|
Strømme Syndrome
Strømme syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic condition characterised by intestinal atresia (in which part of the intestine is missing), eye abnormalities and microcephaly. The intestinal atresia is of the "apple-peel" type, in which the remaining intestine is twisted around its main artery. The front third of the eye is typically underdeveloped, and there is usually moderate developmental delay. Less common features include an atrial septal defect, increased muscle tone or skeletal abnormalities. Physical features may include short stature, large, low-set ears, a small jaw, a large mouth, epicanthic folds, or fine, sparse hair. The syndrome is caused by mutations in both copies of the ''CENPF'' gene, which codes for centromere protein F. This protein is involved in cell division, in which it forms part of a disc-shaped protein complex known as a kinetochore. CENPF also has a role in orienting long, cylindrical structures called microtubules to form thin c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcephaly
Microcephaly (from Neo-Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it may develop in the first few years of life. Brain development is often affected; people with this disorder often have an intellectual disability, poor motor function, poor speech, abnormal facial features, seizures and dwarfism. The disorder is caused by a disruption to the genetic processes that form the brain early in pregnancy, though the cause is not identified in most cases. Many genetic syndromes can result in microcephaly, including chromosomal and single-gene conditions, though almost always in combination with other symptoms. Mutations that result solely in microcephaly (primary microcephaly) exist but are less common. External toxins to the embryo, such as alcohol during pregnancy or vertically transmitted infections, can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with two subtypes, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core, called the axoneme, determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloboma
A coloboma (from the Greek , meaning "defect") is a hole in one of the structures of the eye, such as the iris, retina, choroid, or optic disc. The hole is present from birth and can be caused when a gap called the choroid fissure, which is present during early stages of prenatal development, fails to close up completely before a child is born. Ocular coloboma is relatively uncommon, affecting less than one in every 10,000 births. The classical description in medical literature is of a keyhole-shaped defect. A coloboma can occur in one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). Most cases of coloboma affect only the iris. The level of vision impairment of those with a coloboma can range from having no vision problems to being able to see only light or dark, depending on the position and extent of the coloboma (or colobomata if more than one is present). Signs and symptoms Visual effects may be mild to more severe depending on the size and location of the coloboma. If, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenal Atresia
Duodenal atresia is the congenital absence or complete closure of a portion of the lumen (anatomy), lumen of the duodenum. It causes increased levels of amniotic fluid during pregnancy (polyhydramnios) and intestinal obstruction in newborn babies. Newborns present with bilious or non-bilous vomiting (depending on where in the duodenum the obstruction is) within the first 24 to 48 hours after birth, typically after their first oral feeding. Radiography shows a distended stomach and distended duodenum, which are separated by the pyloric valve, a finding described as the Double bubble (radiology), double-bubble sign. Treatment includes suctioning out any fluid that is trapped in the stomach, providing fluids intravenously, and surgical repair of the intestinal closure. Signs and symptoms History and physical examination During pregnancy, duodenal atresia is associated with increased amniotic fluid in the uterus, which is called polyhydramnios. This increase in amniotic fluid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Malrotation
Intestinal malrotation is a congenital anomaly of rotation of the midgut. It occurs during the first trimester as the fetal gut undergoes a complex series of growth and development. Malrotation can lead to a dangerous complication called volvulus, in which cases emergency surgery is indicated. Malrotation can refer to a spectrum of abnormal intestinal positioning, often including: * The small intestine found predominantly on the right side of the abdomen * The cecum displaced from its usual position in the right lower quadrant into the epigastrium or right hypochondrium * An absent or displaced ligament of Treitz * Fibrous peritoneal bands called bands of Ladd running across the vertical portion of the duodenum * An unusually narrow, stalk-like mesentery The position of the intestines, narrow mesentery and Ladd's bands can contribute to several severe gastrointestinal conditions. The narrow mesentery predisposes some cases of malrotation to midgut volvulus, a twisting of the enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialized for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The jejunum lies between the duodenum and the ileum and is considered to start at the suspensory muscle of the duodenum, a location called the duodenojejunal flexure. The division between the jejunum and ileum is not anatomically distinct. In adult humans, the small intestine is usually long (post mortem), about two-fifths of which (about ) is the jejunum. Structure The interior surface of the jejunum—which is exposed to ingested food—is covered in finger–like projections of mucosa, called villi, which increase the surface area of tissue available to absorb nutrients from ingested foodstuffs. The epithelial cells which line these villi have microvilli. The transport of nutrien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Bowel Obstruction
Neonatal bowel obstruction (NBO) or neonatal intestinal obstruction is the most common surgical emergency in the neonatal period. It may occur due to a variety of conditions and has an excellent outcome based on timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention. Presentation The neonatal bowel obstruction is suspected based on polyhydramnios in utero, bilious vomiting, failure to pass meconium in the first day of life, and abdominal distension. The presentations of NBO may vary. It may be subtle and easily overlooked on physical examination or can involve massive abdominal distension, respiratory distress and cardiovascular collapse. Unlike older children, neonates with unrecognized intestinal obstruction deteriorate rapidly. Diagnosis Neonatal bowel obstruction is grouped into two general categories: high, or proximal, obstruction and low, or distal obstruction, both of which are suspected by failure to pass meconium at birth. High obstruction can be suspected based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
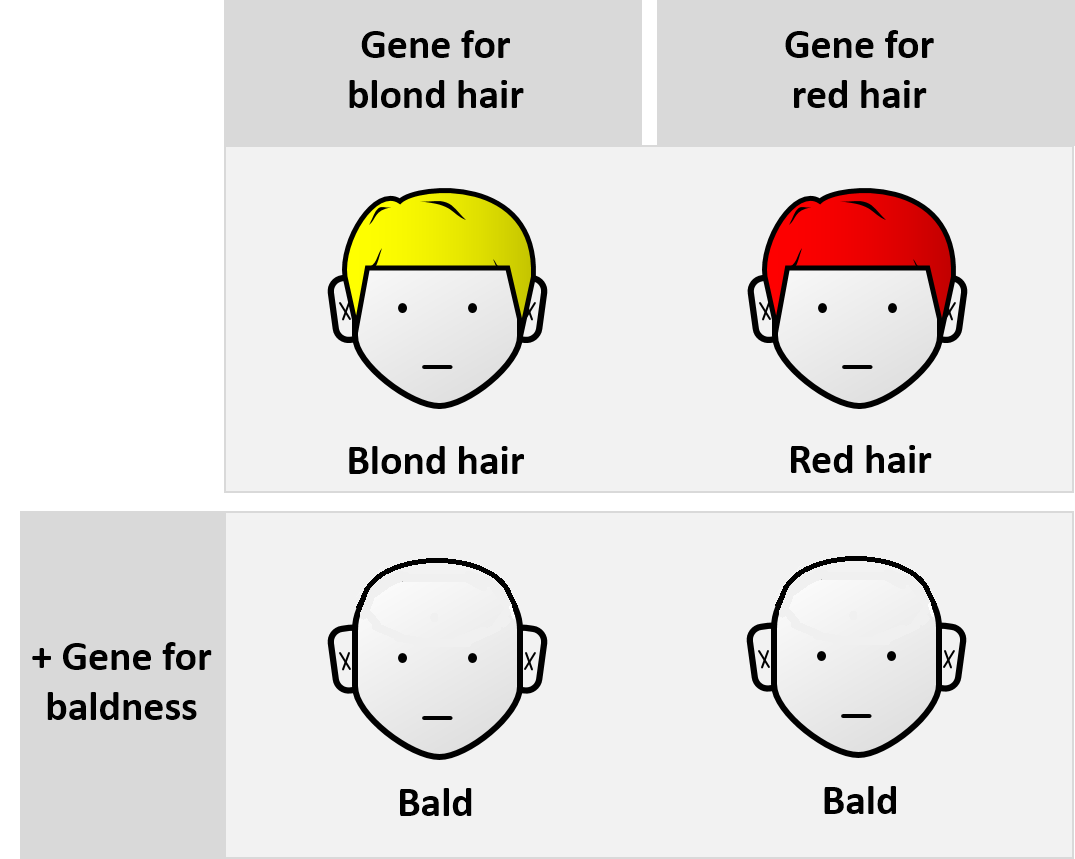
Epistasis
Epistasis is a phenomenon in genetics in which the effect of a gene mutation is dependent on the presence or absence of mutations in one or more other genes, respectively termed modifier genes. In other words, the effect of the mutation is dependent on the genetic background in which it appears. Epistatic mutations therefore have different effects on their own than when they occur together. Originally, the term ''epistasis'' specifically meant that the effect of a gene variant is masked by that of different gene. The concept of ''epistasis'' originated in genetics in 1907 but is now used in biochemistry, computational biology and evolutionary biology. The phenomenon arises due to interactions, either between genes (such as mutations also being needed in regulators of gene expression) or within them (multiple mutations being needed before the gene loses function), leading to non-linear effects. Epistasis has a great influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes, which leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Anastomosis
A surgical anastomosis is a surgical technique used to make a new connection between two body structures that carry fluid, such as blood vessels or bowel. For example, an Artery, arterial anastomosis is used in vascular bypass and a Colon (anatomy), colonic anastomosis is used to restore colonic continuity after the resection of Colorectal cancer#surgery, colon cancer. A surgical anastomosis can be created using suture sewn by hand, mechanical staplers and biological glues, depending on the circumstances. While an anastomosis may be end-to-end, equally it could be performed side-to-side or end-to-side depending on the circumstances of the required reconstruction or Coronary artery bypass surgery, bypass. The term reanastomosis is also used to describe a surgical reconnection usually reversing a prior surgery to disconnect an anatomical anastomosis, e.g. tubal reversal after tubal ligation. __TOC__ Medical uses * Blood vessels: Arteries and veins. Most vascular procedures, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliopathy
Ciliopathies are a group of genetically diverse disorders caused by defects in the structure or function of the primary cilium, a highly specialized and evolutionarily conserved organelle found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. The primary cilium plays a central role in regulating signal transduction and making it essential for numerous developmental and physiological processes. Because of the widespread presence of primary cilia in different tissues, dysfunction can lead to a broad spectrum of clinical features. Syndromic ciliopathies, such as Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS), typically involve multiple organ systems, including the retina, kidneys, central nervous system, and skeletal system These manifestations highlight the importance of cilia in embryonic development, sensory perception, and tissue homeostasis. The genetic basis of ciliopathies is complex, with significant allelic heterogeneity and pleiotropy, meaning the same gene may cause different disorders, while diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Metabolic composition, however, gets dramatically altered where st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |