|
Structural Alignment Software
This list of structural comparison and alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise or multiple structural comparison and structural alignment. Structural comparison and alignment Key map: * Class: :* Cα -- Backbone Atom (Cα) Alignment; :* AllA -- All Atoms Alignment; :* SSE -- Secondary Structure Elements Alignment; :* Seq -- Sequence-based alignment :* Pair -- Pairwise Alignment (2 structures *only*); :* Multi -- Multiple Structure Alignment (MStA); :* C-Map -- Contact Map :* Surf -- Connolly Molecular Surface Alignment :* SASA -- Solvent Accessible Surface Area :* Dihed -- Dihedral Backbone Angles :* PB -- Protein Blocks * Flexible: :* No -- Only rigid-body transformations are considered between the structures being compared. :* Yes -- The method allows for some flexibility within the structures being compared, such as movements around hinge regions. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Structural Alignment Software Structural bioinformatics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Comparison
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Alignment
Structural alignment attempts to establish homology between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures but can also be used for large RNA molecules. In contrast to simple structural superposition, where at least some equivalent residues of the two structures are known, structural alignment requires no ''a priori'' knowledge of equivalent positions. Structural alignment is a valuable tool for the comparison of proteins with low sequence similarity, where evolutionary relationships between proteins cannot be easily detected by standard sequence alignment techniques. Structural alignment can therefore be used to imply evolutionary relationships between proteins that share very little common sequence. However, caution should be used in using the results as evidence for shared evolutionary ancestry because of the possible confounding effects of convergent evolution by which mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Operating Environment
Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) is a drug discovery software platform that integrates visualization, modeling and simulations, as well as methodology development, in one package. MOE scientific applications are used by biologists, medicinal chemists and computational chemists in pharmaceutical, biotechnology and academic research. MOE runs on Windows, Linux, Unix, and macOS. Main application areas in MOE include structure-based design, Fragment-based lead discovery, fragment-based design, ligand-based design, pharmacophore discovery, medicinal chemistry applications, biologics applications, structural biology and bioinformatics, protein and antibody modeling, Molecular modelling, molecular modeling and simulations, virtual screening, Cheminformatics toolkits, cheminformatics & QSAR. The Scientific Vector Language (Scientific Vector Language, SVL) is the built-in command, scripting and application development language of MOE. History The Molecular Operating Environment was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PyMOL
PyMOL is a source-available molecular visualization system created by Warren Lyford DeLano. It was commercialized initially by DeLano Scientific LLC, which was a private software company dedicated to creating useful tools that become universally accessible to scientific and educational communities. It is currently commercialized by Schrödinger, Inc. As the original software license was a permissive licence, they were able to remove it; new versions are no longer released under the Python license, but under a custom license (granting broad use, redistribution, and modification rights, but assigning copyright to any version to Schrödinger, LLC.), and some of the source code is no longer released. PyMOL can produce high-quality 3D images of small molecules and biological macromolecules, such as proteins. PyMOL is widely used. PyMOL is one of the few mostly open-source model visualization tools available for use in structural biology. The ''Py'' part of the software's name refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klara Kedem
Klara Kedem (Hebrew: קלרה קדם) is an Israeli computer scientist, a professor of computer science at Ben-Gurion University in Beer-Sheva, Israel Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University, retrieved 2012-09-30. and an adjunct faculty member in computer science at in . Kedem received her Ph.D. in 1989 from , under the supervision of |
UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera (or simply Chimera) is an extensible program for interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, supramolecular assemblies, sequence alignments, docking results, trajectories, and conformational ensembles. High-quality images and movies can be created. Chimera includes complete documentation and can be downloaded free of charge for noncommercial use. Chimera is developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics (RBVI) at the University of California, San Francisco. Development is partially supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIGMS grant P41-GM103311). Chimera is no longer actively developed and is superseded by UCSF ChimeraX. General structure analysis * automatic identification of atom * hydrogen addition and partial charge assignment * high-quality hydrogen bond, contact, and clash detection * measurements: distances, angles, surface area, volume * calculation of cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
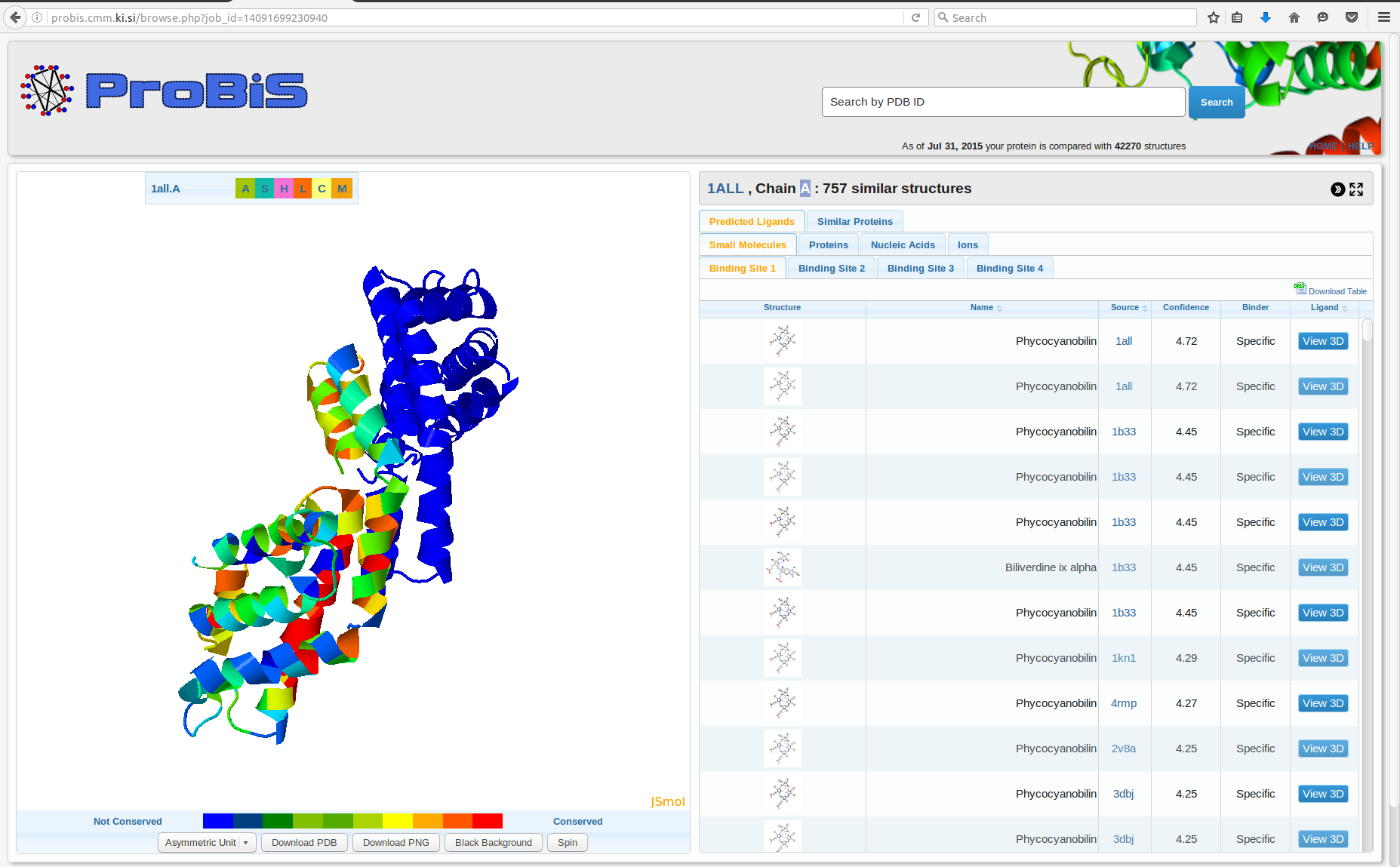
ProBiS
ProBiS is a computer software which allows prediction of binding sites and their corresponding ligands for a given protein structure. Initially ProBiS was developed as a ProBiS algorithm by Janez Konc and Dušanka Janežič in 2010 and is now available as ProBiS server, ProBiS CHARMMing server, ProBiS algorithm and ProBiS plugin. The name ProBiS originates from the purpose of the software itself, that is to predict for a given Protein structure Binding Sites and their corresponding ligands. Description ProBiS software started as ProBiS algorithm that detects structurally similar sites on protein surfaces by local surface structure alignment using a MaxCliqueDyn maximum clique algorithm, fast maximum clique algorithm. The ProBiS algorithm was followed by ProBiS server which provides access to the program ProBiS that detects protein binding sites based on local structural alignments. There are two ProBiS servers available, ProBiS server and ProBiS CHARMMing server. The latter connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, which is overseen by the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB). This structural data is obtained and deposited by biologists and biochemists worldwide through the use of experimental methodologies such as X-ray crystallography, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, NMR spectroscopy, and, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy. All submitted data are reviewed by expert Biocuration, biocurators and, once approved, are made freely available on the Internet under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication. Global access to the data is provided by the websites of the wwPDB member organizations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB PDB, and BMRB). The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Permutation In Proteins
A circular permutation is a relationship between proteins whereby the proteins have a changed order of amino acids in their peptide sequence. The result is a protein structure with different connectivity, but overall similar three-dimensional (3D) shape. In 1979, the first pair of circularly permuted proteins – concanavalin A and lectin – were discovered; over 2000 such proteins are now known. Circular permutation can occur as the result of evolutionary events, posttranslational modifications, or protein engineering, artificially engineered mutations. The two main models proposed to explain the evolution of circularly permuted proteins are ''permutation by duplication'' and ''fission and fusion''. Permutation by duplication occurs when a gene undergoes gene duplication, duplication to form a tandem repeat, before redundant sections of the protein are removed; this relationship is found between prosaposin, saposin and swaposin. Fission and fusion occurs when partial proteins fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioassembly
Biofabrication is a branch of biotechnology specialising in the research and development of biologically engineered processes for the automated production of biologically functional products through bioprinting or bioassembly and subsequent tissue maturation processes; as well as techniques such as directed assembly, which employs localised external stimuli guide the fabrication process; enzymatic assembly, which utilises selective biocatalysts to build macromolecular structures; and self-assembly, in which the biological material guides its own assembly according to its internal information. These processes may facilitate fabrication at the micro- and nanoscales. Biofabricated products are constructed and structurally organised with a range of biological materials including bioactive molecules, biomaterials, living cells, cell aggregates such as micro- tissues and micro- organs on chips, and hybrid cell-material constructs. Biofabrication is defined as "the automated generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |