|
Superior Epigastric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior epigastric artery is a terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery that provides arterial supply to the abdominal wall, and upper rectus abdominis muscle. It enters the rectus sheath to descend upon the inner surface of the rectus abdominis muscle. It ends by anastomosing with the inferior epigastric artery. Structure Origin The superior epigastric artery arises from the internal thoracic artery (referred to as the internal mammary artery in the accompanying diagram). Course and relations The superior epigastric artery pierces the diaphragm to enter the rectus sheath and descend upon the deep surface of the rectus abdominis. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the superior epigastric vein. Anastomoses It anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery within the rectus abdominis muscle at the umbilicus. Distribution Where it anastomoses, the superior epigastric artery supplies the anterior par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Thoracic Artery
The internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries. Structure The internal thoracic artery arises from the anterior surface of the subclavian artery near its origin. It has a width of between 1-2 mm. It travels downward on the inside of the rib cage, approximately 1 cm from the sides of the sternum, and thus medial to the nipple. It is accompanied by the internal thoracic vein. It runs deep to the abdominal external oblique muscle, but superficial to the vagus nerve. In adults, the internal thoracic artery lies closest to the sternum at the first intercostal space. The gap between the artery and lateral border of the sternum increases when going downwards, up to 1.1 cm to 1.3 cm at the sixth intercost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
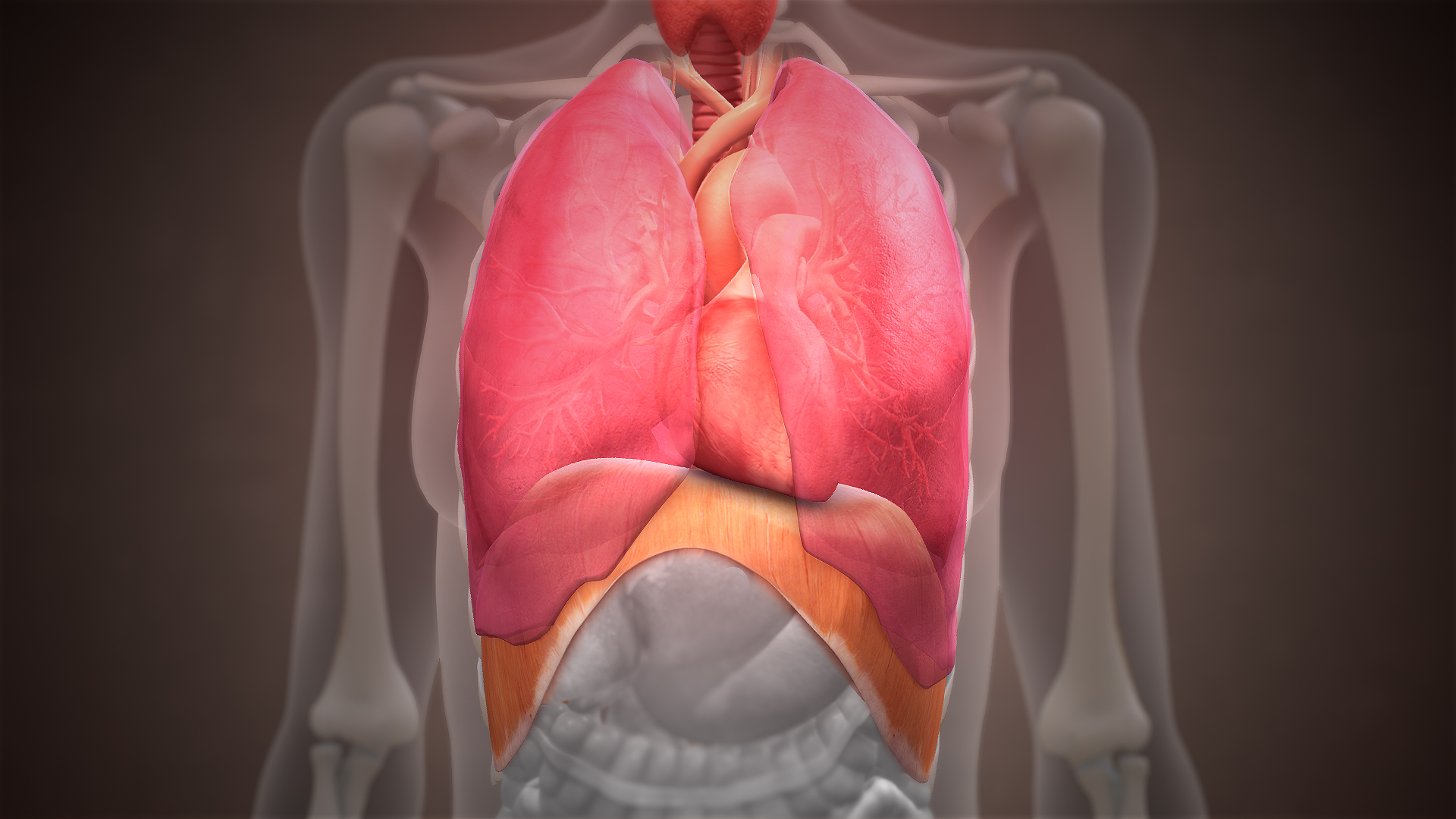
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver rests beneath the right half of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Epigastric Artery
In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold (which represents the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.) The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath. Structure Origin The inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery, immediately superior to the inguinal ligament. Course and relations It curves forward in the subperitoneal tissue, and then ascends obliquely along the medial margin of the abdominal inguinal ring; continuing its course upward, it pierces the transversalis fascia, and, passing in front of the linea semicircularis, ascends betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terms For Anatomical Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coarctation Of The Aorta
Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a congenital condition whereby the aorta is narrow, usually in the area where the ductus arteriosus ( ligamentum arteriosum after regression) inserts. The word ''coarctation'' means "pressing or drawing together; narrowing". Coarctations are most common in the aortic arch. The arch may be small in babies with coarctations. Other heart defects may also occur when coarctation is present, typically occurring on the left side of the heart. When a patient has a coarctation, the left ventricle has to work harder. Since the aorta is narrowed, the left ventricle must generate a much higher pressure than normal in order to force enough blood through the aorta to deliver blood to the lower part of the body. If the narrowing is severe enough, the left ventricle may not be strong enough to push blood through the coarctation, thus resulting in a lack of blood to the lower half of the body. Physiologically its complete form is manifested as interrupted ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Limb
Lower may refer to: *Lower (album), ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England See also *Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture). ''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing is caused by contraction of smooth muscle (e.g. achalasia, prinzmetal angina); ''stenosis'' is usually used when narrowing is caused by lesion that reduces the space of lumen (e.g. atherosclerosis). The term coarctation is another synonym, but is commonly used only in the context of aortic coarctation. Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis after a procedure. Examples Examples of vascular stenotic lesions include: * Intermittent claudication (peripheral artery stenosis) * Angina ( coronary artery stenosis) * Carotid artery stenosis which predispose to (strokes and transient ischaemic episodes) * Renal artery stenosis Types In heart valves The types of stenoses in heart valves are: * Pulmonary valve stenosis, which is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax). Structure The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the diaphragm, crossing it via the aortic hiatus, technically behind the diaphragm, at the vertebral level of T12. It travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, anterior to the vertebral column. It thus follows the curvature of the lumbar vertebrae, that is, convex anteriorly. The peak of this convexity is at the level of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). It runs parallel to the inferior vena cava, which is located just to the right of the abdominal aorta, and becomes smaller in diameter as it gives off branches. This is thought to be due to the large size of its principal branches. At the 11th rib, the diameter is 122mm long and 55mm wide and this is because of the constant pressure. The abdominal aorta is clinically divided into 2 segments: # Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Aorta
The thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta. At its commencement, it is situated on the left of the vertebral column; it approaches the median line as it descends; and, at its termination, lies directly in front of the column. The thoracic aorta has a curved shape that faces forward, and has small branches. It has a radius of approximately 1.16 cm. Structure The thoracic aorta is part of the descending aorta, which has different parts named according to their structure or location. The thoracic aorta is a continuation of the descending aorta and becomes the abdominal aorta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collateral Circulation
Collateral circulation is the alternate Circulatory system, circulation around a blocked blood vessel, artery or vein via another path, such as nearby minor vessels. It may occur via preexisting vascular redundancy (analogous to redundancy (engineering), engineered redundancy), as in the circle of Willis in the brain, or it may occur via new branches formed between adjacent blood vessels (neovascularization), as in the eye after a retinal embolism or in the brain when an instance of arterial constriction occurs due to Moyamoya disease. Its formation may be related by pathological conditions such as high vascular resistance or ischaemia. It is occasionally also known as accessory circulation, auxiliary circulation, or secondary circulation. It has surgery, surgically created analogues in which shunt (medical), shunts or circulatory anastomosis, anastomoses are constructed to bypass circulatory problems. An example of the usefulness of collateral circulation is a systemic thromboem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Artery
The brachiocephalic artery, brachiocephalic trunk, or innominate artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm, head, and neck. It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic artery divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery come directly off the aortic arch. Despite this, there are two brachiocephalic veins. Structure The brachiocephalic artery arises on a level with the upper border of the second right costal cartilage from the start of the aortic arch on a plane anterior to the origin of the left carotid artery. It ascends obliquely upward, backward, and to the right to the level of the upper border of the right sternoclavicular articulation, where it divides into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian arteries. The artery then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |