|
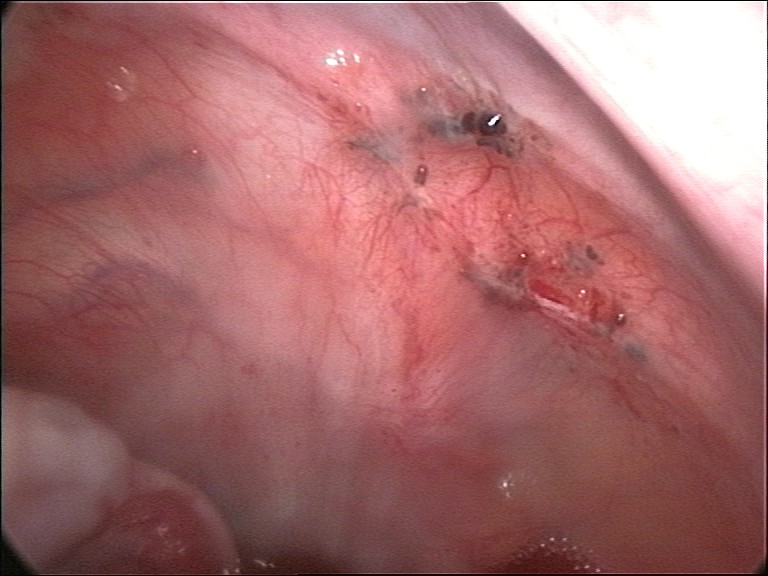
Stenosis Of Uterine Cervix
Cervical stenosis means that the opening in the cervix (the endocervical canal) is more narrow than is typical. In some cases, the endocervical canal may be completely closed. A stenosis is any passage in the body that is more narrow than it should typically be. Signs and symptoms Symptoms depend on whether the cervical canal is partially or completely obstructed and on the patient's menopausal status. Pre-menopausal patients may have a build up of blood inside the uterus which may cause infection, sporadic bleeding, or pelvic pain. Patients also have an increased risk of infertility and endometriosis.The Merck Manual Home Edition. Last full review/revision December 2008 by S. Gene McNeeley.Cervical Stenosis/ref> Fertility Cervical stenosis may impact natural fertility by impeding the passage of sperm into the uterus. In the context of infertility treatments, cervical stenosis may complicate or prevent the use of intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences) is the area of medicine concerned with conditions affecting the Female reproductive system, female reproductive system. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy and childbirth, thereby forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN). Gynaecology encompasses both Primary care, primary and Preventive healthcare, preventative care of issues related to female reproduction and sexual health, such as the uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and breasts; subspecialties include family planning; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric and adolescent gynecology; and pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. While gynaecology has traditionally centered on Cisgender, cisgender women, it increasingly encompasses anyone with female organs, including transgender, intersex, and Non-binary gender, nonbinary individuals; however, many non-cis women face acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture). ''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing is caused by contraction of smooth muscle (e.g. achalasia, prinzmetal angina); ''stenosis'' is usually used when narrowing is caused by lesion that reduces the space of lumen (e.g. atherosclerosis). The term coarctation is another synonym, but is commonly used only in the context of aortic coarctation. Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis after a procedure. Examples Examples of vascular stenotic lesions include: * Intermittent claudication (peripheral artery stenosis) * Angina ( coronary artery stenosis) * Carotid artery stenosis which predispose to (strokes and transient ischaemic episodes) * Renal artery stenosis Types In heart valves The types of stenoses in heart valves are: * Pulmonary valve stenosis, which is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Of The Cervix
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix which connects the vagina to the main cavity of the uterus in most mammals. Anatomy The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus (or internal os) and with the vagina via the external orifice of the uterus (ostium of uterus or external os). The internal orifice of the uterus is an interior narrowing of the uterine cavity. It corresponds to a slight constriction known as the ''isthmus'' that can be seen on the surface of the uterus about midway between the apex and base. The external orifice of the uterus is a small, depressed, somewhat circular opening on the rounded extremity of the cervix, opening to the vagina. Through this aperture, the cervical cavity communicates with that of the vagina. The external orifice is bounded by two lips, an anterior and a posterior. The anterior is shorter and thicker, though it projects lower than the posterior because of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can vary. Menopause is usually a natural change related to a decrease in circulating blood estrogen levels. It can occur earlier in those who smoke tobacco. Other causes include surgery that removes both ovaries, some types of chemotherapy, or anything that leads to a decrease in hormone levels. At the physiological level, menopause happens because of a decrease in the ovaries' production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. While typically not needed, measuring hormone levels in the blood or urine can confirm a diagnosis. Menopause is the opposite of menarche, the time when periods start. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to Sexual reproduction, reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of fertility, reproductive capacity, are excluded. It is also a normal state in women after menopause. In humans, ''infertility'' is defined as the inability to become pregnant after at least one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner. There are many causes of infertility, including some that Assisted reproductive technology, medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year, with estimates ranging from 12% to 28%. Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which Tissue (biology), tissue similar to the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, grows in other places in the body, outside the uterus. It occurs in women and a limited number of other female mammals. Endometrial tissue most often grows on or around reproductive organs such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes, on the outside surface of the uterus, or the tissues surrounding the uterus and the ovaries (peritoneum). It can also grow on other organs in the pelvic region like the Gastrointestinal tract, bowels, stomach, bladder, or the cervix. Rarely, it can also occur in other parts of the body. Symptoms can be very different from person to person, varying in range and intensity. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms, while for some it can be a debilitating disease. Common symptoms include pelvic pain, Heavy menstrual bleeding, heavy and Dysmenorrhea, painful periods, pain with bowel movements, Dysuria, painful urination, Dyspareunia, pain dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Fertility
Natural fertility is the fertility that exists without birth control or other medical interventions. The control is the number of children birthed to the parents and is modified as the number of children reaches the maximum. Natural fertility tends to decrease as a society modernizes. Women in a pre-modernized society typically have given birth to a large number of children by the time they are 50 years old, while women in post-modernized society only bear a small number by the same age. However, during modernization natural fertility rises, before family planning is practiced. Historical populations have traditionally honored the idea of natural fertility by displaying fertility symbols. Birth control Natural fertility is a concept developed by the French historical demographer Louis Henry to refer to the level of fertility that would prevail in a population that makes no conscious effort to limit, regulate, or control fertility, so that fertility depends only on physiological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which Cellular differentiation, differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their Ploidy, chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The sper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Insemination
Artificial insemination is the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female's cervix or uterine cavity for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse. It is a fertility treatment for humans, and is a common practice in animal breeding, including dairy cattle (see frozen bovine semen) and pigs. Artificial insemination may employ assisted reproductive technology, sperm donation and animal husbandry techniques. Artificial insemination techniques available include intracervical insemination (ICI) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). Where gametes from a third party are used, the procedure may be known as 'assisted insemination'. Humans History The first recorded case of artificial insemination was John Hunter in 1790, who helped impregnate a linen draper's wife. The first reported case of artificial insemination by donor occurred in 1884: William H. Pancoast, a professor in Philadelphia, took sperm from his "bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating the ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the ovaries and enabling sperm to fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After a fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility, enable gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoid the transmission of abnormal genetic conditions. When a fertilised egg from egg and sperm donors implants in the uterus of a genetically unrelated surrogate, the resulting child is also genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulated the availability of IVF treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |