|
Swithland Railway Station
Swithland was a railway station which was constructed on the Great Central Main Line between Rothley railway station, Rothley and Quorn and Woodhouse railway station, Quorn and Woodhouse. The station was due to open in March 1899 but was never completed although the line opened as planned in March 1899. The line through the station site was closed in May 1969. The line through the station was reopened in 1990 as the Great Central Railway (Nottingham), Great Central Railway. History The original plans for the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway, MS&LR's Great Central Main Line, London Extension had a station situated at Swithland instead of Rothley, although Rothley was much the larger village of the two, and only slightly further from the line. Local pressure, much of it spearheaded by Frederick Merttens, Lord of Rothley Manor, forced a change in the plans and the proposed site changed to Rothley; however, this did not mean that Swithland station was abandoned. The rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway. History New name On assuming its new title, the Great Central Railway had a main line from Manchester London Road Station via , Sheffield Victoria, and Grimsby to . A second line left the line at Penistone and served , and Scunthorpe, before rejoining the Grimsby line at . Other lines linked Sheffield to Barnsley (via ) and Doncaster (via Rotherham) and also and Wrawby Junction. Branch lines in north Lincolnshire ran to Barton-upon-Humber and New Holland and served ironstone quarries in the Scunthorpe area. In the Manchester area, lines ran to Stalybridge and Glossop. In the 1890s, the MS&LR began constructing its Derbyshire lines, the first part of its push southwards. Leaving its east–west main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
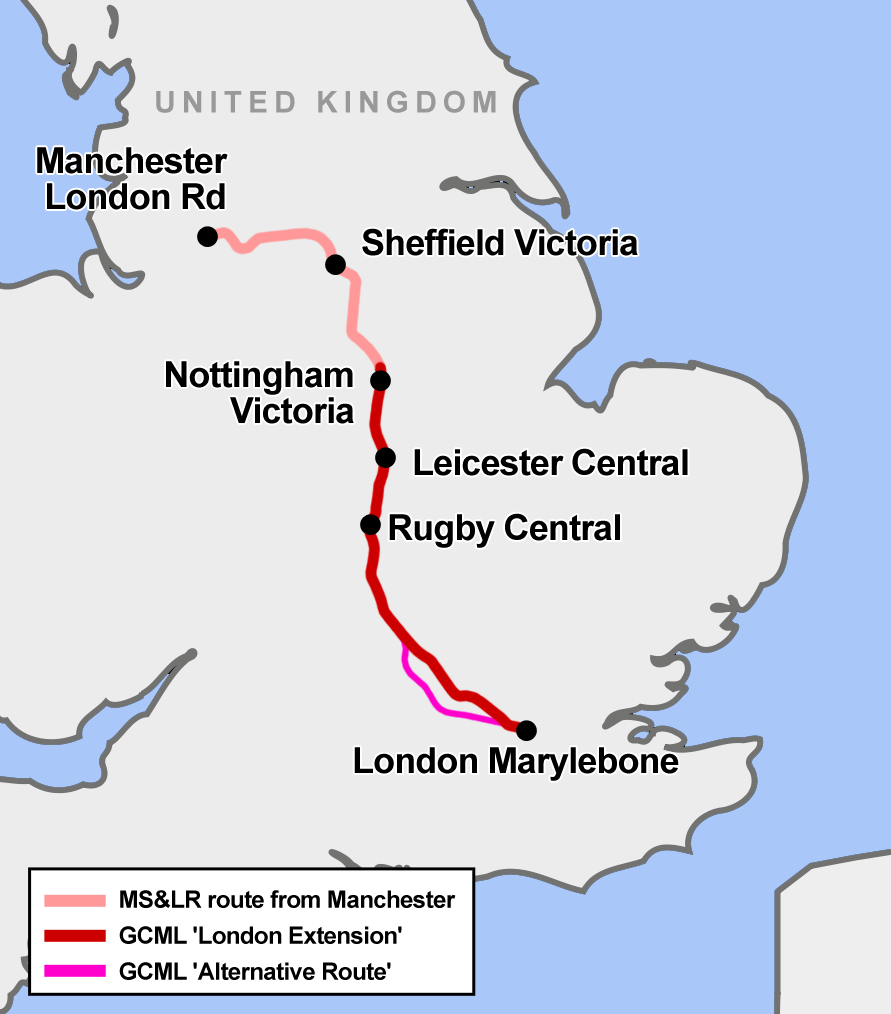
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield Victoria railway station, Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham Victoria railway station, Nottingham and Leicester Central railway station, Leicester to Marylebone station, Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian era, Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothley Railway Station
Rothley railway station is a heritage railway station on the preserved section of the Great Central Railway's ''London Extension''. Built to the standard island platform pattern of country stations on the line, it originally opened on 15 March 1899 and has been restored to late Edwardian era condition, circa 1910. Route description Climbing south from milepost 97, the formation of the Mountsorrel quarry branch joins the line from the east, crossing over the quadruple spanned bridge 352 to reach '' Swithland Sidings''. Here, the up and down lines have parted as this site was originally to be the location of a projected Swithland station. The entrance archway from the road below can still be seen from passing trains, even though a platform was never built.Original s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quorn And Woodhouse Railway Station
Quorn and Woodhouse railway station is a heritage station on the Great Central Railway (preserved) serving Quorn & Woodhouse in Leicestershire. Travelling south from Loughborough, it is the first station that is reached. Here there is a large station yard which is suitable for parking. There is also disabled access through the yard (Loughborough now has a lift for disabled as well as access via stairs). Quorn is laid out to appear as it would in the 1940s, as a typical rural LNER station. The signal box is not original but was taken from Market Rasen. The station is grade II listed In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ir ... and has a number of attractions, including the 1940s era NAAFI Tea Room situated underneath the station road bridge, a period Station Master's offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway (Nottingham)
The Nottingham Heritage Railway (formerly known as Great Central Railway (Nottingham) and Nottingham Transport Heritage Centre) is a heritage railway and transport museum on the south side of the village of Ruddington in Nottinghamshire. The route consists of almost of the former Great Central Railway Main Line from Loughborough South Junction (with the Midland Main Line) to Fifty Steps Bridge and the site of Ruddington's former GCR station, plus a branch line from Fifty Steps Bridge to Ruddington Fields station which is located on a former Ministry of Defence site next to Rushcliffe Country Park. There are stations open to the public at Ruddington Fields (within the main centre site) and at Rushcliffe Halt. The GCR(N) aim to re-open the former station at East Leake in the longer term. The railway is currently not connected to Great Central Railway (at Loughborough Central in Leicestershire), although there are plans well underway and work has started to reunite the two pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester, Sheffield And Lincolnshire Railway
The Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR) was formed in 1847 when the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway joined with authorised but unbuilt railway companies, forming a proposed network from Manchester to Grimsby. It pursued a policy of expanding its area of influence, especially in reaching west to Liverpool, which it ultimately did through the medium of the Cheshire Lines Committee network in joint partnership with the Great Northern Railway and the Midland Railway. Its dominant traffic was minerals, chiefly coal, and the main market was in London and the south of England. It was dependent on other lines to convey traffic southward. The London and North Western Railway was an exceptionally hostile partner, and in later years the MS&LR allied itself with the Great Northern Railway. Passenger traffic, especially around Manchester, was also an important business area, and well-patronised express trains to London were run in collaboration with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swithland
Swithland is a linear village in the Charnwood borough of Leicestershire, England. The civil parish population was put at 230 in 2004 and 217 in the 2011 census. It is in the old Charnwood Forest, between Cropston, Woodhouse and Woodhouse Eaves. It has a village hall, a parish church and a public house, the ''Griffin Inn''. The village is known for the slate that was quarried in the area. History Swithland was originally held by Groby. Part of the village had become held by the Danvers (originally called D'Anvers) family by 1412, and between 1509 and 1796, the whole village was held by the Danvers family.C. N. Hadfield (1952), ''Charnwood Forest – a Survey'', Edgar Backus, pp. 59–60. The village includes the 13th-century St Leonard's parish church, which retains the original arcades and has an 18th-century west tower built for Sir John Danvers.Pevsner, Nikolaus (1960) ''The Buildings of England: Leicestershire and Rutland'', Penguin Books, pp. 246–247. It includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothley
Rothley ( ) is a village and civil parish within the Borough of Charnwood in Leicestershire, England. Situated around west of the River Soar and north of Leicester, it had a population of 3,612 inhabitants . The population measured at the 2011 census was 3,897. Rothley centres on two greens, Cross Green and the Town Green, both of which are accessed by a road that leads from the crossroads. The crossroads lies on the old route of the A6 road, which now bypasses the village. Rothley is one of Leicestershire's most affluent areas based on number of houses worth more than £1 million – especially in some streets such as The Ridgeway, identified in the ''Sunday Times'' as the most expensive place to live in the East Midlands. Most children of primary schooling age attend Rothley (Church of England) Primary School. The main shopping street in the village is Woodgate. Rothley has four churches, Rothley Baptist Church, the Methodist Church, Sacred Heart RC, and the main parish ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Leake Railway Station
East Leake railway station is a former railway station serving East Leake, Nottinghamshire and is the only surviving Great Central Railway station accessed from an underbridge rather than an overbridge. The station opened on 15 March 1899 and closed on 5 May 1969. The Nottingham Heritage Railway passes through but the station has not reopened mainly due to lack of car parking, and with the station entrance being directly onto the road under the bridge, safety concerns were also a factor. A small goods siding next to the station was redeveloped for housing in the 1990s. The station buildings have been demolished, with the rubble used to fill in the area from the road entrance to the platform. The island platform remains in situ and could still be used if required. Rushcliffe Halt Rushcliffe Halt is a railway station on the former Great Central Railway London Extension from London Marylebone serving the north of East Leake, Nottinghamshire, currently in use as part of the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swithland Sidings
Swithland Sidings is a set of railway sidings on the preserved Great Central Railway, situated just south of Swithland Reservoir and Swithland Viaduct which crosses it. Commercial history The original plans for the MS&LR's London Extension had a station situated at Swithland instead of Rothley, although Rothley was much the larger village of the two, and only slightly further from the line. Local pressure, much of it spearheaded by Frederick Merttens, Lord of Rothley Manor, forced a change in the plans and the proposed site changed to Rothley; however, this did not mean that Swithland station was abandoned. The railway company had visions of turning the area into a tourist spot and the construction of Swithland station was commenced anyway. It would have consisted of an island platform of the standard design that became typical of the line, here the less common "embankment" type reached from a roadway (the Swithland-Rothley road) that passed beneath the line, similar to Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swithland Reservoir
Swithland Reservoir is a reservoir in the English county of Leicestershire. It is north-east of the village of Swithland from which it takes its name, north-west of Rothley and approximately south-west of Mountsorrel Quarry. It is part of the Buddon Wood and Swithland Reservoir Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI). History Leicester's rapidly growing population in the latter half of the 19th century required the construction of a series of reservoirs. In 1854 Thornton Reservoir was opened, serving a population of 61,000. By 1861 the population had increased, with the Waterworks Company now directly supplying 24,000 people, and five years later the company was supplying between 60 and 70,000 people and work began on Bradgate Reservoir (now known as Cropston Reservoir). By 1878 the "water population" had increased to 110,000 and by 1893 to 203,000, requiring further reservoirs to be constructed. In 1890 Leicester City Council sought Parliamentary authority to acquire t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swithland Viaduct
Swithland Viaduct is a railway viaduct in Leicestershire that carries the former Great Central Main Line over Swithland Reservoir. It is unusual in that it carries the line over a reservoir rather than a valley. It actually consists of two separate viaducts, with an embankment over Brazil Island in the centre of the reservoir. The line now carries the Great Central Railway. The viaducts (bridges No. 349 and 350) were constructed in c.1895/7 by Messrs John Aird & Sons, as a sub-contract to Henry Lovatt & Co. of Wolverhampton. Lovatts were contracted to the Great Central to execute contract number 2 on their extension line to London, East Leake to Aylestone, but the Corporation of Leicester insisted that those portions of the work that could delay or hinder the completion of their new water works at Swithland were to be executed by the main contractors for that job. The south viaduct has a skew girder section approximately halfway along its length, this having been provided to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |