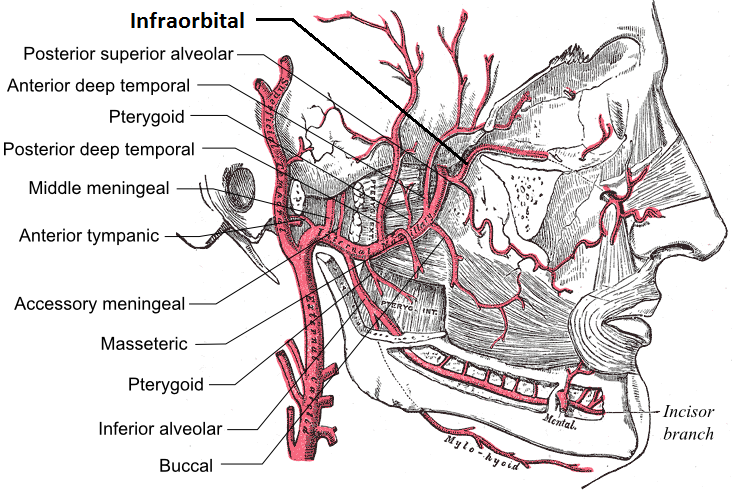
|
Superior Alveolar Artery (other)
The superior alveolar arteries are two or three arteries supplying the upper teeth and related structures: * The posterior superior alveolar artery, a branch of the maxillary artery that serves the upper teeth and other related structures * The anterior superior alveolar artery, a branch of the infraorbital artery, also supplying the upper teeth and related structures * The middle superior alveolar artery, an inconstant branch of the infraorbital artery that forms anastomoses An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf#Veins, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be ... with the other two superior alveolar arteries References * ''Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 39th ed.'' (2005). ISBN 0-443-07168-3 Arteries of the head and neck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Superior Alveolar Artery
The posterior superior alveolar artery (posterior dental artery) is a branch of the maxillary artery. It is one of two or three superior alveolar arteries. It provides arterial supply to the molar and premolar teeth, maxillary sinus and adjacent bone, and the gingiva. Anatomy Origin The artery typically arises from maxillary artery within the pterygopalatine fossa. It frequently arises in conjunction with the infraorbital artery. Course It passes inferior-ward upon the infratemporal surface of maxilla before ramifying. Branches It emits branches that pass through foramina on the posterior aspect of the maxilla alongside the posterior superior alveolar nerves. Some branches enter the alveolar canals to supply the upper molar and premolar teeth as well as the maxillary sinus and adjacent bone. Some branches pass anterior-ward across the alveolar process to supply the gingiva. See also * Anterior superior alveolar arteries * Posterior superior alveolar nerve The post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery (eg, internal maxillary artery) supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the Human mandible, mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into Human mandible, mandibular, Pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine ganglion, pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Superior Alveolar Artery
The anterior superior alveolar artery is one of the two or three superior alveolar arteries. It arises from the infraorbital artery. It passes through the canalis sinuosus. It provides arterial supply the upper incisor and canine teeth as well as the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. References See also * Anterior superior alveolar nerve * Posterior superior alveolar artery The posterior superior alveolar artery (posterior dental artery) is a branch of the maxillary artery. It is one of two or three superior alveolar arteries. It provides arterial supply to the molar and premolar teeth, maxillary sinus and adjacent bo ... Arteries of the head and neck {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Artery
The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. Anatomy Origin The infraorbital artery arises from the maxillary artery; it often arises in conjunction with the posterior superior alveolar artery. It may be considered a continuation of the third part of the maxillary artery and continues the direction of the maxillary artery. Course It passes anterior-ward to enter the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure. In the orbit, it courses along the floor of the orbit with the infraorbital nerve first along the infraorbital groove and then the infraorbital canal. It exits the orbit (with the infraorbital nerve) through infraorbital foramen to reach the face, beneath the infraorbital head of the levator labii superioris muscle. Branches Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Superior Alveolar Artery
The middle superior alveolar artery is an inconstant artery supplying the upper jaw. It is one of the three superior alveolar arteries. When present, it arises from the infraorbital artery and descends upon the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus, forming anastomotic arcades with the other two superior alveolar arteries of the same side before ending near the canine tooth In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more f .... It contributes to the arterial supply to the upper/maxillary incisor and canine teeth. References Arteries of the head and neck {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomoses
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf#Veins, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale (heart), foramen ovale in a fetus' heart) or abnormal (such as the atrial septal defect#Patent foramen ovale, patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital disorder, congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Greek ἀ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |