|
Symptoms And Discomforts Of Pregnancy
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy are common, benign conditions that result from the changes to the body that occur during pregnancy. Signs and symptoms of pregnancy typically change as pregnancy progresses, although several symptoms may be present throughout. Depending on severity, common symptoms in pregnancy can develop into complications. Pregnancy symptoms may be categorized based on trimester as well as region of the body affected. Each pregnancy can be quite different and many people do not experience the same or all of the symptoms. If a person is concerned about their symptoms they should be encouraged to speak with an appropriate healthcare professional. Early pregnancy Many of the early signs of pregnancy will be similar to symptoms that come right before a period, and it can be hard to tell the difference. Implantation bleeding Implantation bleeding is light vaginal bleeding in the first 10–14 days of pregnancy caused by the normal implantation of the embryo in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs following sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), ''gestational age''; this is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, ''fertilization age'', the length is about 38 weeks. Implantation (embryology), Implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after Human fertilization, fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, social bonding, love, reproduction, childbirth, and the Postpartum period, period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to Human sexual activity, sexual activity and during childbirth. It is also available in Oxytocin (medication), pharmaceutical form. In either form, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions to speed up the process of childbirth. In its natural form, it also plays a role in maternal bonding and lactation, milk production. Production and secretion of oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism, where its initial release stimulates production and release of further oxytocin. For example, when oxytocin is released during a contraction of the uterus at the start of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antacid
An antacid is a substance which neutralization (chemistry), neutralizes gastric acid, stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion, or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhea. Marketed antacids contain Salt (chemistry), salts of aluminum, calcium, magnesium, or sodium. Some preparations contain a combination of two Salt (chemistry), salts, such as magnesium carbonate and aluminum hydroxide (e.g., hydrotalcite). Medical uses Antacids are available over the counter and are taken by mouth to quickly relieve occasional heartburn, the major symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease and indigestion. Treatment with antacids alone is Symptomatic treatment, symptomatic and only justified for minor symptoms. Alternative uses for antacids include constipation, diarrhea, hyperphosphatemia, and urinary alkalization. Some antacids are also used as an Adjuvant therapy, adjunct to pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern Ireland) which was created separately and is often referred to locally as "the NHS". The original three systems were established in 1948 (NHS Wales/GIG Cymru was founded in 1969) as part of major social reforms following the Second World War. The founding principles were that services should be comprehensive, universal and free at the point of delivery. Each service provides a comprehensive range of health services, provided without charge for residents of the United Kingdom apart from dental treatment and optical care. In England, NHS patients have to pay prescription charges; some, such as those aged over 60, or those on certain state benefits, are exempt. Taken together, the four services in 2015–16 employed around 1.6 million people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus ( archaic spelling) ( see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''esophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, "I carry") + ἔφαγον (éphagon, "I ate"). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regurgitation (digestion)
Regurgitation is the expulsion of material from the pharynx, or esophagus, usually characterized by the presence of undigested food or blood. Regurgitation is used by a number of species to feed their young. This is typically in circumstances where the young are at a fixed location and a parent must forage or hunt for food, especially under circumstances where the carriage of small prey would be subject to robbing by other predators or the whole prey is larger than can be carried to a den or nest. Some bird species also occasionally regurgitate Pellet (ornithology), pellets of indigestible matter such as bones and feathers. It is in most animals a normal and voluntary process unlike the complex vomiting reflex in response to toxins. Humans Regurgitation can be voluntary or involuntary for humans. It can occur alongside gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), acid reflux and some anatomical abnormalities. In infants however, regurgitation – or spitting up – is quite comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Lying down, bending, lifting, and performing certain exercises can exacerbate heartburn. Causes include acid reflux, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), damage to the esophageal lining, bile acid, mechanical stimulation to the esophagus, and esophageal hypersensitivity. Heartburn affects 25% of the population at least once a month. Endoscopy and esophageal pH monitoring can be used to evaluate heartburn. Some causes of heartburn, such as GERD, may be diagnosed based on symptoms alone. Potential Differential diagnosis, differential diagnoses for heartburn include motility disorders, ulcers, Esophagitis, inflammation of the esophagus, and medication side effects. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, losing weight and avoiding fatty food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysuria
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination. It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency. Diagnosis The clinician should also look for physical findings of fever, rash, direct tenderness over the bladder area, and joint pain. Physical findings of increased temperature, increased pulse, low blood pressure in the presence of dysuria can indicate systemic infection. Urological obstruction due to stone or tumor can result in findings of hematuria, decreased urination, and bladder spasms. All these physical findings should be looked for carefully while obtaining history. History regarding recent sexual activity is crucial. Urinalysis is the most useful test to start the work up in a patient of dysuria. Urinalysis positive for nitrite carries a high predictive value of a positive urine culture. Also, urine dipstick showing leukocytes as equal predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
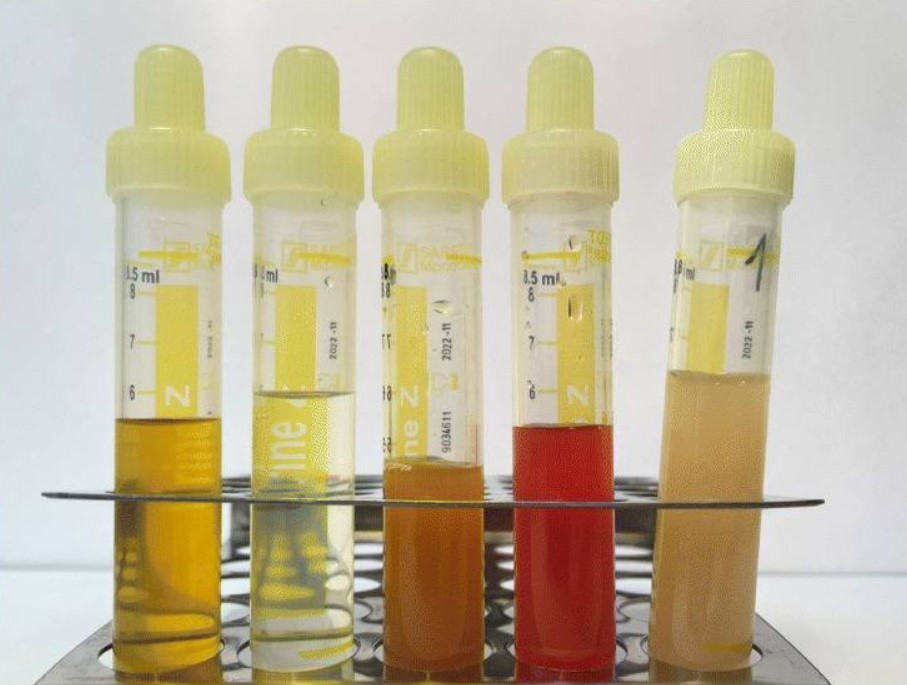
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as Cell (biology), cells, urinary casts, Crystalluria, crystals, and organisms. Background Urine is produced by the filtration of blood in the kidneys. The formation of urine takes place in microscopic structures called nephrons, about one million of which are found in a normal human kidney. Blood enters the kidney though the renal artery and flows through the kidney's vasculature into the Glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus, a tangled knot of capillaries surrounded by Bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Presentation
In obstetrics, a cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a presentation (obstetrics), longitudinal lie and the Human head, head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations) and are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means. Engagement The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called ''head engagement''. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally. Head engagement is known colloquially as the ''baby drop'', and in natural medicine as the ''lightening'' because of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Engagement
In obstetrics, a cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal ( malpresentations) and are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means. Engagement The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called ''head engagement''. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally. Head engagement is known colloquially as the ''baby drop'', and in natural medicine as the ''lightening'' because of the release of pressure on the upper abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
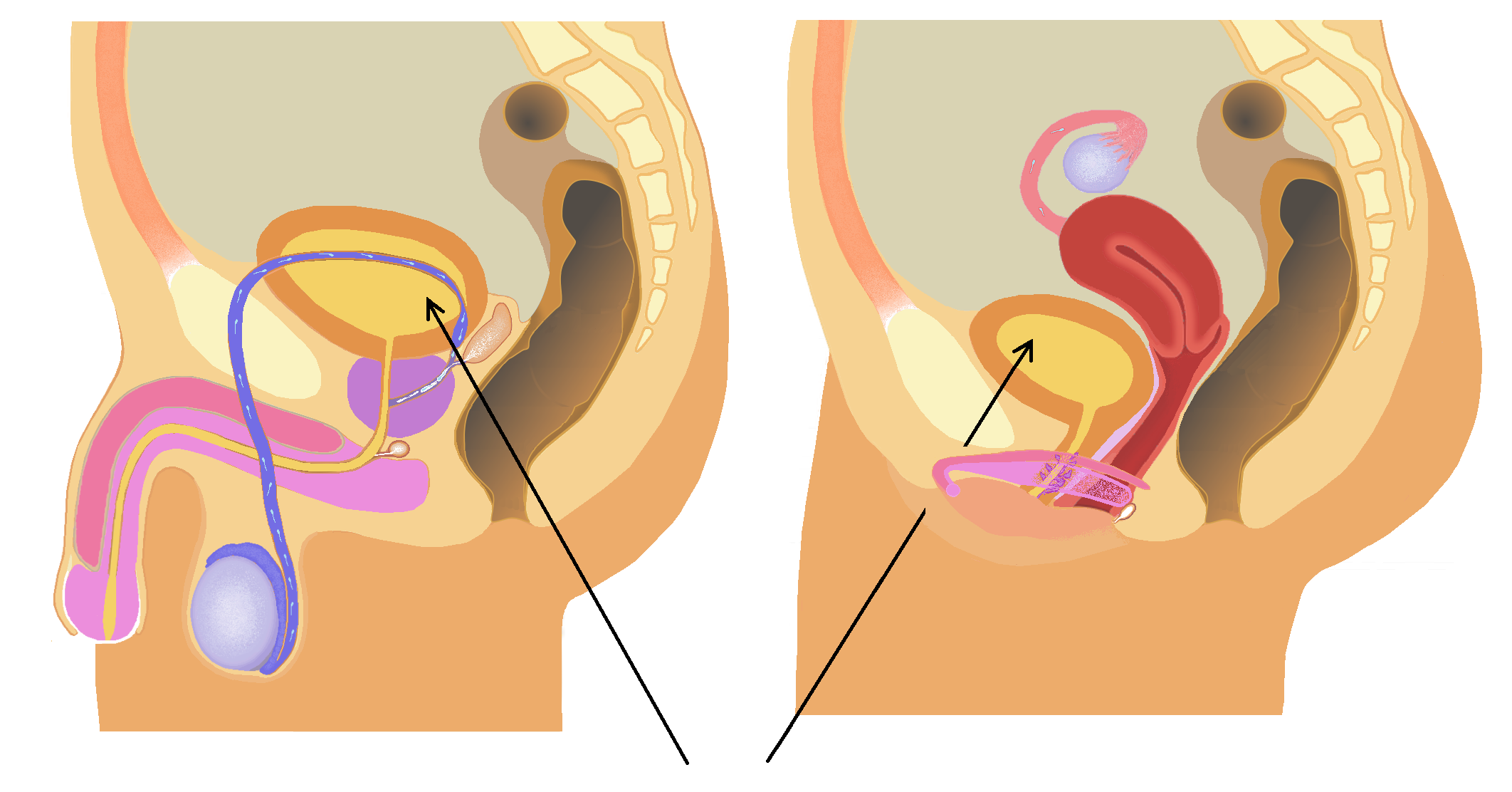
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |