|
Sternarchorhynchus Severii
''Sternarchorhynchus'' is a genus of ghost knifefishes with a long, decurved snout that are found in river basins in tropical South America. Distribution, habitat and conservation Of the 32 recognized species, more than are restricted to the Amazon basin (including the Tocantins River, Tocantins system) in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, 7 species are found in river basins flowing into the Gulf of Paria in Colombia and Venezuela (mostly Orinoco system, but ''S. mendesi'' in Guanipa River, Guanipa and San Juan River (Venezuela), San Juan), ''S. freemani'' is from the Essequibo River, Essequibo basin in Guyana, ''S. galibi'' is from the Maroni (river), Maroni basin in French Guiana and Suriname, and ''S. britskii'' is from the upper Paraná River, Paraná basin in Brazil.de Santana, C. D. and R.P. Vari (2010). Electric fishes of the genus Sternarchorhynchus (Teleostei, Ostariophysi, Gymnotiformes); phylogenetic and revisionary studies. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 159: 223-371. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater River (river Type)
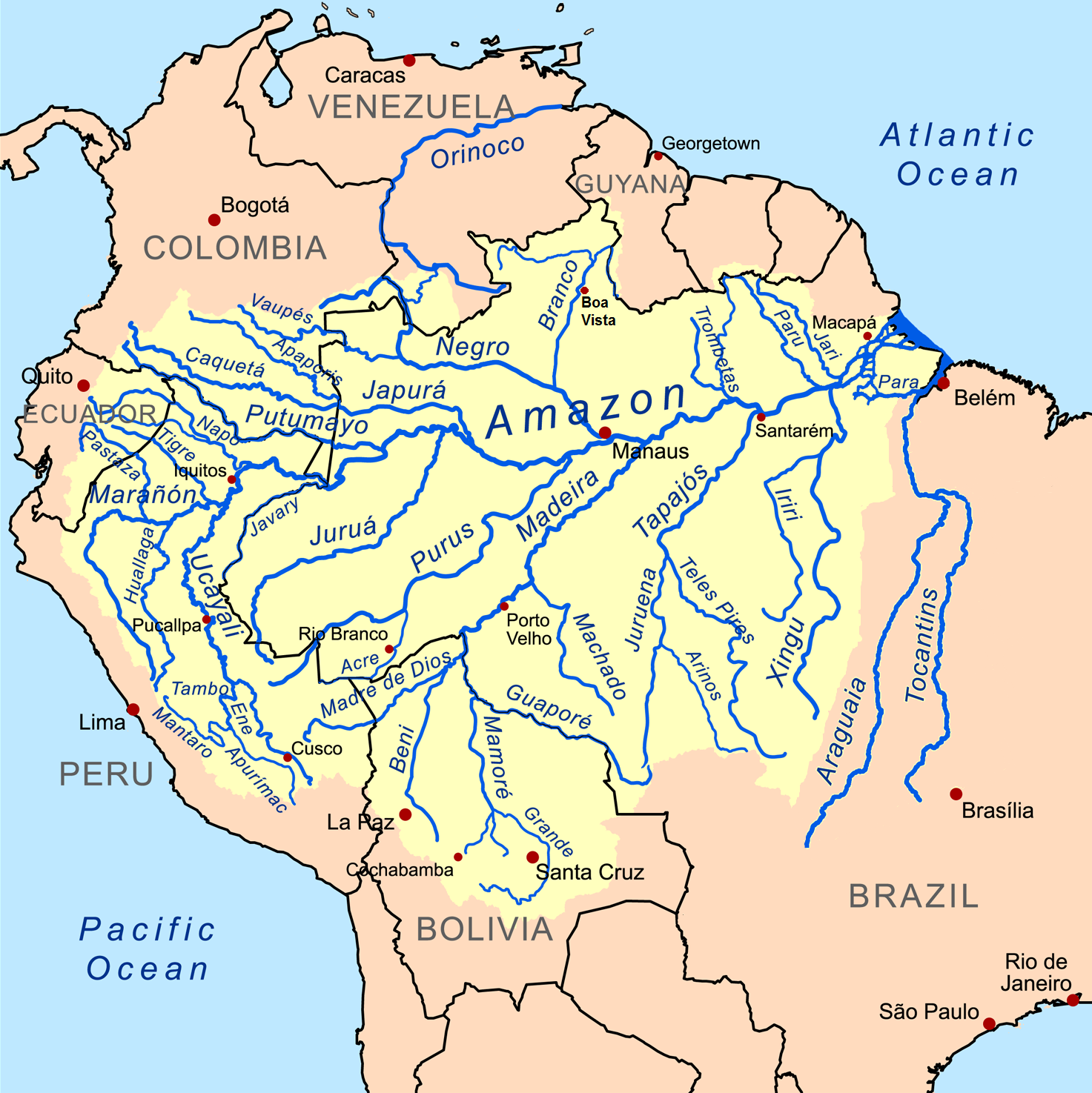
A whitewater river is classified based on its chemistry, sediments and water colour. Whitewater rivers have high levels of suspended sediments, giving the water a pH that is near-neutral, a high electric conductivity and a pale muddy, '' café au lait''-like colour. Whitewater rivers are of great ecological importance and are important to local fisheries. The major seasonal Amazonian floodplains known as '' várzea'' receive their water from them. The best-known whitewater rivers are Amazonian and have their source in the Andes, but there are also whitewater rivers elsewhere in South America and in other continents. Amazonian rivers fall into three main categories: whitewater, blackwater and clearwater. This classification system was first proposed by Alfred Russel Wallace in 1853 based on water colour, but the types were more clearly defined according to chemistry and physics by from the 1950s to the 1980s. Although many Amazonian rivers fall clearly into one of these cate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Specimen
A zoological specimen is an animal or part of an animal preserved for scientific use. Various uses are: to verify the identity of a (species), to allow study, increase public knowledge of zoology. Zoological specimens are extremely diverse. Examples are bird and mammal study skins, mounted specimens, skeletal material, casts, pinned insects, dried material, animals preserved in liquid preservatives, and microscope slides. Natural history museums are repositories of zoological specimens Study skins Bird and mammal specimens are conserved as dry study skins, a form of taxidermy. The skin is removed from the animal's carcass, treated with absorbents, and filled with cotton or polyester batting (In the past plant fibres or sawdust were used). Bird specimens have a long, thin, wooden dowel wrapped in batting at their center. The dowel is often intentionally longer than the bird's body and exits at the animal's vent. This exposed dowel provides a place to handle the bird without distu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroní River
The Caroní River is the second most important river of Venezuela, the second in flow, and one of the longest, from the Kukenan tepui through to its confluence with the Orinoco River. The name "Caroní" is applied starting from the confluence of the Kukenan with the Yuruaní River at from the source of the Kukenan and from its discharge in the Orinoco. The confluence takes place in Bolivar State. The Caroní River is the longest river located entirely within Venezuela. Hydraulic regime The Caroní is one of the rivers with the highest discharge rates in the world, with respect to the area of its basin. The average discharge is , with variations caused by the wet/dry seasons. The average maximum discharge is , and the average minimum is . Among the historic extremes are . The Caroní supplies 15.5 percent of the discharge of the Orinoco river. One of the characteristics of the Caroní's water is the dark color, caused by the high amount of humic acids due to the inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICMBio
The Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation ( Portuguese: ''Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade'', ICMBio) is a government agency under the administration of the Brazilian Ministry of the Environment. It is named after the environmental activist Chico Mendes. Its function is to protect, manage, and administrate protected areas within the country's territory. ICMBio is headquartered in Brasília Brasília ( ; ) is the capital city, capital of Brazil and Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. Located in the Brazilian highlands in the country's Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region, it was founded by President Juscelino .... References Nature conservation in Brazil Executive branch of Brazil Research institutes in Brazil Biodiversity databases Government agencies established in 2007 Environmental organizations established in 2007 2007 establishments in Brazil {{brazil-gov-stub, date=March 2014 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of The Environment (Brazil)
The Ministry of Environment and Climate Change (, abbreviated MMA) is a cabinet-level federal ministry in Brazil. The ministry emerged from the Special Secretariat for the Environment within the now-extinct Ministry of the Interior from 1974 to 1985. It has gone through several name changes since its inception. Responsibilities * National Environmental Policy * Environmental policies and programs for the Amazon and other Brazilian biomes * Water resources policy * National water security policy * Policies for the preservation, conservation and sustainable use of ecosystems, biodiversity and forests * Policies for integrating environmental protection with economic production * Regulatory and economic strategies, mechanisms and instruments for improving environmental quality and the sustainable use of natural resources * National policy on climate change * Ecological-economic zoning and other territorial planning instruments, including marine spatial planning, in articulation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threatened Species
A threatened species is any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which is vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensation'', a mathematical measure of biomass related to population growth rate. This quantitative metric is one method of evaluating the degree of endangerment without direct reference to human activity. IUCN definition The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is the foremost authority on threatened species, and treats threatened species not as a single category, but as a group of three categories, depending on the degree to which they are threatened: *Vulnerable species *Endangered species *Critically endangered species Less-than-threatened categories are near threatened, least concern, and the no longer assigned category of conservation dependent. Species that have not been evaluated (NE), or do not have sufficient data ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Várzea Forest
A várzea forest is a seasonal floodplain forest inundated by whitewater rivers that occurs in the Amazon biome. Until the late 1970s, the definition was less clear and várzea was often used for all periodically flooded Amazonian forests. Although sometimes described as consisting only of forest, várzea also contains more open, seasonally flooded habitats such as grasslands, including floating meadows. Description Along the Amazon River and many of its tributaries, high annual rainfall that occurs mostly within a rainy season results in extensive seasonal flooding of areas from stream and river discharge. The result is a rise in water level, with nutrient rich waters. The Iquitos várzea ecoregion covers the margins of the upper Amazon and its tributaries. Further down are the Purus várzea in the middle Amazon, the Monte Alegre várzea and Gurupa várzea on the lower Amazon and the Marajó várzea at the mouth of the Amazon. The Marajó várzea is affected by both freshw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenmannia Vicentespelaea
''Eigenmannia vicentespelaea'' is a species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Sternopygidae. Native to the São Domingos karst area in central Brazil, it is the only known knifefish to exclusively inhabit caves. Measuring up to long, ''E. vicentespelaea'' can be distinguished from its relatives by its translucent body and reduced or absent eyes. As some individuals retain well-developed eyes, this fish may have colonized caves only recently in evolutionary time. Taxonomy Brazilian ichthyologist Mauro Luís Triques described ''E. vicentespelaea'' in a 1996 volume of the scientific journal ''Revue Française de Aquariologie'', from two specimens caught in 1978. He chose the specific epithet ''vicentespelaea'' from the São Vicente I cave, the type locality, and ''speleum'', Latin for "cave". Based on color pattern and morphology, it is included in the '' E. virescens'' species group with ''E. virescens'', '' E. trilineata'', and a third undescribed species. Distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavefish
Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, Troglomorphism, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreatic fish, and hypogean fish.Romero, Aldemaro, editor (2001). ''The Biology of Hypogean Fishes.'' Developments in Environmental Biology of Fishes. Helfman, G.S. (2007). ''Fish Conservation: A Guide to Understanding and Restoring Global Aquatic Biodiversity and Fishery Resources'', pp. 41–42. Island Press. There are more than 200 Species description, scientifically described species of obligate cavefish found on all continents, except Antarctica. Although widespread as a group, many species have very small ranges and are Threatened species, threatened.Fenolio, D.B.; Zhao, Y.; Niemiller, M.L.; and Stout, J. (2013). ''In-situ observations of seven enigmatic cave loaches and one cave barbel from Guangxi, China, with notes on conservation sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xingu River
The Xingu River ( ; ; ) is a river in north Brazil. It is a southeast tributary of the Amazon River and one of the largest clearwater rivers in the Amazon basin, accounting for about 5% of its water. __TOC__ Description and history The first Indigenous Park in Brazil was created in the river basin by the Brazilian government in the early 1960s. This park marks the first indigenous territory recognized by the Brazilian government and it was the world's largest indigenous preserve on the date of its creation. Currently, fourteen tribes live within Xingu Indigenous Park, surviving on natural resources and extracting from the river most of what they need for food and water. The Brazilian government built the Belo Monte Dam on the Lower Xingu, which began operations in 2019 and is the world's fifth-largest hydroelectric dam. Construction of this dam was under legal challenge by environment and indigenous groups, who assert the dam would have negative environmental and social i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearwater River (river Type)
A clearwater river is classified based on its chemistry, sediments and water colour. Clearwater rivers have a low conductivity, relatively low levels of dissolved solids, typically have a neutral to slightly acidic pH and are very clear with a greenish colour. Clearwater rivers often have fast-flowing sections. The main clearwater rivers are South American and have their source in the Brazilian Plateau or the Guiana Shield. Outside South America the classification is not commonly used, but rivers with clearwater characteristics are found elsewhere. Amazonian rivers fall into three main categories: clearwater, blackwater and whitewater. This classification system was first proposed by Alfred Russel Wallace in 1853 based on water colour, but the types were more clearly defined according to chemistry and physics by from the 1950s to the 1980s. Although many Amazonian rivers fall clearly into one of these categories, others show a mix of characteristics and may vary depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |