|
Synthetic Radionuclide
A synthetic radioisotope is a radionuclide that is not found in nature: no natural process or mechanism exists which produces it, or it is so unstable that it decays away in a very short period of time. Frédéric Joliot-Curie and Irène Joliot-Curie were the first to produce a synthetic radioisotope in the 20th century. Examples include technetium-98 and promethium-146. Many of these are found in, and harvested from, spent nuclear fuel assemblies. Some must be manufactured in particle accelerators. Production Some synthetic radioisotopes are extracted from spent nuclear reactor fuel rods, which contain various fission products. For example, it is estimated that up to 1994, about 49,000 terabecquerels (78 metric tons) of technetium were produced in nuclear reactors; as such, anthropogenic technetium is far more abundant than technetium from natural radioactivity. Some synthetic isotopes are produced in significant quantities by fission but are not yet being reclaimed. Other i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body, such as: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical—a radioisotope attached to a drug—is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an ordinary electron, the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine-131
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nuclear energy, medical diagnostic and treatment procedures, and natural gas production. It also plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and was a significant contributor to the health hazards from open-air atomic bomb testing in the 1950s, and from the Chernobyl disaster, as well as being a large fraction of the contamination hazard in the first weeks in the Fukushima nuclear crisis. This is because 131I is a major fission product of uranium and plutonium, comprising nearly 3% of the total products of fission (by weight). See fission product yield for a comparison with other radioactive fission products. 131I is also a major fission product of uranium-233, produced from thorium. Due to its mode of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsealed Source Radiotherapy
Radionuclide therapy (RNT, also known as unsealed source radiotherapy or molecular radiotherapy) uses radioactive substances called radiopharmaceuticals to treat medical conditions, particularly cancer. These are introduced into the body by various means (injection or ingestion are the two most commonplace) and localise to specific locations, organs or tissues depending on their properties and administration routes. This includes anything from a simple compound such as sodium iodide that locates to the thyroid via trapping the iodide ion, to complex biopharmaceuticals such as recombinant antibodies which are attached to radionuclides and seek out specific antigens on cell surfaces. This is a type of targeted therapy which uses the physical, chemical and biological properties of the radiopharmaceutical to target areas of the body for radiation treatment. The related diagnostic modality of nuclear medicine employs the same principles but uses different types or quantities of radioph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium-235
Uranium-235 ( or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nature as a primordial nuclide. Uranium-235 has a half-life of 703.8 million years. It was discovered in 1935 by Arthur Jeffrey Dempster. Its fission cross section for slow thermal neutrons is about Barn (unit), barns. For fast neutrons it is on the order of 1 barn. Most neutron absorptions induce fission, though a minority (about 15%) result in the formation of uranium-236. Fission properties The fission of one atom of uranium-235 releases () inside the reactor. That corresponds to 19.54 TJ/mole (unit), mol, or 83.14 TJ/kg. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Molybdenum
Molybdenum (42Mo) has 39 known isotopes, ranging in atomic mass from 81 to 119, as well as four metastable nuclear isomers. Seven isotopes occur naturally, with atomic masses of 92, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, and 100. All unstable isotopes of molybdenum decay into isotopes of zirconium, niobium, technetium, and ruthenium. Molybdenum-100, with a half-life of 7.07 years, is the only naturally occurring radioisotope. It undergoes double beta decay into ruthenium-100. Molybdenum-98 is the most common isotope, comprising 24.14% of all molybdenum on Earth. List of isotopes , -id=Molybdenum-81 , rowspan=2, 81Mo , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 42 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 39 , rowspan=2, 80.96623(54)# , rowspan=2, 1# ms 400 ns, β+? , 81Nb , rowspan=2, 5/2+# , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , - , β+, p? , 80Zr , -id=Molybdenum-82 , rowspan=2, 82Mo , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 42 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 40 , rowspan=2, 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technetium-99m Generator
A technetium-99m generator, or colloquially a technetium cow or moly cow, is a device used to extract the metastable isotope 99mTc of technetium from a decaying sample of molybdenum-99. 99Mo has a half-life of 66 hours and can be easily transported over long distances to hospitals where its decay product technetium-99m (with a half-life of only 6 hours, inconvenient for transport) is extracted and used for a variety of nuclear medicine diagnostic procedures, where its short half-life is very useful. Parent isotope source 99Mo can be obtained by the neutron activation (n,γ reaction) of 98Mo in a high- neutron-flux reactor. However, the most frequently used method is through fission of uranium-235 in a nuclear reactor. While most reactors currently engaged in 99Mo production use highly enriched uranium-235 targets, proliferation concerns have prompted some producers to transition to low-enriched uranium targets. The target is irradiated with neutrons to form 99Mo as a fiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz () and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (), gamma ray photons have the highest photon energy of any form of electromagnetic radiation. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900, he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used Radiopharmacology, medical radioisotope in the world. Technetium-99m is used as a radioactive tracer and can be detected in the body by medical equipment (gamma cameras). It is well suited to the role, because it emits readily detectable gamma rays with a photon energy of 140 kiloelectronvolt, keV (these 8.8 Picometre, pm photons are about the same wavelength as emitted by conventional X-ray diagnostic equipment) and its half-life for gamma emission is 6.0058 hours (meaning 93.7% of it decays to 99Tc in 24 hours). The relatively "short" physical half-life of the isotope and its biological half-life of 1 day (in terms of human activity and metabolism) allows for scanning procedures which collect data rapidly but keep total patient radiatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
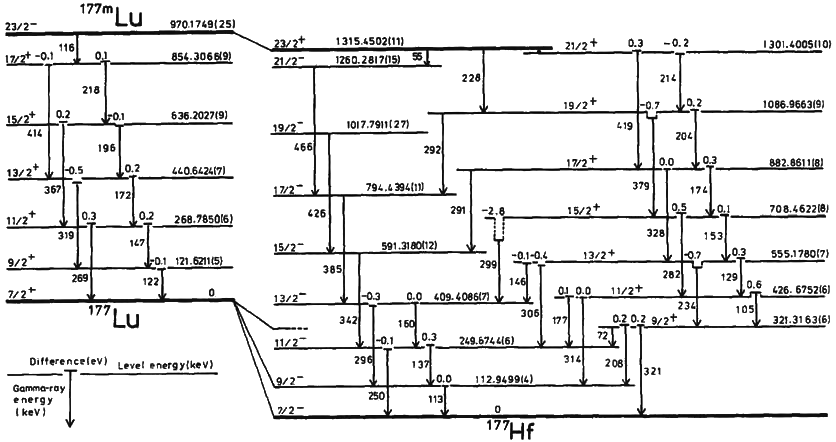
Nuclear Isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer, 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). Some references recommend seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" Induced gamma emission, gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the Isotopes of tantalum#Tantalum-180m, nuclear isomer survives so long (at least years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as isotopes of rhenium, , isotopes of iridium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Camera
A gamma camera (γ-camera), also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy. The applications of scintigraphy include early drug development and nuclear medical imaging to view and analyse images of the human body or the distribution of medically injected, inhaled, or ingested radionuclides emitting gamma rays. Imaging techniques Scintigraphy ("scint") is the use of gamma cameras to capture emitted radiation from internal radioisotopes to create two-dimensional images. SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) imaging, as used in nuclear cardiac stress testing, is performed using gamma cameras. Usually one, two or three detectors or heads, are slowly rotated around the patient. Construction A gamma camera consists of one or more flat crystal planes (or detectors) optically coupled to an array of photomultiplier tubes in an assembly known as a "head", mounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |