|
Stentrode
Stentrode (Stent-electrode recording array) is a small stent-mounted electrode array permanently brain implant, implanted into a blood vessel in the brain, without the need for open brain surgery. It is in clinical trials as a brain–computer interface (BCI) for people with paralyzed or missing limbs, who will use their Action potential, neural signals or thoughts to control external devices, which currently include computer operating systems. The device may ultimately be used to control powered exoskeletons, robotic prosthesis, computers or other devices. The device was conceived by Australian neurologist Thomas Oxley (neurologist), Thomas Oxley and built by Australian biomedical engineer Nicholas Opie, who have been developing the medical implant since 2010, using sheep for testing. Human trials started in August 2019 with participants who suffer from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a type of motor neuron disease. Graeme Felstead was the first person to receive the implant. To da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain–computer Interface
A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication link between the brain's electrical activity and an external device, most commonly a computer or robotic limb. BCIs are often directed at researching, Brain mapping, mapping, assisting, Augmented cognition, augmenting, or repairing human Cognitive skill, cognitive or Sensory-motor coupling, sensory-motor functions. They are often conceptualized as a human–machine interface that skips the intermediary of moving body parts (e.g. hands or feet). BCI implementations range from non-invasive (EEG, Magnetoencephalography, MEG, MRI) and partially invasive (ECoG and endovascular) to invasive (microelectrode array), based on how physically close electrodes are to brain tissue. Research on BCIs began in the 1970s by Jacques Vidal at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) under a grant from the National Science Foundation, followed by a contract from the Defense Adva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Oxley (neurologist)
Thomas J. Oxley is the chief executive officer of Synchron and neurointerventionist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. Trained as a vascular and interventional neurologist, he established the Vascular Bionics laboratory at the University of Melbourne and is currently co-head of this lab. Oxley is best known for founding Synchron, a company building next-generation brain computer interface solutions that has recently announced the first clinical data on a novel stent electrode (Stentrode) neural interface that is inserted through blood vessels. The company was initiated sometime after hicold-call to DARPAfor funding, and has received substantial funding from the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and the Australian government to research this minimally-invasive neural interface technology. Work in brain-computer interface While Oxley has been conducting research in motor systems since 2003, he is said to have conceived the idea for the Stentrode™ i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Implant
Brain implants, often referred to as neural implants, are technological devices that connect directly to a biological subject's brain – usually placed on the surface of the brain, or attached to the brain's cortex. A common purpose of modern brain implants and the focus of much current research is establishing a biomedical prosthesis circumventing areas in the brain that have become dysfunctional after a stroke or other head injuries. This includes sensory substitution, e.g., in vision. Other brain implants are used in animal experiments simply to record brain activity for scientific reasons. Some brain implants involve creating interfaces between neural systems and computer chips. This work is part of a wider research field called brain–computer interfaces. (Brain–computer interface research also includes technology such as EEG arrays that allow interface between mind and machine but do not require direct implantation of a device.) Neural implants such as deep brain stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Opie
Nicholas Opie is an Australian biomedical engineer who co-founded Synchron in 2012. He invented the Stentrode alongside Thomas Oxley. Opie serves as the head of Vascular Bonic Laboratory at the University of Melbourne The University of Melbourne (colloquially known as Melbourne University) is a public university, public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in the state .... References Living people Academic staff of the University of Melbourne Biomedical engineers Year of birth missing (living people) {{Australia-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Implant
A cortical implant is a subset of neuroprosthetics that is in direct connection with the cerebral cortex of the brain. By directly interfacing with different regions of the cortex, the cortical implant can provide stimulation to an immediate area and provide different benefits, depending on its design and placement. A typical cortical implant is an implantable microelectrode array, which is a small device through which a neural signal can be received or transmitted. The goal of a cortical implant and neuroprosthetic in general is "to replace neural circuitry in the brain that no longer functions appropriately." Overview Cortical implants have a wide variety of potential uses, ranging from restoring vision to blind patients or helping patients with dementia. With the complexity of the brain, the possibilities for these brain implants to expand their usefulness are nearly endless. Some early work in cortical implants involved stimulation of the visual cortex, using implants made fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other human organs, organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually extremely rare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
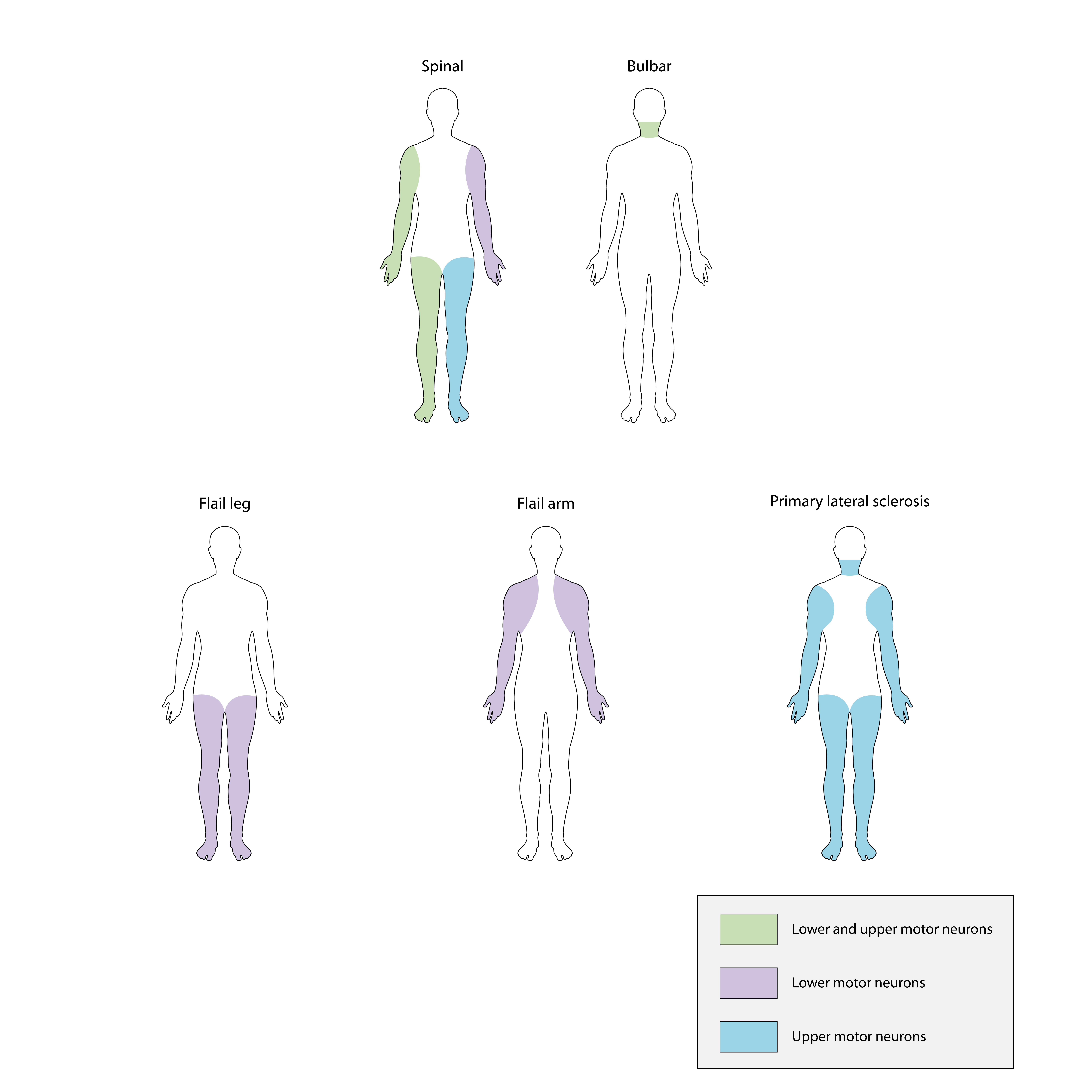
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
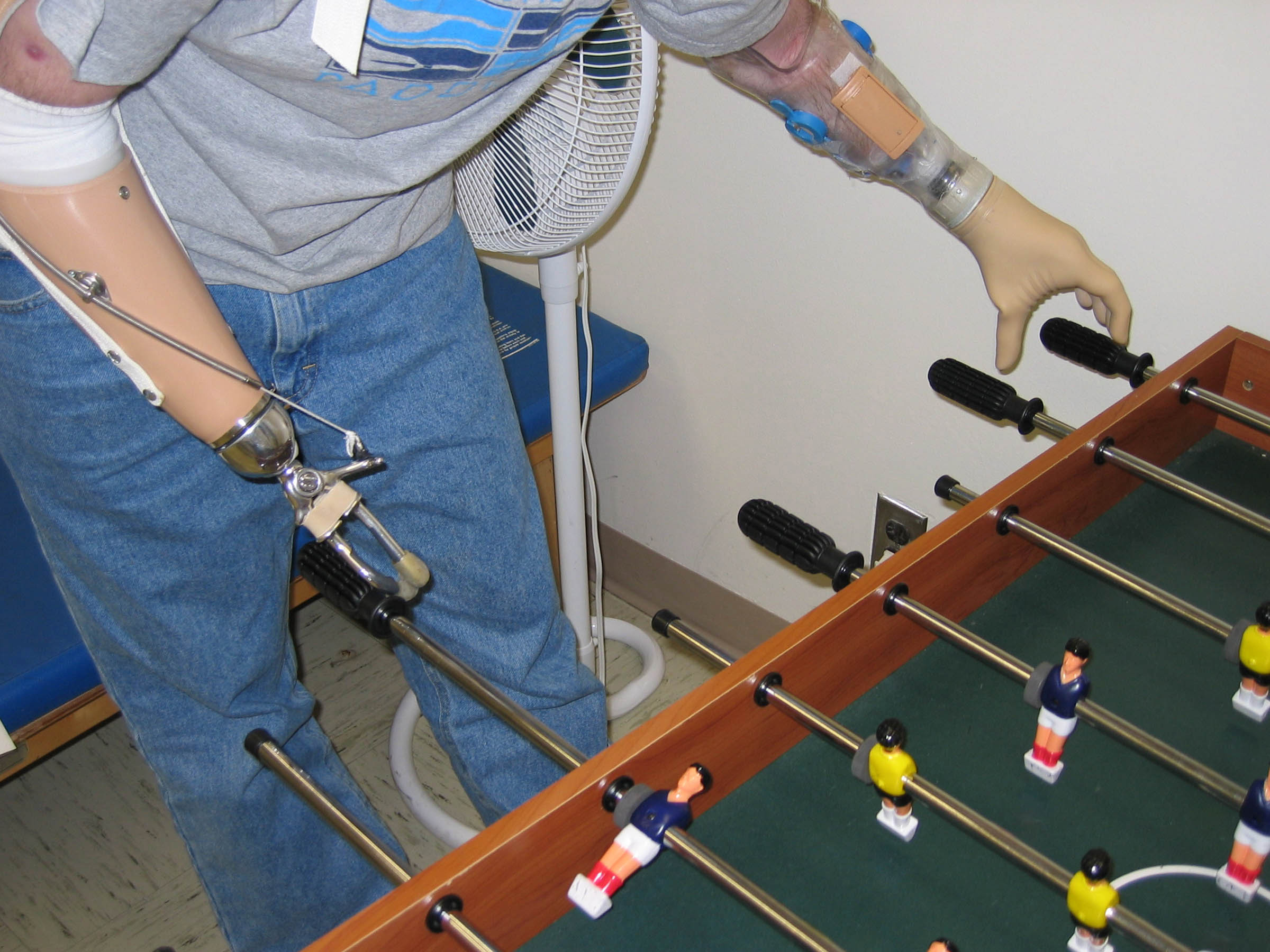
Prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (: prostheses; from ), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through physical trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (Congenital, congenital disorder). Prostheses may restore the normal functions of the missing body part, or may perform a cosmetic function. A person who has undergone an amputation is sometimes referred to as an Amputation, amputee, however, this term may be offensive. Rehabilitation for someone with an amputation is primarily coordinated by a Physical medicine and rehabilitation, physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated Technical drawing, 2-D and 3D computer graphics, 3-D graphics as well as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Vincent's Hospital, Melbourne
St Vincent's Hospital is a major hospital in Fitzroy, Melbourne, Australia. It is operated by the St Vincent's Health service, previously known as the Sisters of Charity Health Service, Melbourne. It is situated at the corner of Nicholson Street and Victoria Street. The hospital is a tertiary referral centre which offers a variety of medical, surgical and mental health specialities. History St Vincent's Hospital was opened in 1893 as a Catholic hospital owned and operated by the Sisters of Charity. Initially conceived as a branch of the Sydney institution of the same name, the hospital was intended to be a charitable institution, which was hoped would help bolster Melbourne's minimal health care. This idea was given avid support by Melbourne's Catholic Archbishop Dr Thomas Carr, who welcomed the idea of a hospital to take care of the 'poor and sick and abandoned children... the young girls of poor parents and servants...' These ideals corresponded directly with prevalent V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombus
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis in or out of the circulatory system. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through a healthy blood vessel in the circulatory system. In the microcirculation consisting of the very small and smallest blood vessels the capillaries, tiny thrombi known as microclots can obstruct the flow of blood in the capillaries. This can cause a number of problems particularly affecting the pulmonary alveolus, alveoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |