|
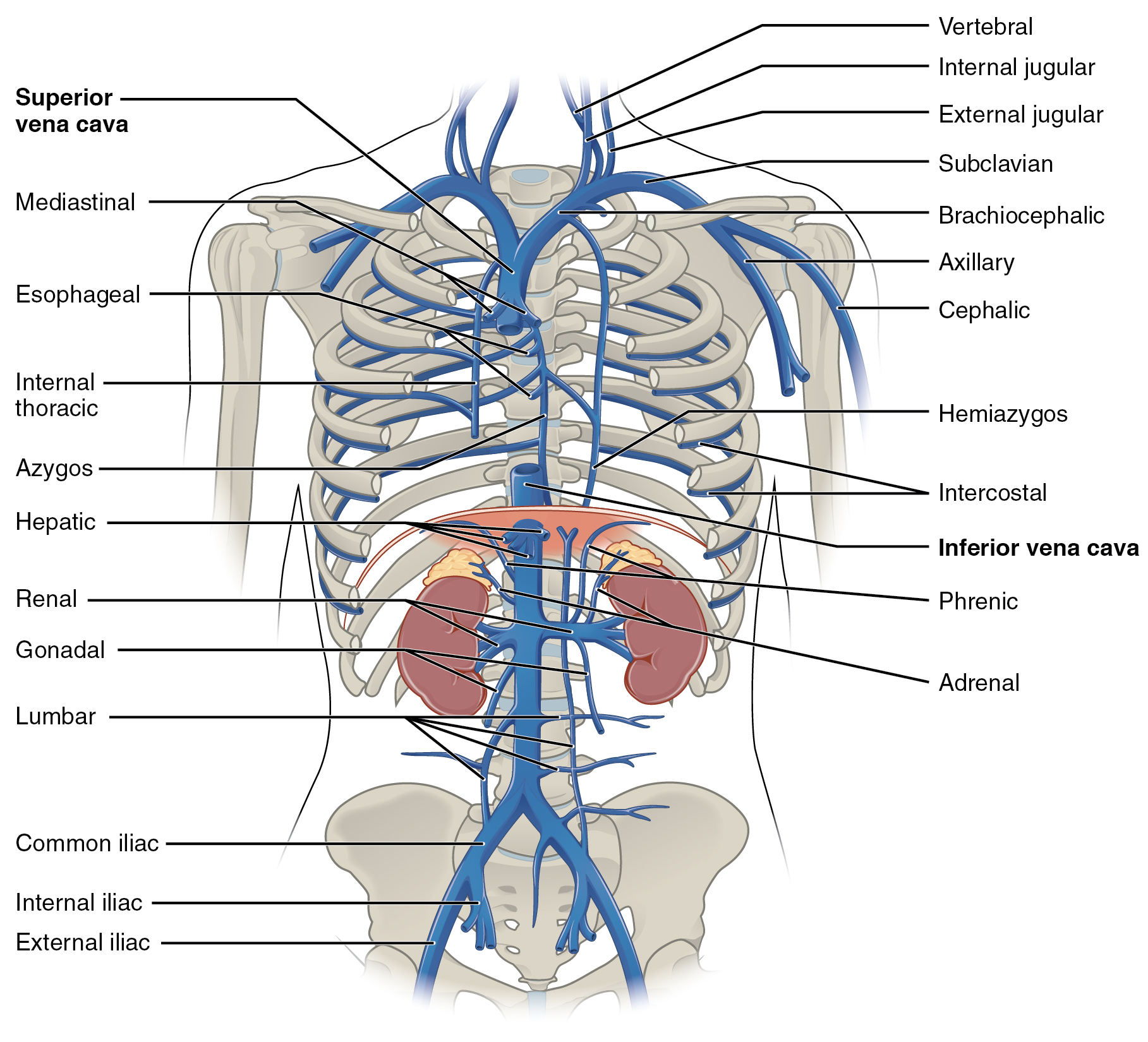
Superior Intercostal Vein
The superior intercostal veins are two veins that drain the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th intercostal spaces, one vein for each side of the body. Right superior intercostal vein The right superior intercostal vein drains the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th posterior intercostal veins on the right side of the body. It flows into the azygos vein. Left superior intercostal vein The left superior intercostal vein drains the 2nd and 3rd posterior intercostal veins on the left side of the body. It usually drains into the left brachiocephalic vein. It may also communicate with the accessory hemiazygos vein. As it passes posteriorly above the aortic arch, it crosses deep to the phrenic nerve and the pericardiacophrenic vessels and then superficial to the vagus nerve. See also * Supreme intercostal vein The supreme intercostal vein (highest intercostal vein) is a paired vein that drains the first intercostal space on its corresponding side. It usually drains into the brachiocephalic vein. Alternatively, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Intercostal Veins
The posterior intercostal veins are veins that drain the intercostal spaces posteriorly. They run with their corresponding posterior intercostal artery on the underside of the rib, the vein superior to the artery. Each vein also gives off a dorsal branch that drains blood from the muscles of the back. There are eleven posterior intercostal veins on each side. Their patterns are variable, but they are commonly arranged as: * The 1st posterior intercostal vein, supreme intercostal vein, drains into the brachiocephalic vein or the vertebral vein. * The 2nd and 3rd (and often 4th) posterior intercostal veins drain into the superior intercostal vein. * The remaining posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein The azygos vein (from Ancient Greek ἄζυγος (ázugos), meaning 'unwedded' or 'unpaired') is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superio ... on the right, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azygos Vein
The azygos vein (from Ancient Greek ἄζυγος (ázugos), meaning 'unwedded' or 'unpaired') is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked. Structure The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava. It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending to the right of the descending aorta and thoracic duct, passing behind the right crus of diaphragm, anterior to the vertebral bodies of T12 to T5 and right posterior intercostal arteries. At the level of T4 vertebrae, it arches over the root of the right lung from behind to the front to join the superior vena cava. The tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the Thorax, upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein (the so-called venous angle) behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. These veins merge to form the superior vena cava, a great vessel, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage with the Manubrium, manubrium of the sternum. The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava. Left and right veins Left brachiocephalic vein The left brachiocephalic vein is about 6cm, more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. and is formed by the confluence of the left subclavian vein, subclavian and left internal jugular veins. In addition the left vein receives drainage from the following tributaries: * The left vertebral vein, internal thor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostal Arteries
The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space (the space between two adjacent ribs). There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branchthe musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta. Each anterior intercostal artery anastomose, anastomoses with the corresponding posterior intercostal artery arising from the thoracic aorta. Anterior intercostal arteries Origin The upper six anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery (anterior intercostal branches of internal thoracic artery). The internal thoracic artery then divides into its two terminal branches, one of which - the musculophrenic artery - proceeds to issue anterior intercostal arteries to the remaining 7th, 8th, and 9th intercostal spaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins. There are three sizes of veins: large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins are often closer to the skin than arteries. Veins have less smooth muscle and connective tissue and wider internal diameters than arteries. Because of their thinner walls and wider lumens they are able to expand and hold more blood. This greater capacity gives them the term of ''capacitance vessels''. At any time, nearly 70% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostal Spaces
The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs (Lat. costa). Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it. Structures in intercostal space * several kinds of intercostal muscle * intercostal arteries and intercostal veins * intercostal lymph nodes * intercostal nerves Order of components Muscles There are 3 muscular layers in each intercostal space, consisting of the external intercostal muscle, the internal intercostal muscle, and the thinner innermost intercostal muscle. These muscles help to move the ribs during breathing. Neurovascular bundles Neurovascular bundles are located between the internal intercostal muscle and the innermost intercostal muscle. The neurovascular bundle has a strict order of vein-artery-nerve (VAN), from top to bottom. This neurovascular bundle runs high in the intercostal space, and the smaller collateral neurovascular bundle runs just superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Intercostal Veins
The posterior intercostal veins are veins that drain the intercostal spaces posteriorly. They run with their corresponding posterior intercostal artery on the underside of the rib, the vein superior to the artery. Each vein also gives off a dorsal branch that drains blood from the muscles of the back. There are eleven posterior intercostal veins on each side. Their patterns are variable, but they are commonly arranged as: * The 1st posterior intercostal vein, supreme intercostal vein, drains into the brachiocephalic vein or the vertebral vein. * The 2nd and 3rd (and often 4th) posterior intercostal veins drain into the superior intercostal vein. * The remaining posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein The azygos vein (from Ancient Greek ἄζυγος (ázugos), meaning 'unwedded' or 'unpaired') is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superio ... on the right, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azygos Vein
The azygos vein (from Ancient Greek ἄζυγος (ázugos), meaning 'unwedded' or 'unpaired') is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked. Structure The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava. It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending to the right of the descending aorta and thoracic duct, passing behind the right crus of diaphragm, anterior to the vertebral bodies of T12 to T5 and right posterior intercostal arteries. At the level of T4 vertebrae, it arches over the root of the right lung from behind to the front to join the superior vena cava. The tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Hemiazygos Vein
The accessory hemiazygos vein, also called the superior hemiazygous vein, is a vein on the left side of the vertebral column that generally drains the fourth through eighth intercostal spaces on the left side of the body. Structure The accessory hemiazygos vein varies inversely in size with the left superior intercostal vein. It usually receives the posterior intercostal veins from the 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th intercostal spaces between the left superior intercostal vein and highest tributary of the hemiazygos vein; the left bronchial vein sometimes opens into it. The vein usually crosses the body of the eighth thoracic vertebra to join the azygos vein. Alternatively, it ends in the hemiazygos vein. When this vein is small, or altogether absent, the left superior intercostal vein The superior intercostal veins are two veins that drain the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th intercostal spaces, one vein for each side of the body. Right superior intercostal vein The right superior intercost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
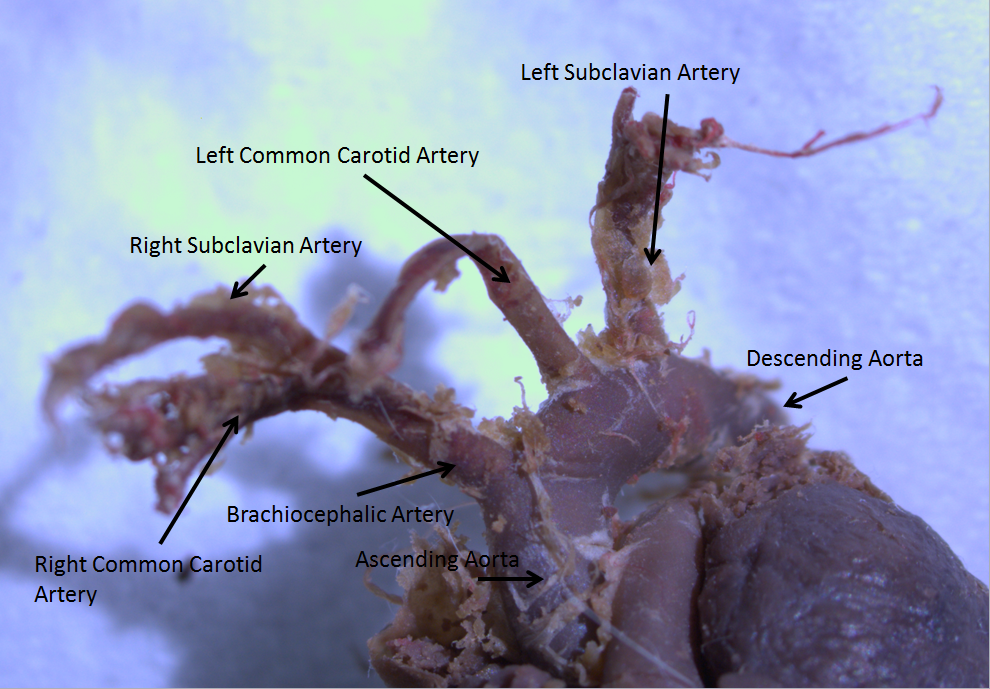
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the C3–C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerve roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic nerve or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |