|
Succinate—CoA Ligase (ADP-forming)
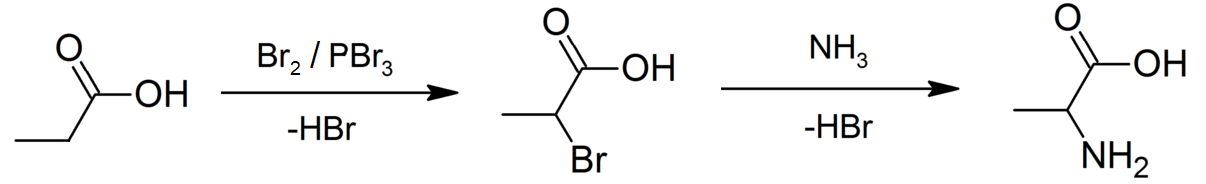
In enzymology, a succinate-CoA ligase (ADP-forming) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + succinate + CoA \rightleftharpoons ADP + phosphate + succinyl-CoA The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, succinate, and CoA, whereas its 3 products are ADP, phosphate, and succinyl-CoA. This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, specifically those forming carbon-sulfur bonds as acid-thiol ligases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is succinate:CoA ligase (ADP-forming). Other names in common use include succinyl-CoA synthetase (ADP-forming), succinic thiokinase, succinate thiokinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, succinyl coenzyme A synthetase (adenosine diphosphate-forming), succinyl coenzyme A synthetase, A-STK (adenin nucleotide-linked succinate thiokinase), STK, and A-SCS. This enzyme participates in 4 metabolic pathways: Citric acid cycle, propanoate metabolism, c5-branched dibasic acid metabolism, and reductive carboxylate cycle (CO2 fixation). Struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
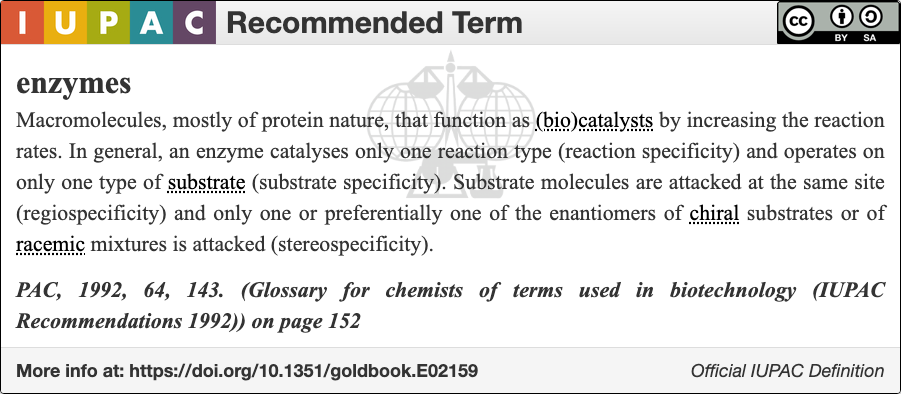
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligase
In biochemistry, a ligase is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining ( ligation) of two molecules by forming a new chemical bond. This is typically via hydrolysis of a small pendant chemical group on one of the molecules, typically resulting in the formation of new C-O, C-S, or C-N bonds. For example, DNA ligase can join two complementary fragments of nucleic acid by forming phosphodiester bonds, and repair single stranded breaks that arise in double stranded DNA during replication. In general, a ligase catalyzes the following dehydration reaction, thus joining molecules A and B: A-OH + B-H → A–B + H2O Nomenclature The naming of ligases is inconsistent and so these enzymes are commonly known by several different names. Generally, the common names of ligases include the word "ligase", such as in DNA ligase, an enzyme commonly used in molecular biology laboratories to join together DNA fragments. However, many common names use the term "synthetase" or "synthase" instead, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, which is overseen by the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB). This structural data is obtained and deposited by biologists and biochemists worldwide through the use of experimental methodologies such as X-ray crystallography, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, NMR spectroscopy, and, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy. All submitted data are reviewed by expert Biocuration, biocurators and, once approved, are made freely available on the Internet under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication. Global access to the data is provided by the websites of the wwPDB member organizations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB PDB, and BMRB). The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Carboxylate Cycle
Reduction, reduced, or reduce may refer to: Science and technology Chemistry * Reduction (chemistry), part of a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. ** Organic redox reaction, a redox reaction that takes place with organic compounds ** Ore reduction: see smelting Computing and algorithms * Reduction (complexity), a transformation of one problem into another problem * Reduction (recursion theory), given sets A and B of natural numbers, is it possible to effectively convert a method for deciding membership in B into a method for deciding membership in A? * Bit Rate Reduction, an audio compression method * Data reduction, simplifying data in order to facilitate analysis * Graph reduction, an efficient version of non-strict evaluation * L-reduction, a transformation of optimization problems which keeps the approximability features * Partial order reduction, a technique for reducing the size of the state-space to be searched b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propanoate Metabolism
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA Redox, oxidation. The energy released is available in the form of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. The Hans Krebs (biochemist), Krebs cycle is used by organisms that generate energy via Cellular respiration, respiration, either anaerobic respiration, anaerobically or aerobic respiration, aerobically (organisms that Fermentation, ferment use different pathways). In addition, the cycle provides precursor (chemistry), precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, which are used in other reactions. Its central importance to many Metabolic pathway, biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest metabolism components. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-coenzyme A, abbreviated as succinyl-CoA () or SucCoA, is a thioester of succinic acid and coenzyme A. Sources It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from Alpha-Ketoglutaric acid, α-ketoglutarate by Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through decarboxylation. During the process, coenzyme A is added. With B12 as an enzymatic cofactor, it is also synthesized from propionyl coenzymeA, propionyl CoA, the odd-numbered fatty acid, which cannot undergo beta-oxidation. Propionyl-CoA is carboxylated to D-methylmalonyl-CoA, isomerized to L-methylmalonyl-CoA, and rearranged to yield succinyl-CoA via a vitamin B12, vitamin B12-dependent enzyme. While Succinyl-CoA is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle, it cannot be readily incorporated there because there is no net consumption of Succinyl-CoA. Succinyl-CoA is first converted to malate, and then to pyruvate where it is then transported to the matrix to enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |