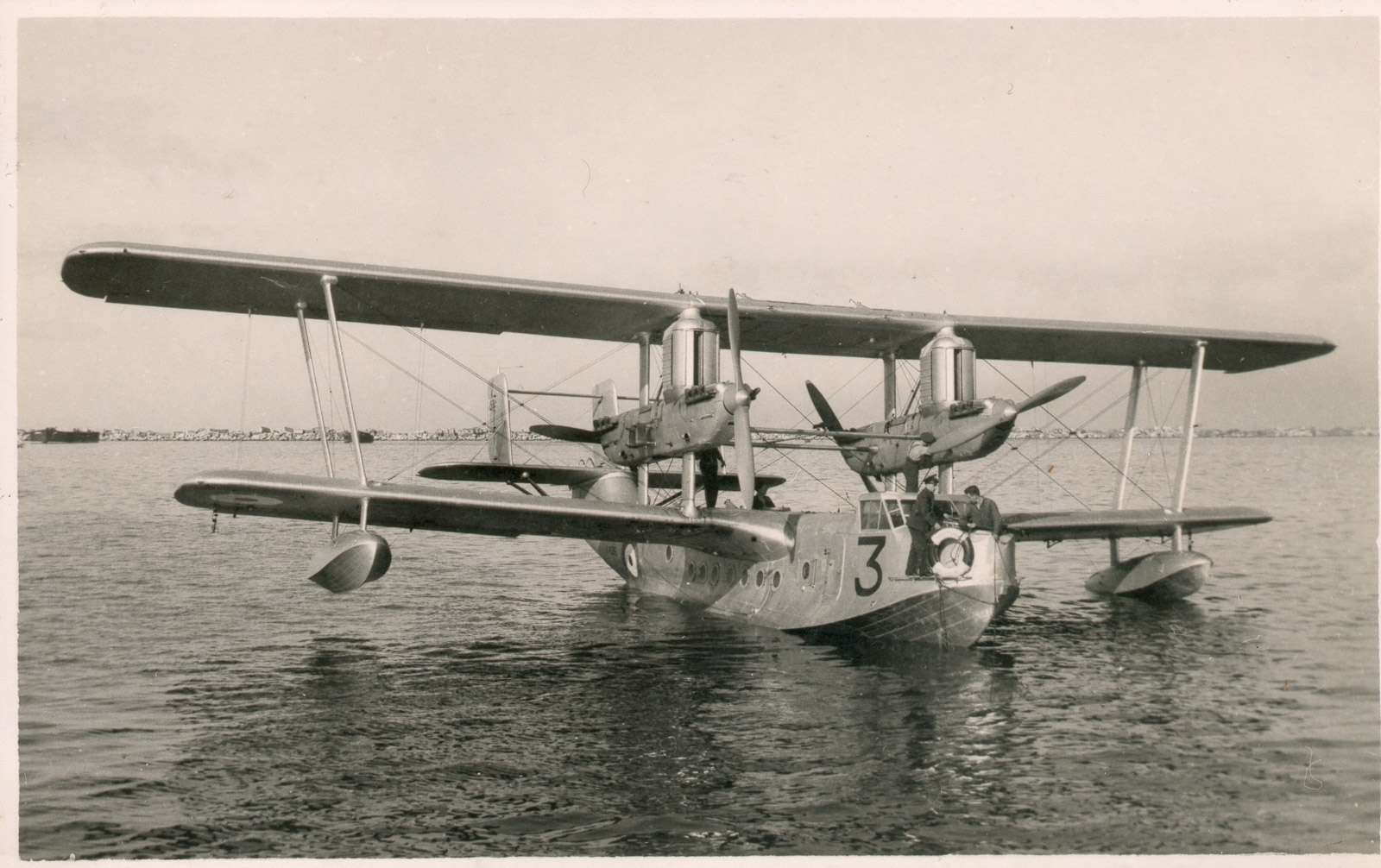
230sqd-ShortSingaporeIII
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Machine Gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a Water cooling, water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and operate it: one fired, one fed the ammunition, the others helped to carry the weapon, its ammunition, and spare parts. It was in service from before the First World War until the 1960s, with air-cooled versions of it on many Allies of World War I, Allied World War I fighter aircraft. The weapon had a reputation for great solidity and reliability. Ian V. Hogg, in ''Weapons & War Machines'', describes an action that took place in August 1916, during which the British 100th Company of the Machine Gun Corps fired their ten Vickers guns to deliver sustained fire for twelve hours. Using 100 barrels, they fired a million rounds without breakdowns. "It was this absolute foolproof reliability which endeared the Vickers to every Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Kestrel
The Kestrel or type F is a 21 litre (1,300 in³) 700 horsepower (520 kW) class V-12 aircraft engine from Rolls-Royce, their first cast-block engine and the pattern for most of their future piston-engine designs. Used during the interwar period, it provided excellent service on a number of British fighters and bombers of the era, such as the Hawker Fury and Hawker Hart family, and the Handley Page Heyford. The engine also sold to international air forces, and it was even used to power prototypes of German military aircraft types that were later used during the Battle of Britain. Several Kestrel engines remain airworthy today. Design and development Origin The Kestrel came about as a result of the excellent Curtiss D-12, one of the first truly successful cast-block engines. Earlier designs had used individually machined steel cylinders that were screwed onto a crankcase, whereas the cast-block design used a single block of aluminium that was machined to form cylinders. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Air Ministry Specifications
This is a partial list of the British Air Ministry (AM) specifications for aircraft. A specification stemmed from an Operational Requirement, abbreviated "OR", describing what the aircraft would be used for. This in turn led to the specification itself, e.g. a two-engined fighter with four machine guns. So for example, OR.40 for a heavy bomber led to Specification B.12/36. Aircraft manufacturers would be invited to present design proposals to the ministry, following which prototypes of one or more of the proposals might be ordered for evaluation. On very rare occasions, a manufacturer would design and build an aircraft using their own money as a "private venture" (PV). This would then be offered to the ministry for evaluation. If the aircraft generated interest in the ministry or RAF due to performance or some other combination of features then the ministry might well issue a specification based on the private venture aircraft. The system of producing aircraft to a specification ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State for Air. Organisations before the Air Ministry The Air Committee On 13 April 1912, less than two weeks after the creation of the Royal Flying Corps (which initially consisted of both a naval and a military wing), an Air Committee was established to act as an intermediary between the Admiralty and the War Office in matters relating to aviation. The new Air Committee was composed of representatives of the two war ministries, and although it could make recommendations, it lacked executive authority. The recommendations of the Air Committee had to be ratified by the Admiralty Board and the Imperial General Staff and, in consequence, the Committee was not particularly effective. The increasing separation of army and naval aviation from 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push-pull Configuration
An aircraft constructed with a push-pull configuration has a combination of forward-mounted tractor (pull) propellers, and backward-mounted ( pusher) propellers. Historical The earliest known examples of "push-pull" engined-layout aircraft include a trio of experimental German World War I designs: chronologically comprising the only Fokker twin-engined design of the period, the Fokker K.I from 1915; followed by the unusual Siemens-Schuckert DDr.I triplane fighter design of late 1917, and concluding with the laterally-offset "push-pull" Gotha G.VI bomber prototype of 1918. An early post-World War I example of a "push-pull" aircraft was the Short Tandem Twin: another was the Caproni Ca.1 of 1914 which had two wing-mounted tractor propellers and one centre-mounted pusher propeller. Around 450 of these and their successor, the Ca.3 were built. One of the first to employ two engines on a common axis (tandem push-pull) was the one-off, ill-fated Siemens-Schuckert DDr.I fighter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pusher Configuration
In an aircraft with a pusher configuration (as opposed to a tractor configuration), the propeller(s) are mounted behind their respective engine(s). Since a pusher propeller is mounted behind the engine, the drive shaft is in compression in normal operation. Pusher configuration describes this specific (propeller or ducted fan) thrust device attached to a craft, either aerostat (airship) or aerodyne (aircraft, WIG, paramotor, rotorcraft) or others types such as hovercraft, airboat and propeller-driven snowmobiles. "Pusher configuration" also describes the layout of a fixed-wing aircraft in which the thrust device has a pusher configuration. This kind of aircraft is commonly called a pusher. Pushers have been designed and built in many different layouts, some of them quite radical. History The rubber-powered "Planophore", designed by Alphonse Pénaud in 1871, was an early successful model aircraft with a pusher propeller. Many early aircraft (especially biplanes) were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tractor Configuration
In aviation, the term tractor configuration refers to an aircraft constructed in the standard configuration with its engine mounted with the propeller in front of it so that the aircraft is "pulled" through the air. Oppositely, the pusher configuration places the airscrew behind and propels the aircraft forward. Through common usage, the word "propeller" has come to mean any airscrew, whether it actually propels or pulls the plane. In the early years of powered aviation both tractor and pusher designs were common. However, by the midpoint of the First World War, interest in pushers declined and the tractor configuration dominated. Today, propeller-driven aircraft are assumed to be tractors unless it is stated otherwise. Origins The first airplane to have a "tractor" configuration was the Goupy No.2 (first flight on 11 March 1909) designed by Mario Calderara and financed by Ambroise Goupy at the French firm Blériot Aéronautique. When it was constructed, it was the fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



