|
Superluminal
Faster-than-light (superluminal or supercausal) travel and communication are the conjectural propagation of matter or information faster than the speed of light in vacuum (). The special theory of relativity implies that only particles with zero rest mass (i.e., photons) may travel ''at'' the speed of light, and that nothing may travel faster. Particles whose speed exceeds that of light (tachyons) have been hypothesized, but their existence would violate causality and would imply time travel. The scientific consensus is that they do not exist. According to all observations and current scientific theories, matter travels at slower-than-light (subluminal) speed with respect to the locally distorted spacetime region. Speculative faster-than-light concepts include the Alcubierre drive, Krasnikov tubes, traversable wormholes, and quantum tunneling. Some of these proposals find loopholes around general relativity, such as by expanding or contracting space to make the object appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superluminal Motion
In astronomy, superluminal motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the relativistic jets emitted from these objects can have a proper motion that appears greater than the speed of light. All of these sources are thought to contain a black hole, responsible for the ejection of mass at high velocities. Light echoes can also produce apparent superluminal motion. Explanation Superluminal motion occurs as a special case of a more general phenomenon arising from the difference between the apparent speed of distant objects moving across the sky and their actual speed as measured at the source. In tracking the movement of such objects across the sky, a calculation of their speed can be determined by a simple distance divided by time formula. If the distance of the object from the Earth is known and the angular sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyon04s
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels Faster-than-light, faster than light. Physicists posit that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are inconsistent with the known Scientific law#Laws of physics, laws of physics. If such particles did exist they perhaps could be used to send signals faster than light and into the past. According to the theory of relativity this would violate Causality (physics), causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a Quantum field theory, quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
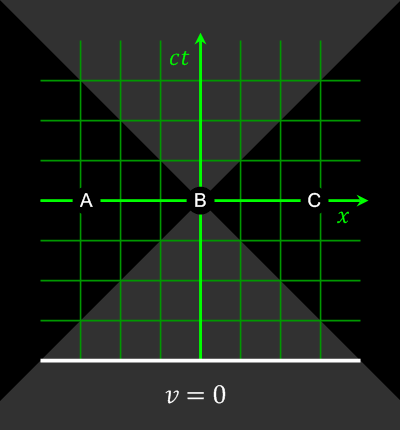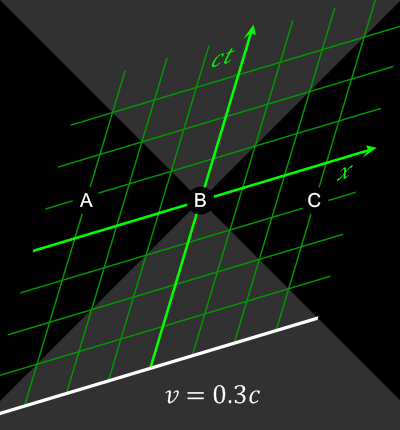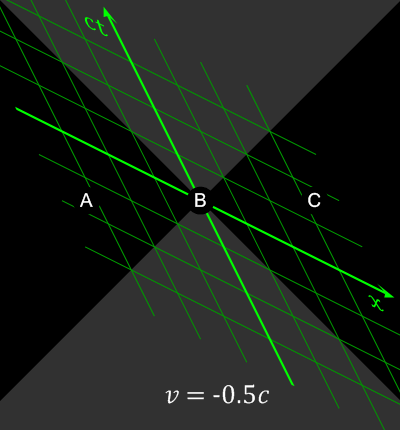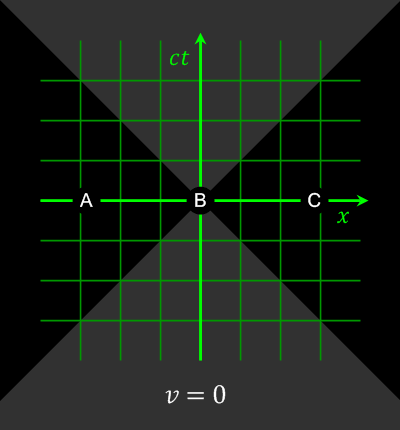
Special Theory Of Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just two postulates: # The laws of physics are invariant (identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see '' Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ideas. The non-technical ideas include: * speed or velocity, how the relative distance between an object and a reference point changes with time. * speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels Faster-than-light, faster than light. Physicists posit that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are inconsistent with the known Scientific law#Laws of physics, laws of physics. If such particles did exist they perhaps could be used to send signals faster than light and into the past. According to the theory of relativity this would violate Causality (physics), causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a Quantum field theory, quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnikov Tube
A Krasnikov tube is a speculative mechanism for space travel involving the warping of spacetime into permanent superluminal tunnels. The resulting structure is analogous to a wormhole or an immobile Alcubierre drive (and like them requires exotic matter with negative energy density) with the endpoints displaced in time as well as space. The idea was proposed by Sergey Krasnikov in 1995. Structure The tube is a distortion of spacetime that can be intentionally created (using hypothetical technology) in the wake of travel near the speed of light. The Krasnikov tube allows for a return trip that takes travelers back to the time right after they left. Experiencing the effect requires that the traveler race along the tube at speeds close to that of light. Causality violations One-tube case Krasnikov argues that despite the time-machine-like aspects of his metric, it cannot violate the law of causality (that a cause must always precede its effects in all coordinate systems and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superluminal Communication
Faster-than-light communication, also called superluminal communication, is a hypothetical process in which information is conveyed at faster-than-light speeds. The current scientific consensus is that faster-than-light communication is not possible, and to date it has not been achieved in any experiment. Faster-than-light communication other than possibly through wormholes is likely impossible because, in a Lorentz-invariant theory, it could be used to transmit information into the past. This would complicate causality, but no theoretical arguments conclusively preclude this possibility. A number of theories and phenomena related to faster-than-light communication have been proposed or studied, including tachyons, neutrinos, quantum nonlocality, wormholes, and quantum tunneling. Proposed mechanisms Tachyons Tachyonic particles are hypothetical particles that travel faster than light, which could conceivably allow for superluminal communication. Because such a particle wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Travel
Time travel is the hypothetical activity of traveling into the past or future. Time travel is a concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. In fiction, time travel is typically achieved through the use of a device known as a time machine. The idea of a time machine was popularized by H. G. Wells's 1895 novel ''The Time Machine''. It is uncertain whether time travel to the past would be physically possible. Such travel, if at all feasible, may give rise to questions of causality. Forward time travel, outside the usual sense of the perception of time, is an extensively observed phenomenon and is well understood within the framework of special relativity and general relativity. However, making one body advance or delay more than a few milliseconds compared to another body is not feasible with current technology. As for backward time travel, it is possible to find solutions in general relativity that allow for it, such as a rotating black hole. Traveling t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcubierre Drive
The Alcubierre drive () is a speculative warp drive idea according to which a spacecraft could achieve apparent faster-than-light travel by contracting space in front of it and expanding space behind it, under the assumption that a configurable energy-density field lower than that of vacuum (that is, negative mass) could be created. Proposed by theoretical physicist Miguel Alcubierre in 1994, the Alcubierre drive is based on a solution of Einstein's field equations. Since those solutions are metric tensors, the Alcubierre drive is also referred to as Alcubierre metric. Objects cannot accelerate to the speed of light within normal spacetime; instead, the Alcubierre drive shifts space around an object so that the object would arrive at its destination more quickly than light would in normal space without breaking any physical laws. Although the metric proposed by Alcubierre is consistent with the Einstein field equations, construction of such a drive is not necessarily poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wormhole
A wormhole is a hypothetical structure that connects disparate points in spacetime. It can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are based on a special Solutions of the Einstein field equations, solution of the Einstein field equations. More precisely they are a transcendental bijection of the spacetime continuum, an Asymptote, asymptotic projection of the Calabi–Yau manifold manifesting itself in anti-de Sitter space. Wormholes are consistent with the General relativity, general theory of relativity, but whether they actually exist is unknown. Many physicists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a Four-dimensional space, fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |