|
Stele Of Ankh-ef-en-Khonsu
The Stele of Ankh-ef-en-Khonsu or Stele of Revealing is a painted, wooden offering stele located in Cairo, Egypt. It was discovered in 1858 by the French Egyptologist François Auguste Ferdinand Mariette at the mortuary temple of the 18th Dynasty Pharaoh Hatshepsut, located at Deir el-Bahari. It was originally made for the Montu-priest Ankh-ef-en-Khonsu i, and was discovered near his coffin ensemble of two sarcophagi and two anthropomorphic inner coffins. It dates to ''circa'' 680–70 BCE, the period of the late 25th Dynasty/early 26th Dynasty. Originally located in the former Boulaq Museum under inventory number 666, the stele was moved around 1902 to the newly opened Egyptian Museum of Cairo (inventory number A 9422; Temporary Register Number 25/12/24/11), where it remains today. The stele is made of wood and covered with a plaster gesso, which has been painted. It measures 51.5 centimeters high and 31 centimeters wide. On the front, Ankh-ef-en-Khonsu can be seen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-fifth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXV, alternatively 25th Dynasty or Dynasty 25), also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt that occurred after the Kushite invasion. The 25th dynasty was a line of pharaohs who originated in the Kingdom of Kush, located in present-day northern Sudan and Upper Egypt. Most of this dynasty's kings saw Napata as their spiritual homeland. They reigned in part or all of Ancient Egypt for nearly a century, from 744 to 656 BC. The 25th dynasty was highly Egyptianized, using the Egyptian language and writing system as their medium of record and exhibiting an unusual devotion to Egypt's religious, artistic, and literary traditions. Earlier scholars have ascribed the origins of the dynasty to immigrants from Egypt, particularly the Egyptian Amun priests. The third intermediate-period Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
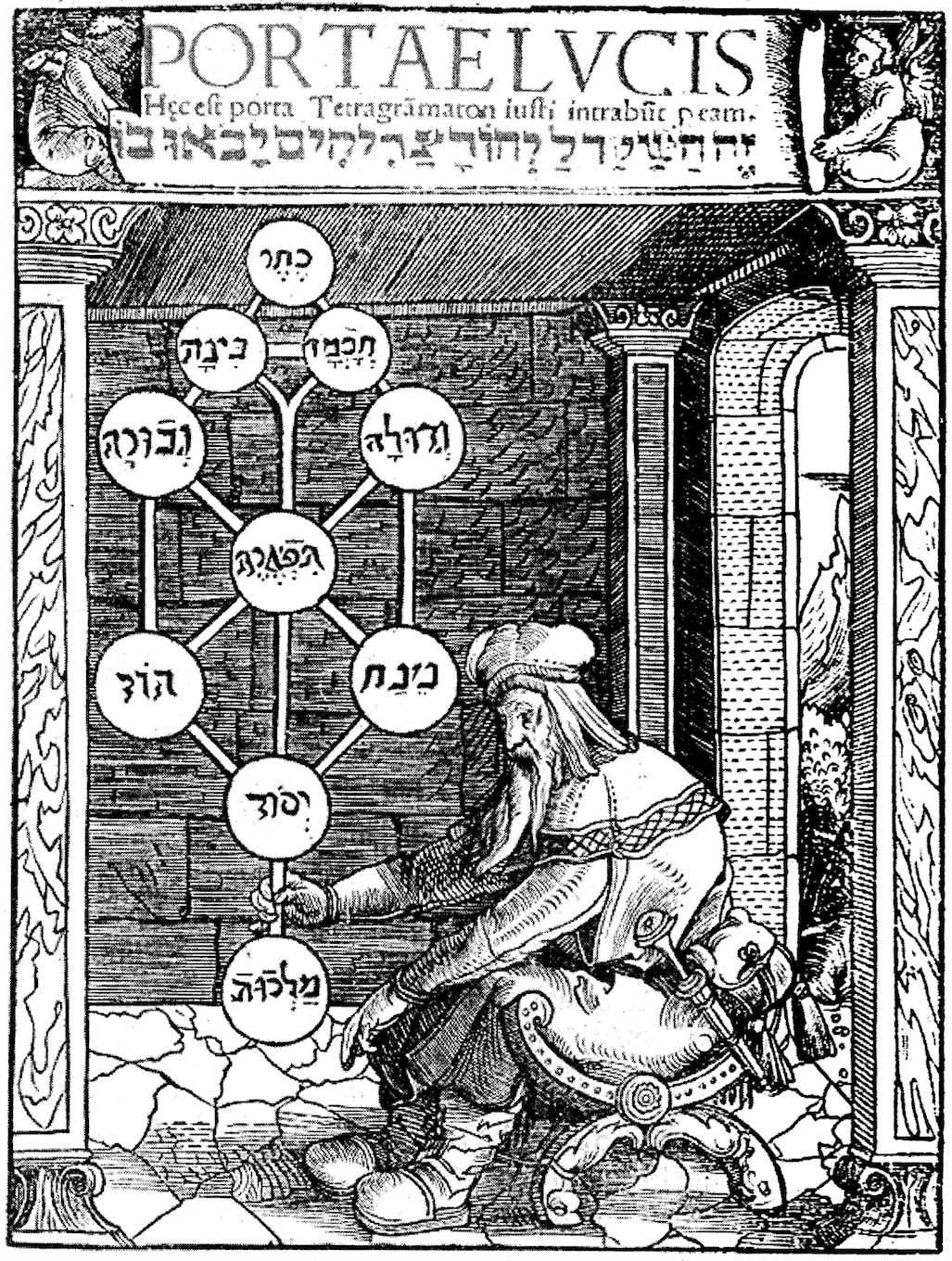
Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley ( ; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, novelist, mountaineer, and painter. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the prophet entrusted with guiding humanity into the Aeon of Horus, Æon of Horus in the early 20th century. A prolific writer, he published widely over the course of his life. Born to a wealthy family in Royal Leamington Spa, Warwickshire, Crowley rejected his parents' fundamentalist Christian Plymouth Brethren faith to pursue an interest in Western esotericism. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, Trinity College at the University of Cambridge, where he focused his attention upon mountaineering and poetry, resulting in several publications. Some biographers allege that here he was recruited into a British intelligence agency, further suggesting that he remained a spy throughout his life. In 1898, he joined the esoteric Hermetic Order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Magic
Ceremonial magic (also known as magick, ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of Magic (supernatural), magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism. The synonym ''magick'' is an archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance, which was revived by Aleister Crowley to differentiate occult magic from magic (illusion), stage magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including ordinary acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occultist
The occult () is a category of esoteric or supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of organized religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving a 'hidden' or 'secret' agency, such as magic and mysticism. It can also refer to paranormal ideas such as extra-sensory perception and parapsychology. The term occult sciences was used in 16th-century Europe to refer to astrology, alchemy, and natural magic. The term occultism emerged in 19th-century France, among figures such as Antoine Court de Gébelin. It came to be associated with various French esoteric groups connected to Éliphas Lévi and Papus, and in 1875 was introduced into the English language by the esotericist Helena Blavatsky. Throughout the 20th century, the term 'occult' was used idiosyncratically by a range of different authors. By the 21st century the term 'occultism' was commonly employed –including by academic scholars in the field of Western esotericism studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esotericism, Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and a new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. Central to Thelema is the concept of discovering and following one's True Will, a divine and individual purpose that transcends ordinary desires. Crowley's system begins with ''The Book of the Law'', a text he maintained was dictated to him by a non-corporeal entity named Aiwass. This work outlines key principles, including the axioms "Do what thou wilt shall be the whole of the Law" and "love is the law, love under will", emphasizing personal freedom and the pursuit of one's true path. The Thelemic cosmology features deities inspired by ancient Egyptian religion. The highest deity is Nuit, the night sky symbolized as a naked woman covered in stars, representing the ultimate source of possibilities. Hadit, the infinitely small poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behdet
Edfu (, , , ; also spelt Idfu, or in modern French as Edfou) is an Egyptian city, located on the west bank of the Nile River between Esna and Aswan, with a population of approximately 60,000 people. Edfu is the site of the Ptolemaic Temple of Horus and an ancient settlement, Tell Edfu. About south of Edfu are remains of ancient pyramids. Ancient history Ancient Tell Edfu The remains of the ancient settlement of Edfu are situated about 50 m to the west of the Ptolemaic temple – to the left of the older temple pylon. This settlement is known as ''Wetjeset-hor'' and the Greek name was ''Apollinopolis Magna'' (Ancient Greek: ''Apollinòpolis'', ''Απολλινόπολις''). According to ''Notitia Dignitatum'', part of Legio II ''Traiana Fortis'' was camped in ''Apollo superior'', which was the Roman name for the town. Although unassuming and unglamorous to the visiting tourists, Tell Edfu is a monument that contains evidence of more Egyptian history and is of more ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horus
Horus (), also known as Heru, Har, Her, or Hor () in Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as the god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun, and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Egypt (Roman province), Roman Egypt. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history, and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptology, Egyptologists."The Oxford Guide: Essential Guide to Egyptian Mythology", Edited by Donald B. Redford, Horus: by Edmund S. Meltzer, pp. 164–168, Berkley, 2003, . These various forms may be different manifestations of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or Syncretism, syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality. He was most often depicted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Deities
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to '' maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art of ancient Egypt, art—as animals, humans, objects, and combinations of different forms—also all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clergy Of Ancient Egypt
typical depiction of an ancient Egyptian priest with a Leopard skin The clergy of ancient Egypt was made up of a multitude of priestsAlthough the word priest is commonly used to designate the ancient Egyptians who worked in the service of the gods, it can be misleading, as their function was so far from that of Catholic priests in Western culture.''ḥm-nṯr'' literally person of the god, an expression translated by the Greeks as "prophet". and priestesses who worshipped the many gods of the Egyptian religion. Function In Egyptian thought, the gods shape the Earth and establish a harmonious order ( Maat) that allows the miracle of life to unfold day after day. It's up to Pharaoh alone, a descendant of the gods, to ensure the continuity of this harmony and to combat the forces of Evil that continually seek to break it. Pharaoh is the only intermediary between the divinities and mortals. Since the maintenance of divine harmony requires numerous daily services throughout the lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesso
A restored gesso panel representing St. Martin of Tours, from St. Michael and All Angels Church, Lyndhurst, Hampshire Gesso (; 'chalk', from the , from ), also known as "glue gesso" or "Italian gesso", is a white paint mixture used to coat rigid surfaces such as wooden painting panels or masonite as a permanent absorbent primer substrate for painting. It consists of a binder mixed with chalk, gypsum, pigment, or any combination of these. Gesso is used in painting as a preparation for any number of substrates such as wood panels, canvas and sculpture as a base for paint and other materials that are applied over it. Characteristics The colour of gesso is usually white or off-white. Its absorbency makes it work with all painting media, including water-based media, different types of tempera and oil paint. Mixing and applying it is a craft in itself, as it is usually applied in ten or more extremely thin layers. The hide glue mixture used to make the traditional gesso is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |