|
SMAD (protein)
Smads (or SMADs) comprise a family of structurally similar proteins that are the main signal transducers for receptors of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) superfamily, which are critically important for regulating cell development and growth. The abbreviation refers to the homologies to the ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' SMA ("small" worm phenotype) and Mothers against decapentaplegic, MAD family ("Mothers Against Decapentaplegic") of genes in ''Drosophila''. There are three distinct sub-types of Smads: receptor-regulated Smads (R-SMAD, R-Smads), common partner Smads (Co-Smads), and inhibitory Smads (I-SMAD, I-Smads). The eight members of the Smad family are divided among these three groups. Protein trimer, Trimers of two receptor-regulated SMADs and one co-SMAD act as transcription factors that regulate the expression of certain genes. Sub-types The R-Smads consist of mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1, Smad1, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2, Smad2, mothers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 7
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD7'' gene. SMAD7 is a protein that, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene: " Mothers against decapentaplegic". It belongs to the SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the TGFβ superfamily of ligands. Like many other TGFβ family members, SMAD7 is involved in cell signalling. It is a TGFβ type 1 receptor antagonist. It blocks TGFβ1 and activin associating with the receptor, blocking access to SMAD2. It is an inhibitory SMAD ( I-SMAD) and is enhanced by SMURF2. Smad7 enhances muscle differentiation. Structure Smad proteins contain two conserved domains. The Mad Homology domain 1 (MH1 domain) is at the N-terminal and the Mad Homology domain 2 (MH2 domain) is at the C-terminal. Between them there is a linker region which is full of regulatory sites. The MH1 domain has DNA binding activity while the MH2 domain has transcriptional activity. The linke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words ''luciferin'' and ''luciferase'', for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word ''lucifer'', meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (''lux)'' and "to bring or carry" (''ferre)''.Luciferases are widely used in biotechnology, for bioluminescence imaging microscopy and as reporter genes, for many of the same applications as fluorescent proteins. However, unlike fluorescent proteins, luciferases do not require an external light source, but do require addition of luciferin, the consumable substrate. Examples A variety of organisms regulate their light production using different luciferases in a variety of light-emitting reactions. The majority of studied luciferases have been found in anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytostasis
Cytostasis (cyto – cell; stasis – stoppage) is the inhibition of cell growth and multiplication. Cytostatic refers to a cellular component or medicine that inhibits cell division and induce cell death. Cytostasis is an important prerequisite for structured multicellular organisms. Without regulation of cell growth and division only unorganized heaps of cells would be possible. Chemotherapy of cancer, treatment of skin diseases and treatment of infections are common use cases of cytostatic drugs; although they can also affect normal and healthy cells and tissues. Active hygienic products generally contain cytostatic substances. Cytostatic mechanisms and drugs generally occur together with cytotoxic ones. Activators Nitric oxide – activated macrophages produce large amounts of nitric oxide (NO), which induces both cytostasis and cytotoxicity to tumor cells both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''. Nitric oxide-induced cytostasis targets ribonucleotide reductase by rapid and rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine/threonine Kinase
A serine/threonine protein kinase () is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases (STK). In enzymology, the term ''serine/threonine protein kinase'' describes a class of enzymes in the family of transferases, that transfer phosphates to the oxygen atom of a serine or threonine side chain in proteins. This process is called phosphorylation. Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes and is a very important post-translational modification. The chemical reaction performed by these enzymes can be written as :ATP + a protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + a phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and a protein, whereas its two products are ADP and phosphoprotein. The systematic name of this enzyme class i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WW Domain
The WW domain (also known as the rsp5-domain or WWP repeating structural motif, motif) is a modular protein domain that mediates specific interactions with protein ligands. This domain is found in a number of unrelated signaling and structural proteins and may be repeated up to four times in some proteins. Apart from binding preferentially to proteins that are proline-rich, with particular proline-motifs, [AP]-P-P-[AP]-Y, some WW domains bind to phosphoserine- and phosphothreonine-containing motifs. Structure and ligands The WW domain is one of the smallest protein modules, composed of only 40 amino acids, which mediates specific protein-protein interactions with short proline-rich or proline-containing motifs. Named after the presence of two conserved tryptophans (W), which are spaced 20-22 amino acids apart within the sequence, the WW domain folds into a meandering triple-stranded beta sheet. The identification of the WW domain was facilitated by the analysis of two splice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
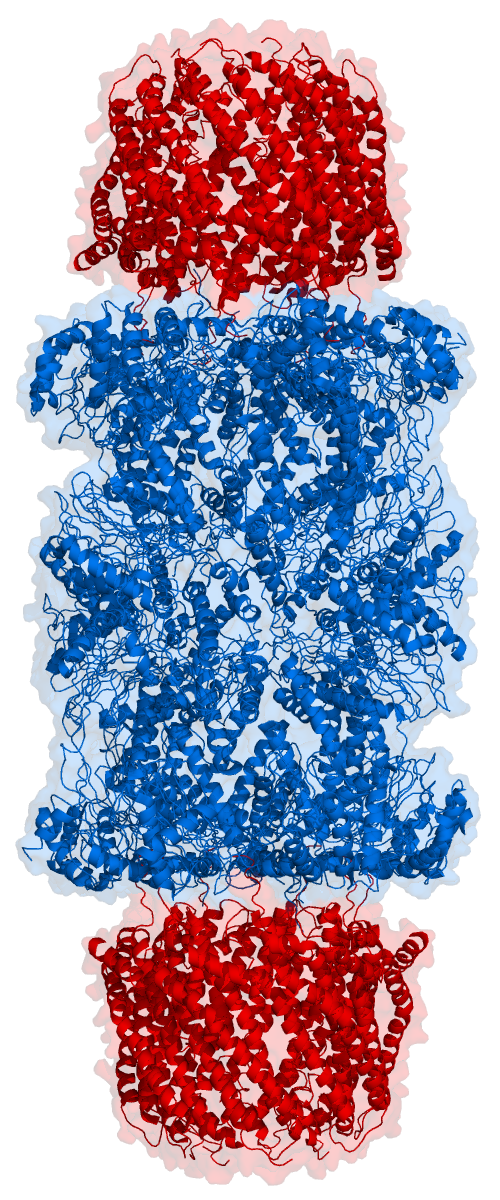
Proteasome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, proteasomes are located both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation pathway is essential for many cellular processes, including the cell cycle, the regulation of gene expression, and responses to oxidative stress. The importance of proteolytic degradation inside cells and the role of ubiquitin in proteolytic pathways was acknowledged in the award of the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose. The core 20S proteasome (blue in the adjacent figure) is a cylindrical, compartmental protein complex of four stacked rings forming a central pore. Each ring is composed of seven individual proteins. The inner two rings a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
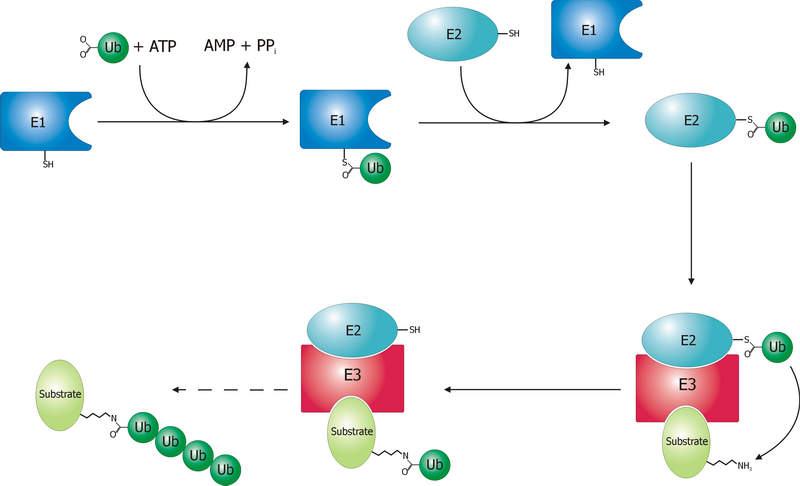
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another protein (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols: : This equation can be written in several ways that are nearly equivalent that describe the behaviors of various protonated states of ATP, ADP, and the phosphorylated product. As is clear from the equation, a phosphate group per se is not transferred, but a phosphoryl group (PO3-). Phosphoryl is an electrophile. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. During respiration Phosphorylation is essential to the processes of both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, which involve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "high-energy" exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMP4
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by ''BMP4'' gene. BMP4 is found on chromosome 14q22-q23. BMP4 is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein family which is part of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. The Protein family, superfamily includes large families of growth and differentiation factors. BMP4 is highly conserved evolutionarily. BMP4 is found in early embryonic development in the ventral marginal zone and in the eye, heart blood and otic vesicle. Discovery Bone morphogenetic proteins were originally identified by an ability of demineralized bone extract to induce endochondral osteogenesis in vivo in an extraskeletal site. Function BMP4 is a polypeptide belonging to the Transforming growth factor beta, TGF-β superfamily of proteins. It, like other bone morphogenetic proteins, is involved in bone and cartilage development, specifically tooth and limb development and fracture repair. This particular family member plays an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos'' = strange, πους, ''pous'' = foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are '' Xenopus laevis'' and '' Xenopus tropicalis'', which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects. The genus is also known for its polyploidy, with some species having up to 12 sets of chromosomes. Characteristics ''Xenopus laevis'' is a rather inactive creature. It is incredibly hardy and can live up to 15 years. At times the ponds that ''Xenopus laevis'' is found in dry up, compelling it, in the dry season, to burrow into the mud, leaving a tunnel for air. It may lie dormant for up to a year. If the pond dries up in the rainy season, ''Xenopus laevis'' may migrate long di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |