|
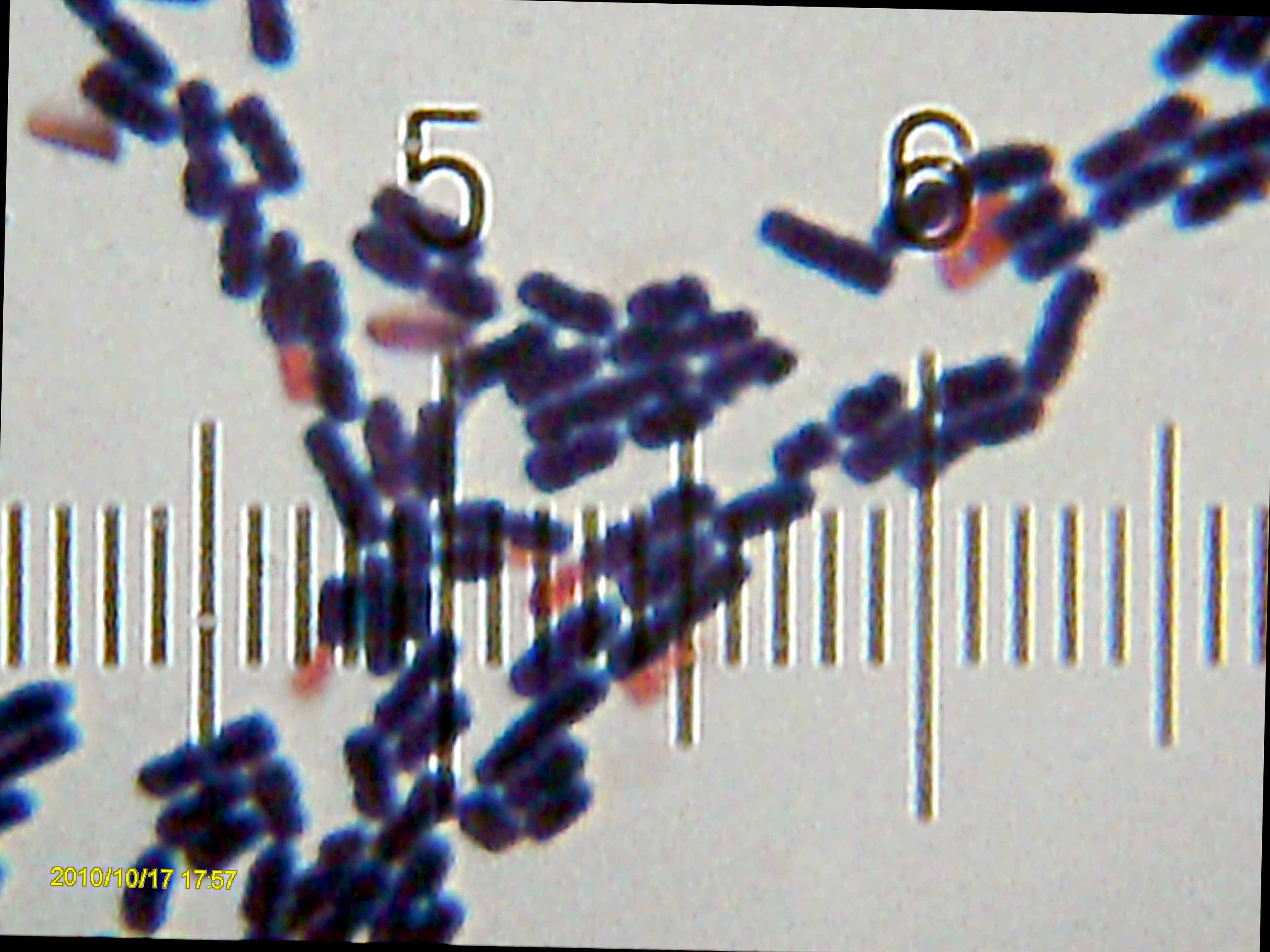
Streptomyces Griseus
''Streptomyces griseus'' is a species of bacteria in the genus '' Streptomyces'' commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, ''S. griseus'' strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of ''S. griseus''. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed. The taxonomic history of ''S. griseus'' and its phylogenetically related strains has been turbulent. ''S. griseus'' was first described in 1914 by Krainsky, who called the species '' Actinomyces griseus''. The name was changed in 1948 by Waksman and Henrici to ''Streptomyces griseus''. The interest in these strains stems f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selman Waksman
Selman Abraham Waksman (July 22, 1888 – August 16, 1973) was a Russian-born American inventor, biochemist and microbiologist, whose research into the decomposition of organisms that live in soil enabled the discovery of streptomycin and several other antibiotics. For his work he won the 1952 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Waksman emigrated to the United States in 1910 and became a naturalized U.S. citizen in 1916. A professor of biochemistry and microbiology at Rutgers University for four decades, he discovered several antibiotics (and introduced the modern sense of that word to name them), and he introduced procedures that have led to the development of many others. The proceeds earned from the licensing of his patents funded a foundation for microbiological research, which established the Waksman Institute of Microbiology located at the Rutgers University Busch Campus in Piscataway, New Jersey (USA). After receiving the Nobel Prize, Waksman and his foundation later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinomycetota
The Actinomycetota (or Actinobacteria) are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, Actinomycetota are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, as fungi do, and the name of an important order of the phylum, Actinomycetales (the actinomycetes), reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota (such as '' Frankia'') live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus ''Mycobacterium'', are important pathogens. Beyond th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the Biological life cycle, life cycles of many plants, algae, fungus, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word ''alkali'' is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lime''), a far more strongly basic substance known as ''caustic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaliphilic
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline ( pH roughly 8.5–11) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10. These bacteria can be further categorized as obligate alkaliphiles (those that require high pH to survive), facultative alkaliphiles (those able to survive in high pH, but also grow under normal conditions) and haloalkaliphiles (those that require high salt content to survive).Horikoshi, Koki. "Alkaliphiles: Some applications of their products for biotechnology." Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 63.4 (1999): 735-50. Print. Background information Microbial growth in alkaline conditions presents several complications to normal biochemical activity and reproduction, as high pH is detrimental to normal cellular processes. For example, alkalinity can lead to denaturation of DNA, instability of the plasma membrane and inactivation of cytosolic enzymes, as well as other unfavorable physiological changes.Higashibata, Akira, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multilocus Sequence Typing
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) is a technique in molecular biology for the typing of multiple loci, using DNA sequences of internal fragments of multiple housekeeping genes to characterize isolates of microbial species. The first MLST scheme to be developed was for '' Neisseria meningitidis'', the causative agent of meningococcal meningitis and septicaemia. Since its introduction for the research of evolutionary history, MLST has been used not only for human pathogens but also for plant pathogens. Principle MLST directly measures the DNA sequence variations in a set of housekeeping genes and characterizes strains by their unique allelic profiles. The principle of MLST is simple: the technique involves PCR amplification followed by DNA sequencing. Nucleotide differences between strains can be checked at a variable number of genes depending on the degree of discrimination desired. The workflow of MLST involves: 1) data collection, 2) data analysis and 3) multilocus sequence a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, and its behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code (its genotype) and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA genes and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Terminology The descriptor ''16S'' refers to the size of these ribosomal subunits as reflected indirectly by the speed at which they sediment when samples are centrifuged. Thus ''16S'' means 16 Svedburg units. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosmin
Geosmin ( ) is an irregular sesquiterpenoid with a distinct earthy or musty odor, which most people can easily smell. The geosmin odor detection threshold in humans is very low, ranging from 0.006 to 0.01 micrograms per liter in water. Geosmin, along with the irregular monoterpene 2-methylisoborneol, together account for the majority of biologically-caused taste and odor outbreaks in drinking water worldwide and in Fish farming, farmed fish. Geosmin is also responsible for the earthy taste of beetroots and a contributor to the strong scent, known as petrichor, that occurs when rain falls after a spell of dry weather or when soil is disturbed. In chemical terms, geosmin is a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with chemical formula, formula , a derivative of decalin. It is produced from the universal sesquiterpene precursor farnesyl pyrophosphate (also known as farnesyl diphosphate), in a two-step -dependent reaction. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |