|
Swedish Financial Transaction Tax
The Swedish financial transaction tax was a 0.5% financial transaction tax (FTT) applied to equity securities, fixed income securities and financial derivatives between 1984 and 1991. History In January 1984, Sweden introduced a 0.5% tax on the purchase or sale of an equity security. Hence, a round trip (purchase and sale) transaction resulted in a 1% tax. The tax applied to all equity security trades in Sweden using local brokerage services as well as to stock options. In July 1986, the rate was doubled, and in January 1989, a considerably lower tax of 0.002% on fixed-income securities was introduced (applying only for those with a maturity of 90 days or less). On a bond with a maturity of five years or more, the tax was 0.003%. 15 months later, on 15 April 1990, the tax on fixed-income securities was abolished. In January 1991 the rates on the remaining taxes were cut by half and by the end of the year, they were also abolished completely. Once the taxes were eliminated, trading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Transaction Tax
A financial transaction tax (FTT) is a levy on a specific type of financial transaction for a particular purpose. The tax has been most commonly associated with the financial sector for transactions involving intangible property rather than real property. It is not usually considered to include consumption taxes paid by consumers. A transaction tax is levied on specific transactions designated as taxable rather than on any other attributes of financial institutions. If an institution is never a party to a taxable transaction, then no transaction tax will be levied from it. If an institution carries out one such transaction, then it will be levied the tax for the one transaction. This tax narrower in scope than a financial activities tax (FAT), and is not directly an industry or sector tax like a Financial stability contribution (FSC), or " bank tax", for example. These distinctions are important in discussions about the utility of financial transaction tax as a tool to selectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility Risk
Volatility risk is the risk of a change of price of a portfolio as a result of changes in the volatility of a risk factor. It usually applies to portfolios of derivatives instruments, where the volatility of its underlying is a major influencer of prices. Sensitivity to volatility A measure for the sensitivity of a price of a portfolio (or asset) to changes in volatility is vega, the rate of change of the value of the portfolio with respect to the volatility of the underlying asset. Risk management This kind of risk can be managed using appropriate financial instruments whose price depends on the volatility of a given financial asset (a stock, a commodity, an interest rate, etc.). Examples are Futures contracts such as VIX for equities, or caps, floors and swaptions for interest rates. Risk management is the configuration and identification of analyzing, and or acceptance during investment decision-making. In essence this occurs whenever an investor or portfolio manager eval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
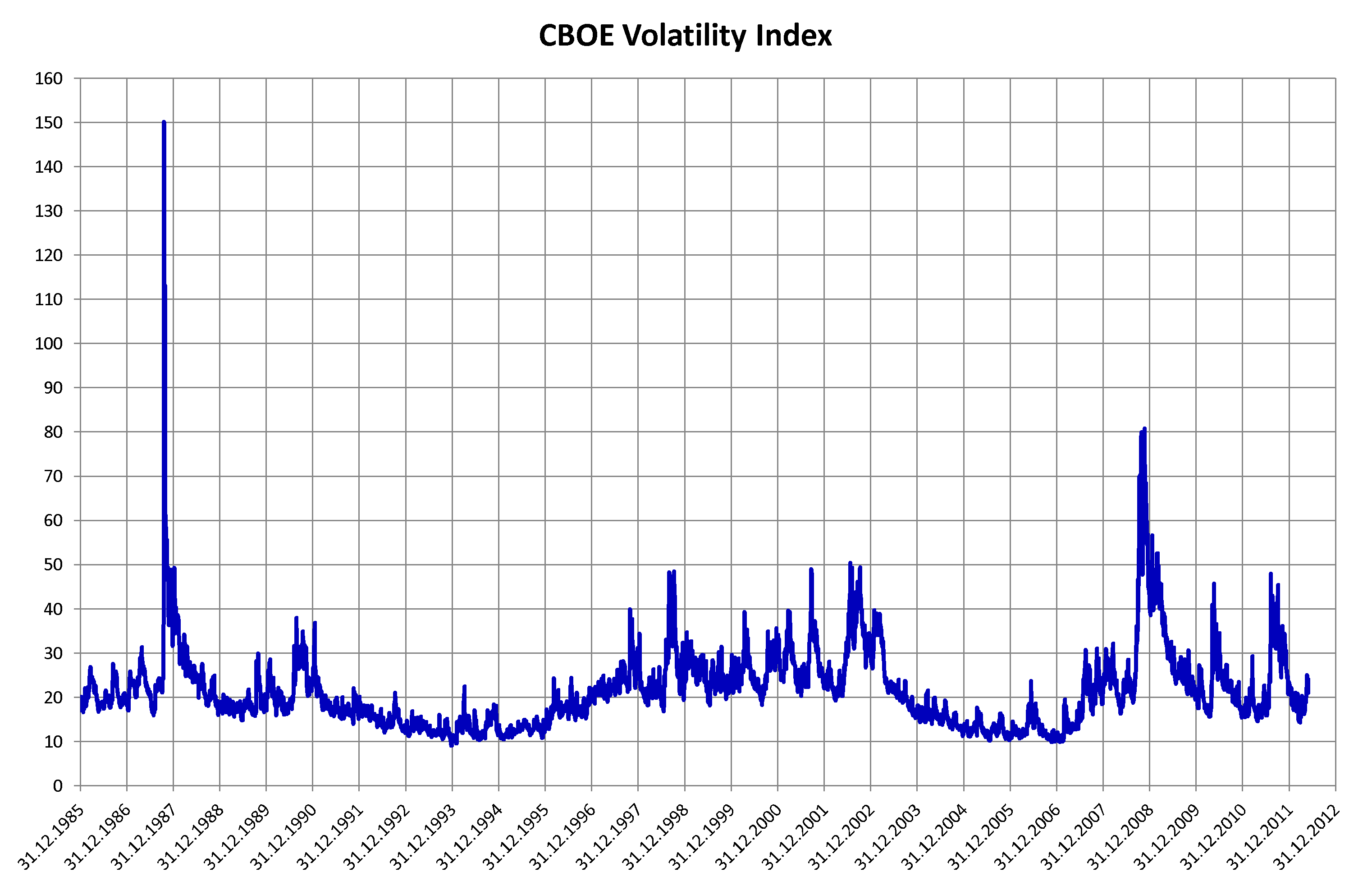
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn calculated using the sum of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Tax
A transfer tax is a tax on the passing of title to property from one person (or entity) to another. In a narrow legal sense, a transfer tax is essentially a transaction fee imposed on the transfer of title to property from one entity to another. This kind of tax is typically imposed where there is a legal requirement for registration of the transfer, such as transfers of real estate, shares, or bond. Examples of such taxes include some forms of stamp duty, real estate transfer tax, and levies for the formal registration of a transfer. In some jurisdictions, transfers of certain forms of property require confirmation by a notary. While notarial fees may add to the cost of the transaction, they are not a transfer tax in the strict sense of the term. UK In England and Northern Ireland, property transfers between living persons or other legal entities incur a Stamp Duty Land Tax. Similar provisions exist in Scotland and Wales. When property is transferred from the estate of a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobin Tax
A Tobin tax was originally defined as a tax on all spot conversions of one currency into another. It was suggested by James Tobin, an economist who won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Tobin's tax was originally intended to penalize short-term financial round-trip excursions into another currency. By the late 1990s, the term Tobin tax was being applied to all forms of short term transaction taxation, whether across currencies or not. The concept of the Tobin tax is being picked up by various tax proposals currently being discussed, amongst them the European Union Financial Transaction Tax as well as the Robin Hood tax. Tobin's original proposal Tobin suggested his currency transaction tax in 1972 in his Janeway Lectures at Princeton, shortly after the Bretton Woods system of monetary management ended in 1971. Prior to 1971, one of the chief features of the Bretton Woods system was an obligation for each country to adopt a monetary policy that maintaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.) Many speculators pay little attention to the fundamental value of a security and instead focus purely on price movements. In principle, speculation can involve any tradable good or financial instrument. Speculators are particularly common in the markets for stocks, bonds, commodity futures, currencies, fine art, collectibles, real estate, and derivatives. Speculators play one of four primary roles in financial markets, along with hedgers, who engage in transactions to offset some other pre-existing risk, arbitrageus who seek to profit from situations where fungible instruments trade at different prices in different market segments, and investors who seek profit through long-term ownership of an instrument's underlying attributes. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Market
The money market is a component of the economy that provides short-term funds. The money market deals in short-term loans, generally for a period of a year or less. As short-term securities became a commodity, the money market became a component of the financial market for assets involved in short-term borrowing, lending, buying and selling with original maturities of one year or less. Trading in money markets is done over the counter and is wholesale. There are several money market instruments in most Western countries, including treasury bills, commercial paper, banker's acceptances, deposits, certificates of deposit, bills of exchange, repurchase agreements, federal funds, and short-lived mortgage- and asset-backed securities. The instruments bear differing maturities, currencies, credit risks, and structures. A market can be described as a money market if it is composed of highly liquid, short-term assets. Money market funds typically invest in government securiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market. The main participants in this market are the larger international banks. Financial centers around the world function as anchors of trading between a wide range of multiple types of buyers and sellers around the clock, with the exception of weekends. Since currencies are always traded in pairs, the foreign exchange market does not set a currency's absolute value but rather determines its relative value by setting the market price of one currency if paid for with another. Ex: USD 1 is worth X CAD, or CHF, or JPY, etc. The foreign exchange market works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Markets
A financial market is a market in which people trade financial securities and derivatives at low transaction costs. Some of the securities include stocks and bonds, raw materials and precious metals, which are known in the financial markets as commodities. The term "market" is sometimes used for what are more strictly ''exchanges'', organizations that facilitate the trade in financial securities, e.g., a stock exchange or commodity exchange. This may be a physical location (such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), London Stock Exchange (LSE), JSE Limited (JSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) or an electronic system such as NASDAQ. Much trading of stocks takes place on an exchange; still, corporate actions (merger, spinoff) are outside an exchange, while any two companies or people, for whatever reason, may agree to sell the stock from the one to the other without using an exchange. Trading of currencies and bonds is largely on a bilateral basis, although some bonds trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security (finance)
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any form of financial instrument, even though the underlying legal and regulatory regime may not have such a broad definition. In some jurisdictions the term specifically excludes financial instruments other than Stock, equities and Fixed income instruments. In some jurisdictions it includes some instruments that are close to equities and fixed income, e.g., Warrant (finance), equity warrants. Securities may be represented by a certificate or, more typically, they may be "non-certificated", that is in electronic (Dematerialization (securities), dematerialized) or "book entry only" form. Certificates may be ''bearer'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights under the security merely by holding the security, or ''registered'', meaning they enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATTAC
The Association pour la Taxation des Transactions financières et pour l'Action Citoyenne (''Association for the Taxation of financial Transactions and Citizen's Action'', ATTAC) is an activist organisation originally created to promote the establishment of a tax on foreign exchange transactions. Background Originally called "Action for a Tobin Tax to Assist the Citizen", ATTAC was a single-issue movement demanding the introduction of the so-called Tobin tax on currency speculation. n the ATTAC: A new European alternative to globalisation, David Moberg, These Times magazine, May 2001/ref> ATTAC has enlarged its scope to a wide range of issues related to globalisation, and monitoring the decisions of the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD,) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). ATTAC representatives attend the meetings of the G8 with the goal of influencing policymakers' decisions. Attac spokesmen recently cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)