|
Stochastic Resonance (sensory Neurobiology)
Stochastic resonance is a phenomenon that occurs in a threshold measurement system (e.g. a man-made instrument or device; a natural cell, organ or organism) when an appropriate measure of information transfer (signal-to-noise ratio, mutual information, coherence, ''d, etc.) is maximized in the presence of a non-zero level of stochastic input noise thereby lowering the response threshold; the system resonates at a particular noise level. The three criteria that must be met for stochastic resonance to occur are: # Nonlinear device or system: the input-output relationship must be nonlinear # Weak, periodic signal of interest: the input signal must be below threshold of measurement device and recur periodically # Added input noise: there must be random, uncorrelated variation added to signal of interest Stochastic resonance occurs when these conditions combine in such a way that a certain average noise intensity results in maximized information transfer. A time-averaged (or, equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Resonance
Stochastic resonance (SR) is a phenomenon in which a signal that is normally too weak to be detected by a sensor, can be boosted by adding white noise to the signal, which contains a wide spectrum of frequencies. The frequencies in the white noise corresponding to the original signal's frequencies will resonate with each other, amplifying the original signal while not amplifying the rest of the white noise – thereby increasing the signal-to-noise ratio, which makes the original signal more prominent. Further, the added white noise can be enough to be detectable by the sensor, which can then filter it out to effectively detect the original, previously undetectable signal. This phenomenon of boosting undetectable signals by resonating with added white noise extends to many other systems – whether electromagnetic, physical or biological – and is an active area of research. Stochastic resonance was first proposed by the Italian physicists Roberto Benzi, Alfonso Sutera and An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuticular
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non-homologous, differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition. Human anatomy In human anatomy, "cuticle" can refer to several structures, but it is used in general parlance, and even by medical professionals, to refer to the thickened layer of skin surrounding fingernails and toenails (the eponychium), and to refer to the superficial layer of overlapping cells covering the hair shaft ( cuticula pili), consisting of dead cells, that locks the hair into its follicle. It can also be used as a synonym for the epidermis, the outer layer of skin. Cuticle of invertebrates In zoology, the invertebrate cuticle or cuticula is a multi-layered structure outside the epidermis of many invertebrates, notably roundworms and arthropods, in which it forms an exoskeleton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlear Implant
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training, cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound. The implant has two main components. The outside component is generally worn behind the ear, but could also be attached to clothing, for example, in young children. This component, the sound processor, contains microphones, electronics that include digital signal processor (DSP) chips, battery, and a coil that transmits a signal to the implant across the skin. The inside component, the actual implant, has a coil to receive signals, electronics, and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
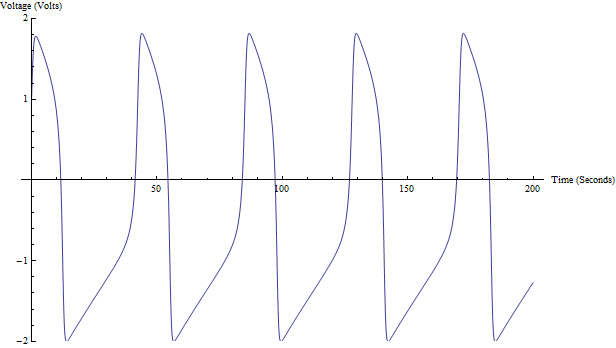
FitzHugh–Nagumo Model
The FitzHugh–Nagumo model (FHN), named after Richard FitzHugh (1922–2007) who suggested the system in 1961 and J. Nagumo ''et al''. who created the equivalent circuit the following year, describes a prototype of an excitable system (e.g., a neuron). The FHN Model is an example of a relaxation oscillator because, if the external stimulus I_ exceeds a certain threshold value, the system will exhibit a characteristic excursion in phase space, before the variables v and w relax back to their rest values. This behaviour is typical for spike generations (a short, nonlinear elevation of membrane voltage v, diminished over time by a slower, linear recovery variable w) in a neuron after stimulation by an external input current. The equations for this dynamical system read : \dot=v-\frac - w + RI_ : \tau \dot = v+a-b w. The dynamics of this system can be nicely described by zapping between the left and right branch of the cubic nullcline. The FitzHugh–Nagumo model is a sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purkinje Cell
Purkinje cells, or Purkinje neurons, are a class of GABAergic inhibitory neurons located in the cerebellum. They are named after their discoverer, Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyně, who characterized the cells in 1839. Structure These cells are some of the largest neurons in the human brain (Betz cells being the largest), with an intricately elaborate dendritic arbor, characterized by a large number of dendritic spines. Purkinje cells are found within the Purkinje layer in the cerebellum. Purkinje cells are aligned like dominos stacked one in front of the other. Their large dendritic arbors form nearly two-dimensional layers through which parallel fibers from the deeper-layers pass. These parallel fibers make relatively weaker excitatory (glutamatergic) synapses to spines in the Purkinje cell dendrite, whereas climbing fibers originating from the inferior olivary nucleus in the medulla provide very powerful excitatory input to the proximal dendrites and cell soma. Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Fixed Point
A fixed point (sometimes shortened to fixpoint, also known as an invariant point) is a value that does not change under a given transformation. Specifically, in mathematics, a fixed point of a function is an element that is mapped to itself by the function. In physics, the term fixed point can refer to a temperature that can be used as a reproducible reference point, usually defined by a phase change or triple point. Fixed point of a function Formally, is a fixed point of a function if belongs to both the domain and the codomain of , and . For example, if is defined on the real numbers by f(x) = x^2 - 3 x + 4, then 2 is a fixed point of , because . Not all functions have fixed points: for example, , has no fixed points, since is never equal to for any real number. In graphical terms, a fixed point means the point is on the line , or in other words the graph of has a point in common with that line. Fixed-point iteration In numerical analysis, ''fixed-point ite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit Cycle
In mathematics, in the study of dynamical systems with two-dimensional phase space, a limit cycle is a closed trajectory in phase space having the property that at least one other trajectory spirals into it either as time approaches infinity or as time approaches negative infinity. Such behavior is exhibited in some nonlinear systems. Limit cycles have been used to model the behavior of a great many real-world oscillatory systems. The study of limit cycles was initiated by Henri Poincaré (1854–1912). Definition We consider a two-dimensional dynamical system of the form x'(t)=V(x(t)) where V : \R^2 \to \R^2 is a smooth function. A ''trajectory'' of this system is some smooth function x(t) with values in \mathbb^2 which satisfies this differential equation. Such a trajectory is called ''closed'' (or ''periodic'') if it is not constant but returns to its starting point, i.e. if there exists some t_0>0 such that x(t + t_0) = x(t) for all t \in \R. An orbit is the image of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical Systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostrum (anatomy)
Rostrum (from Latin ', meaning ''beak'') is a term used in anatomy for a number of phylogenetically unrelated structures in different groups of animals. Invertebrates * In crustaceans, the rostrum is the forward extension of the carapace in front of the eyes. It is generally a rigid structure, but can be connected by a hinged joint, as seen in Leptostraca. * Among insects, the rostrum is the name for the piercing mouthparts of the order Hemiptera as well as those of the snow scorpionflies, among many others. The long snout of weevils is also called a rostrum. * Gastropod molluscs have a rostrum or proboscis. * Cephalopod molluscs have hard beak-like mouthparts referred to as the rostrum. File:Washington DC Zoo - Macrobrachium rosenbergii 6.jpg, Crustacean: the rostrum of the shrimp '' Macrobrachium rosenbergii'' is serrated along both edges. File:Gminatus australis with Beetle.jpg, Insect: assassin bug piercing its prey with its rostrum File:Architeuthis beak.jpg, Ceph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroreceptor
Electroreception and electrogenesis are the closely-related biological abilities to perceive electrical stimuli and to generate electric fields. Both are used to locate prey; stronger electric discharges are used in a few groups of fishes to stun prey. The capabilities are found almost exclusively in aquatic or amphibious animals, since water is a much better conductor of electricity than air. In passive electrolocation, objects such as prey are detected by sensing the electric fields they create. In active electrolocation, fish generate a weak electric field and sense the different distortions of that field created by objects that conduct or resist electricity. Active electrolocation is practised by two groups of weakly electric fish, the Gymnotiformes (knifefishes) and the Mormyridae (elephantfishes), and by '' Gymnarchus niloticus'', the African knifefish. An electric fish generates an electric field using an electric organ, modified from muscles in its tail. The field is call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)