|
Sulfuric Acid Poisoning
Sulfuric acid poisoning refers to ingestion of sulfuric acid, found in lead-acid batteries and some metal cleaners, pool cleaners, drain cleaners and anti-rust products. Signs and symptoms * Brown to black streak from angle of mouth * Brown to black vomitus * Brown to black stomach wall * Black swollen tongue * White (chalky white) teeth * Blotting paper appearance of stomach mucosa * Ulceration of esophagus (fibrosis and stricture) * Perforation of stomach. * The stomach resembles a black spongy mass on post mortem Treatment For superficial injuries, washing ( therapeutic irrigation) is important. Emergency treatments include protecting the airway, which might involve a tracheostomy. Further treatment will vary depending on the severity, but might include investigations to determine the extent of damage ( bronchoscopy for the airways and endoscopy for the gastrointestinal tract), followed by treatments including surgery (to debride and repair) and intravenous fluids. Gastri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure (whether it is acute or chronic), route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia. The word ''toxicology'' () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drain Cleaner
A drain cleaner, also known as drain opener, refers to a person, device, or product used to unblock sewer pipes or clear clogged wastewater drains. This term typically applies to chemical, enzymatic, or mechanical tools such as commercial chemical cleaners, plumber's snakes, drain augers, bio-enzyme solutions, or toilet plungers. In some contexts, it may also refer to a plumber or professional who specializes in drain cleaning and maintenance. Chemical drain cleaners, plungers, handheld drain augers, and air burst drain cleaners are typically used to address clogs in single drain, such as sinks, toilets, tubs, or shower drains. These tools are effective at removing soft obstructions like hair and grease that accumulate near the drain inlet. However, excessive use of chemical drain cleaners can lead to pipe damage. In contrast, enzymatic drain cleaners rely on natural enzymes to break down organic matter such as grease, hair, and food particles, offering a more environmentally fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Stomach
Black stomach is a condition that results from acute gastric necrosis. The tarry black colour is produced by the coagulative necrosis of mucosa resulting in intramucosal haemorrhage and acid hematin deposition. This condition was first described in a patient with acid poisoning. A similar condition has been described in acute esophageal necrosis due to mucosal ischemia resulting from hemodynamic Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously ... compromise.Gurvits, Grigoriy E. “Black Esophagus: Acute Esophageal Necrosis Syndrome.” World Journal of Gastroenterology 16.26 (2010): 3219–3225. References Digestive disease symptoms {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Irrigation
In medicine, therapeutic irrigation or lavage ( or ) is cleaning or rinsing. Types Specific types include: * Antral lavage * Antiseptic lavage * Bronchoalveolar lavage * Whole lung lavage * Gastric lavage * Peritoneal lavage * Arthroscopic lavage * Ductal lavage * Nasal irrigation * Ear lavage * Pulsed lavage - delivery of an irrigant (usually normal saline) under direct pressure that is produced by an electrically powered device, useful in cleaning e.g. chronic wounds. See also * Douche * Ear picking * Enema * Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation * Life extension * Regenerative medicine * Teeth cleaning Teeth cleaning is part of oral hygiene and involves the removal of dental plaque from Human tooth, teeth with the intention of preventing Dental caries, cavities (dental caries), gingivitis, and periodontal disease. People routinely clean their ... References {{Medicine-stub Medical treatments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube (or tracheostomy tube) to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth", refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of the intended permanence of the stoma (hole) at the time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a tracheostomy. This allows the practitioner to examine the patient's airways for abnormalities such as foreign bodies, bleeding, tumors, or inflammation. Specimens may be taken from inside the lungs. The construction of bronchoscopes ranges from rigid metal tubes with attached lighting devices to flexible optical fiber instruments with realtime video equipment. History The German laryngologist Gustav Killian is attributed with performing the first bronchoscopy in 1897. Killian used a rigid bronchoscope to remove a pork bone. The procedure was done in an awake patient using topical cocaine as a local anesthetic. From this time until the 1970s, rigid bronchoscopes were used exclusively. Chevalier Jackson refined the rigid bronchoscope in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
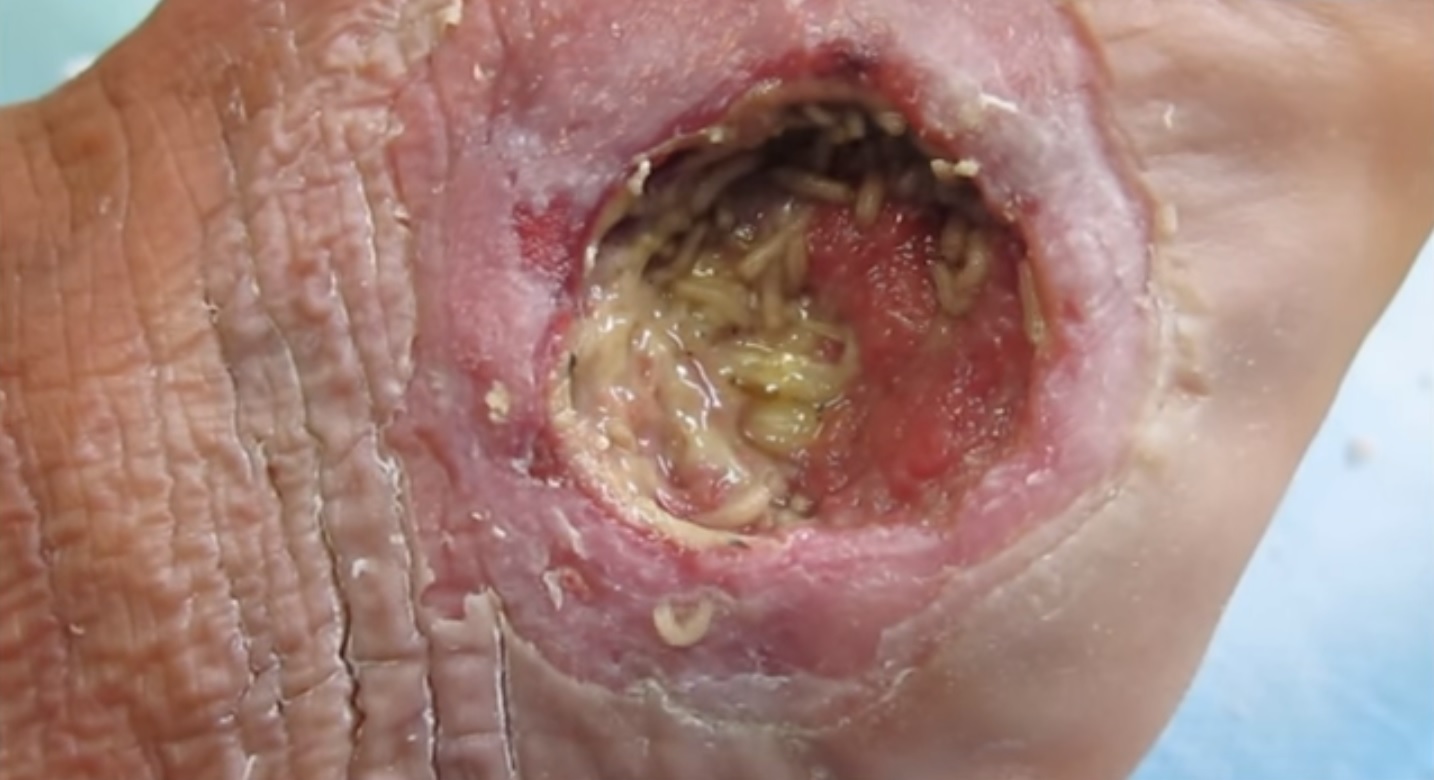
Debride
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), or by maggot therapy. In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas. Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites. Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed. Types There is a lack of high-quality evidence to compare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Lavage
Gastric lavage, also commonly called stomach pumping or gastric irrigation or gastric suction, is the process of cleaning out the contents of the stomach using a tube. Since its first recorded use in the early 19th century, it has become one of the most routine means of eliminating poisons from the stomach. Such devices are normally used on a person who has ingested a poison or overdosed on a drug such as ethanol. They may also be used before surgery, to clear the contents of the digestive tract before it is opened. Apart from toxicology, gastric lavage (or nasogastric lavage) is sometimes used to confirm levels of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract. It may play a role in the evaluation of hematemesis. It can also be used as a cooling technique for hyperthermic patients. Technique Gastric lavage involves the passage of a tube (such as an ''Ewald tube'') via the mouth or nose down into the stomach followed by sequential administration and removal of small volumes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Attack
An acid attack, also called acid throwing, vitriol attack, or vitriolage, is a form of violent assault involving the act of throwing acid or a similarly corrosive substance onto the body of another "with the intention to disfigure, maim, torture, or kill". Perpetrators of these attacks throw corrosive liquids at their victims, usually at their faces, burning them, and damaging skin tissue, often exposing and sometimes dissolving the bones. Acid attacks can lead to permanent, partial or complete blindness. The most common types of acid used in these attacks are sulfuric and nitric acid. Hydrochloric acid is sometimes used but is much less damaging. Aqueous solutions of strongly alkaline materials, such as caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) or ammonia, are used as well, particularly in areas where strong acids are controlled substances. The long-term consequences of these attacks may include blindness, as well as eye burns, with severe permanent scarring of the face and body, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxic Effects Of Substances Chiefly Nonmedicinal As To Source
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell ( cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver ( hepatotoxicity). Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypass animal testing, while maintaining the concept of toxicity endpoints. Etymology In Ancient Greek medical literature, the adjective ''τοξικόν ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |