|
Suprapineal Recess
The suprapineal recess is an anatomical structure in the ventricular system of the brain. It is located in the posterior part of the third ventricle, overlying the cerebral aqueduct The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brai .... In severe cases of hydrocephalus with increased pressure, this structure can dilate causing mass effect on the midbrain resulting in Parinaud's Syndrome with bilateral inward and downward deviation of the eyes. Additional images File:Gray735.png, Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from above. Ventricular system {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
The ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal fluid can flow. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
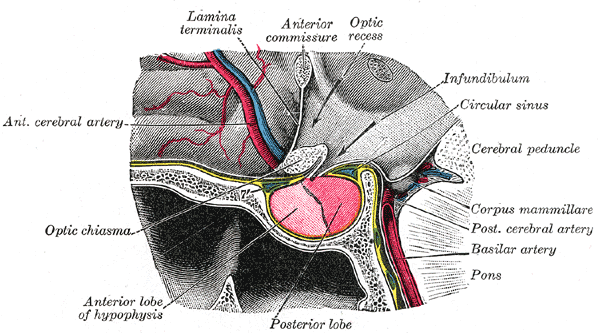
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the brain. It is located in the midbrain dorsal to the pons and ventral to the cerebellum. The cerebral aqueduct is surrounded by an enclosing area of gray matter called the periaqueductal gray, or central gray. It was first named after Franciscus Sylvius. Structure Development The cerebral aqueduct, as other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develops from the central canal of the neural tube, and it originates from the portion of the neural tube that is present in the developing mesencephalon, hence the name "mesencephalic duct." Function The cerebral aqueduct acts like a canal that passes through the midbrain. It connects the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle so that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) moves between the cereb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |