|
Surin Islands
The Surin Islands (, ) is a continental archipelago of five islands in the Andaman Sea, from the Thai mainland. Administratively, the islands are part of Tambon Ko Phra Thong, Khura Buri district, in Phang Nga province, Thailand. Geography Location The Surin Islands consist primarily of two larger islands, Ko Surin Nuea and Ko Surin Tai, which are separated by a channel approximately wide that becomes dry at low tide. In addition to these, the archipelago includes three smaller islands: Ko Khai (also known as Ko Torinla), Ko Glang (or Ko Pachumba), and Ko Chi (also referred to as Ko Satok). There are also two small rocky islets within the group, named Hin Kong and Hin Rap. Additionally, the limestone pinnacle known as Richelieu Rock (Hin Plo Naam), located about east of Ko Khai and from the mainland, is named in honor of admiral Andreas Richelieu, who was the first and only foreign commander-in-chief of the Thai Navy. Geographically, the Thai-Burmese oceanic border l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated from the Bay of Bengal to its west by the Andaman Islands and the Nicobar Islands. Its southern end is at Breueh Island just north of Sumatra, with the Strait of Malacca further southeast. Traditionally, the sea has been used for fishery and transportation of goods between the coastal countries and its coral reefs and islands, which are popular tourist destinations. The fishery and tourist infrastructure was severely damaged by the December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Geography Location The Andaman Sea, which extends over 92°E to 100°E and 4°N to 20°N, occupies a very significant position in the Indian Ocean, yet remained unexplored for a long period. To the south of Myanmar, west of Thailand, and north of Indonesia, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christie Island
Christie Island is an island in the Mergui Archipelago and the southernmost point of Burma (Myanmar). It lies at the southern end of the archipelago to the NNE of Ko Surin Nuea, and the Thai-Burmese oceanic border is located between these two islands. Christie Island is long and has several peaks it covered with thick forest. The tallest is 325 meters high. Murray Island and Sanders Island are small rocky islets off its southern shores. Christie Island is part of the Alladin Islands subgroup. It features a clearing at the top with a helicopter pad and small dusty military base. 1998 massacres In May 1998, Colonel Zaw Min, landed on Christie Island and found 59 Burmese nationals living there to gather wood and bamboo, in violation of Burmese law. General Than Shwe Than Shwe (; ; born 2 February 1933) is a retired Burmese army general who held influential positions within Myanmar's government. Serving as the chairman of the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mergui Archipelago
The Mergui Archipelago (also Myeik Archipelago or ''Myeik Kyunzu''; ) is located in far southern Myanmar (Burma) and is part of the Tanintharyi Region. It consists of around 800 islands, varying in size from very small to hundreds of square kilometres, all lying in the Andaman Sea off the western shore of the Malay Peninsula near its landward (northern) end where it joins the rest of Indochina. They are occasionally referred to as the Pashu Islands because the Malay inhabitants are locally called ''Pashu''. Environment Geologically, the islands are characterized mainly by limestone and granite. They are generally covered with thick tropical growth, including rainforest, and their shorelines are punctuated by beaches, rocky headlands, and in some places, mangrove swamps. Offshore are extensive coral reefs. The archipelago's virtual isolation from most of mankind's influence on the natural environment has given the islands and the surrounding waters of the Andaman Sea a great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
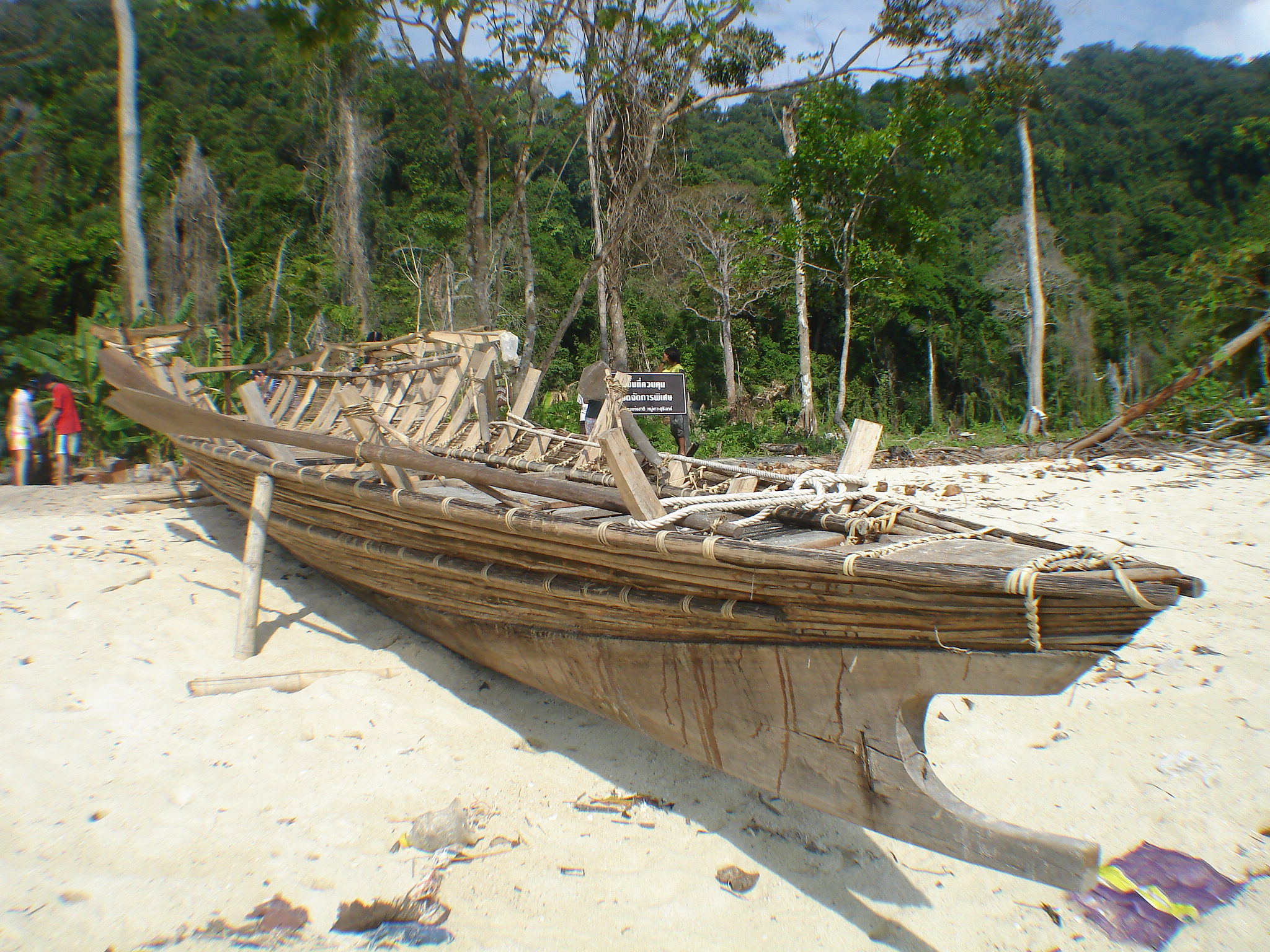
Moken Boat
The Moken (also Mawken or Morgan; ; ) are an Austronesian people of the Mergui Archipelago, a group of approximately 800 islands claimed by both Myanmar and Thailand, and the Surin Islands. Most of the Moken live a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle heavily based on the sea, though this lifestyle is increasingly under threat. The Moken identify in a common culture and some speak the Moken language, a distinct Austronesian language. Attempts by both Myanmar and Thailand to assimilate the Moken into the wider regional culture have met with very limited success. However, the Moken face an uncertain future as their population decreases and their nomadic lifestyle and unsettled legal status leave them marginalized by modern property and immigration laws, maritime conservation and development programs, and tightening border policies. Nomenclature The people refer to themselves as Moken. The name is used for all of the Austronesian speaking tribes who inhabit the coast and islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Of South Asia
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving. The unique geographical features of the Indian subcontinent, along with associated atmospheric, oceanic, and geographical factors, influence the behavior of the monsoon. Because of its effect on agriculture, on flora and fauna, and on the climates of nations such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – among other economic, social, and environmental effects – the monsoon is one of the most anticipated, tracked, and studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granitoids
A granitoid is a broad term referring to a diverse group of coarse-grained igneous rocks that are widely distributed across the globe, covering a significant portion of the Earth's exposed surface and constituting a large part of the continental crust. These rocks are primarily composed of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz-poor monzonites to quartz-rich quartzolites. As only two of the three defining mineral groups (quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar) need to be present for the rock to be called a granitoid, foid-bearing rocks, which predominantly contain feldspars but no quartz, are also granitoids. Nomenclature and classification The terms ''granite'' and ''granitic rock'' are often used interchangeably for granitoids; however, granite is just one particular type of granitoid. Granitoids are diverse. No classification system for granitoids can give a complete and unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dike (geology), dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF diagram, QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Plate
The Sunda plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located. The Sunda plate was formerly considered a part of the Eurasian plate, but the GPS measurements have confirmed its independent movement at 10 mm/yr eastward relative to Eurasia. Extent The Sunda plate includes the South China Sea, the Andaman Sea, southern parts of Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos and Thailand along with Malaysia, Singapore, Cambodia, southern Philippines, and the islands of Bali, Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara, Borneo, Sumatra, Java, and part of Sulawesi in Indonesia. The Sunda is bounded in the east by the Philippine Mobile Belt, Molucca Sea Collision Zone, Molucca Sea plate, Banda Sea plate and Timor plate; to the south and west by the Australian plate; and to the north by the Burma plate, Eurasian plate; and Yangtze plate. The Indo-Australian plate dips beneath the Sunda plate along the Sunda Trench also known as Jav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burma Plate
The Burma plate is a minor tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, sometimes considered a part of the larger Eurasian plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate. This island arc separates the Andaman Sea from the main Indian Ocean to the west. To its east lies the Sunda plate, from which it is separated along a transform boundary, running in a rough north–south line through the Andaman Sea. This boundary between the Burma and Sunda plates is a marginal seafloor spreading centre, which has led to the opening up of the Andaman Sea (from a southerly direction) by "pushing out" the Andaman-Nicobar-Sumatra island arc from mainland Asia, a process which began in earnest approximately 4 million years ago. To the west is the much larger India plate, which is subducting beneath the western facet of the Burma plate. This extensive subduction zone has formed the Sunda Trench. Tectonic history In models of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |