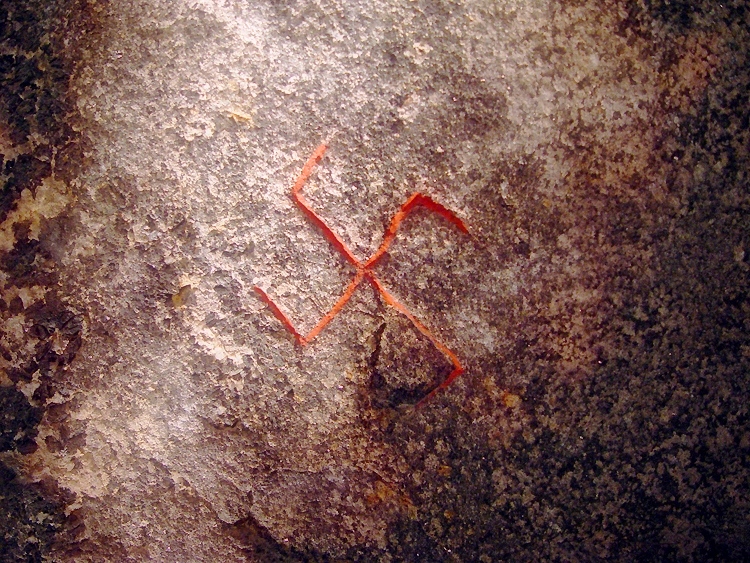|
Strafgesetzbuch §
''Strafgesetzbuch'' (, literally "penal law book"), abbreviated to ''StGB'', is the German penal code. History In Germany the ''Strafgesetzbuch'' goes back to the Penal Code of the German Empire passed in the year 1871 on May 15 in Reichstag which was largely identical to the Penal Code of the North German Confederation from 1870. It came into effect on January 1, 1872. This ''Reichsstrafgesetzbuch'' (Imperial Penal Code) was changed many times in the following decades in response not only to changing moral concepts and constitutional provision granted by the ''Grundgesetz'', but also to scientific and technical reforms. Examples of such new crimes are money laundering or computer sabotage. The Penal Code is a codification of criminal law and the pivotal legal text, while supplementary laws contain provisions affecting criminal law, such as definitions of new types of crime and law enforcement action. The StGB constitutes the legal basis of criminal law in Germany. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Code
A criminal code or penal code is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of, a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain Crime, offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might be imposed for these offences, and some general provisions (such as definitions and prohibitions on Ex post facto law, retroactive prosecution). Criminal codes are relatively common in Civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions, which tend to build legal systems around codes and principles which are relatively abstract and apply them on a case-by-case basis. Conversely they are not as common in common law jurisdictions. Where a jurisdiction is a federation, the administrative division, subnational units of such jurisdiction may or may not use separate penal codes. For example, in India, the entire country (the Government of India, federal government, states, and union territories) all operate under one criminal code, the Bhara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insubordination
Insubordination is the act of willfully disobeying a lawful order of one's superior. It is generally a punishable offense in hierarchical organizations such as the armed forces, which depend on people lower in the chain of command obeying orders. Military Insubordination is when a service member willfully disobeys the lawful orders of a superior officer. If a military officer disobeys the lawful orders of their civilian superiors, this also counts. For example, the head of state in many countries, is also the most superior officer of the military as the Commander in Chief. Generally, however, an officer or soldier may disobey an unlawful order to the point of mutiny (see Nuremberg defense). In the U.S. military, insubordination is covered under Article 91 of the Uniform Code of Military Justice. It covers disobeying lawful orders as well as disrespectful language or even striking a superior. The article for insubordination should not be confused with the article for con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Cross
upright 0.75 , A Celtic cross symbol The Celtic cross is a form of ringed cross, a Christian cross featuring a nimbus or ring, that emerged in the British Isles and Western Europe in the Early Middle Ages. It became widespread through its use in the high crosses erected across the British Isles, especially in regions evangelised by Hiberno-Scottish missionaries, from the ninth through the 12th centuries. A staple of Insular art, the Celtic cross is essentially a Latin cross with a nimbus surrounding the intersection of the arms and stem. Scholars have debated its exact origins, but it is related to earlier crosses featuring rings. The form gained new popularity during the Celtic Revival of the 19th century; the name "Celtic cross" is a convention dating from that time. The shape, usually decorated with interlace and other motifs from Insular art, became popular for funerary monuments and other uses, and has remained so, spreading well beyond Ireland. Early history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odal (SS-rune)
Odal or Othala, sometimes called Winged Odal or Winged Othala, is a Nazi symbolism, Nazi symbol in the shape of an SS-rune, used by the Nazi Germany, Nazi German ''Schutzstaffel'' (''SS''), during the 1930s and -40s, to symbolize several values of central importance to Nazi ideology, such as kinship, family and blood ties, etc. It's based on the historical Runes, rune of the same name, Othala (ᛟ), a writing character of the late Iron Age Germanic peoples (Omega Ω based), but often modified with serifs, or "wings" (also called "feet, hooks, heels" etc). During World War II, it was used by, among others, 7th SS Volunteer Mountain Division Prinz Eugen och Volunteer Legion Netherlands, as well as the SS Race and Settlement Main Office, which was responsible for maintaining the racial purity of the SS. Nowadays it sees continued use with Neo-Nazis and similar far-right collectives. Usage Period use The Nazi-use of runic symbology was largely derrived from the Armanen runes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totenkopf
''Totenkopf'' (, i.e. ''skull'', literally "dead person's head") is the German word for skull. The word is often used to denote a figurative, graphic or sculptural symbol, common in Western culture, consisting of the representation of a human skull – usually frontal, more rarely in profile with or without the mandible. In some cases, other human skeletal parts may be added, often including two crossed long bones (femurs) depicted below or behind the skull (when it may be referred to in English as a " skull and crossbones"). The human skull is an internationally used symbol for death, the defiance of death, danger, or the dead, as well as piracy or toxicity. In English, the term ''Totenkopf'' is commonly associated with 19th- and 20th-century German military use, particularly in Nazi Germany. The german word for skull without emotional connotation is ''Schädel''. Naval use In early modern sea warfare to early modern sea piracy, buccaneers and pirates used the ''Totenkopf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sig Runes
SS runes () is a generic name given to a collection of pseudo-runes used by the ''Schutzstaffel'' (''SS''), from the 1920s to 1945, for Nazi occultism-purposes; featured on flags, uniforms and other items as symbols of various aspects of Nazi ideology and Germanic mysticism. They also represented virtues seen as desirable in SS members, and were based on ''völkisch'' mystic Guido von List's pseudo-runic Armanen runes, which he loosely based on the historical runic alphabets, but the SS-runes also included other esoteric symbols not borrowed from the Armanen runes. Post World War II, these insignias continue to be used by neo-Nazi individuals and groups. SS runes Further reading * https://www.arild-hauge.com/PDF/Nazi-Tyskland-SS_Regalia.pdf See also * Nazi symbolism The 20th-century German Nazi Party made extensive use of graphic symbols, especially the swastika, notably in the form of the swastika flag, which became the co-national flag of Nazi Germany in 1933, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swastikas
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazism
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was frequently referred to as Hitler Fascism () and Hitlerism (). The term " neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideology, which formed after World War II, and after Nazi Germany collapsed. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. Its beliefs include support for dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, anti-Slavism, anti-Romani sentiment, scientific racism, white supremacy, Nordicism, social Darwinism, homophobia, ableism, and the use of eugenics. The ultranationalism of the Nazis originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German ultranationalism since the late 19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal Offence
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Cane and Conoghan (editors), '' The New Oxford Companion to Law'', Oxford University Press, 2008 (), p. 263Google Books). though statutory definitions have been provided for certain purposes. The most popular view is that crime is a category created by law; in other words, something is a crime if declared as such by the relevant and applicable law. One proposed definition is that a crime or offence (or criminal offence) is an act harmful not only to some individual but also to a community, society, or the state ("a public wrong"). Such acts are forbidden and punishable by law. The notion that acts such as murder, rape, and theft are to be prohibited exists worldwide. What precisely is a criminal offence is defined by the criminal law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition (German Penal Code)
Competition in German Penal Code is the assessment of multiple crimes committed by the same person in the context of a legal process. A distinction is made between joint offenses (§ 52 StGB) and distinct offenses (§ 53 StGB). Joint offenses are cases in which the same person commits multiple different or identical crimes through the same act, while distinct offenses are cases where different or identical crimes are committed over multiple distinct acts. Joint and distinct offenses The purpose of the competition provisions is to ensure that, where several violations of the criminal law occur at the same time, a penalty is imposed that is appropriate to the severity of each violation and not simply to add up the penalties for the individual offenses. The Criminal Code provides two procedures for developing a punishment from the sentencing range for each individual criminal offense: joint offense under § 52 StGB and distinct offenses under § 53 StGB (''Differenzierungsprinzip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attempt (German Penal Code)
An attempt () according to § 22-24 German Penal Code (StGB) refers to the commission of a crime for which the perpetrator has intent regarding its completion and which has begun, but which has not been completed. Attempted serious crimes (those with a minimal punishment of more than one year) are always punishable, while attempting a lesser crime requires a specific provision in law to be a crime.BeckOK StGB/Cornelius, 63. Ed. 1.8.2024, StGB § 22 Rn. 22 The specific justification for the prohibition of attempts, particularly attempts that pose no danger, is disputed among legal scholars. An attempt is not punished if the perpetrator abandons the attempt.MüKoStGB/Hoffmann-Holland, 5. Aufl. 2024, StGB § 24 Rn. 1 History and criminological background Criminological background The criminological background for the punishment of attempts is disputed, with a plethora of theories supported by scholarship. The objective theories, which argue for a punishment based on the specific dang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imprisonment
Imprisonment or incarceration is the restraint of a person's liberty for any cause whatsoever, whether by authority of the government, or by a person acting without such authority. In the latter case it is considered " false imprisonment". Imprisonment does not necessarily imply a place of confinement with bolts and bars, but may be exercised by any use or display of force (such as placing one in handcuffs), lawfully or unlawfully, wherever displayed, even in the open street. People become prisoners, wherever they may be, by the mere word or touch of a duly authorized officer directed to that end. Usually, however, imprisonment is understood to imply actual confinement against one's will in a prison employed for the purpose according to the provisions of the law. Generally gender imbalances occur in imprisonment rates, with incarceration of males proportionately more likely than incarceration of females. History Africa Before colonisation, imprisonment was used in sub-Saharan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |