|
Staveley Works Railway Station
Staveley Works railway station was on the outskirts of the town of Staveley, Derbyshire. The station was on the Great Central Chesterfield Loop which ran between Staveley Central and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station) on the Great Central Main Line The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railw .... References Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Great Central Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1892 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1963 {{EastMidlands-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staveley, Derbyshire
Staveley is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England. Located along the banks of the River Rother. It is (5 miles) northeast of Chesterfield, (5 miles) west of Clowne, (5 miles) northwest of Bolsover, (11 miles) southwest of Worksop and (13 miles) southeast of Sheffield. History Staveley was formerly a mining town with several large coal mines in and around the area, the closest being Ireland Pit (Ireland Colliery Brass Band is named after the colliery). However, the pit has closed, along with the others in the area. Staveley Miners Welfare on Market Street was built in 1893 as an indoor market hall by Charles Paxton Markham, for a time owner of Markham & Co. At that time, it was called Markham Hall in memory of his father. Markham played a large role in the industrial development of the area around Staveley. Through his company Markham & Co. and its successor Staveley Coal and Iron Company, Markham owned ironstone quarries, several coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesterfield (borough)
The Borough of Chesterfield is a non-metropolitan district with borough status in Derbyshire, England. It is named after its main settlement of Chesterfield. History The district was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, by a merger of the Municipal Borough of Chesterfield, Staveley Urban District and the Brimington part of Chesterfield Rural District. The borough's main two towns are Chesterfield and Staveley. With its geographical position, the borough offers convenient commuter links to the cities of Sheffield, Nottingham, Derby, Bradford, Wakefield, Manchester, Salford, Leeds and Lincoln, and via its mainline railway station at Chesterfield and the connections to the M1 motorway. Geography The borough is situated around the town of Chesterfield and includes the villages of Old Whittington, Brimington (which also has a parish council), Sheepbridge and New Whittington, and the town of Staveley which maintains a town council. The borough is bordered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey National Grid
The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB) (also known as British National Grid (BNG)) is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. The Ordnance Survey (OS) devised the national grid reference system, and it is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps based on those surveys, whether published by the Ordnance Survey or by commercial map producers. Grid references are also commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books and government planning documents. A number of different systems exist that can provide grid references for locations within the British Isles: this article describes the system created solely for Great Britain and its outlying islands (including the Isle of Man); the Irish grid reference system was a similar system created by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland for the island of Ireland. The Universal Transverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester, Sheffield And Lincolnshire Railway
The Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR) was formed in 1847 when the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway joined with authorised but unbuilt railway companies, forming a proposed network from Manchester to Grimsby. It pursued a policy of expanding its area of influence, especially in reaching west to Liverpool, which it ultimately did through the medium of the Cheshire Lines Committee network in joint partnership with the Great Northern Railway and the Midland Railway. Its dominant traffic was minerals, chiefly coal, and the main market was in London and the south of England. It was dependent on other lines to convey traffic southward. The London and North Western Railway was an exceptionally hostile partner, and in later years the MS&LR allied itself with the Great Northern Railway. Passenger traffic, especially around Manchester, was also an important business area, and well-patronised express trains to London were run in collaboration with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway. History New name On assuming its new title, the Great Central Railway had a main line from Manchester London Road Station via , Sheffield Victoria, and Grimsby to . A second line left the line at Penistone and served , and Scunthorpe, before rejoining the Grimsby line at . Other lines linked Sheffield to Barnsley (via ) and Doncaster (via Rotherham) and also and Wrawby Junction. Branch lines in north Lincolnshire ran to Barton-upon-Humber and New Holland and served ironstone quarries in the Scunthorpe area. In the Manchester area, lines ran to Stalybridge and Glossop. In the 1890s, the MS&LR began constructing its Derbyshire lines, the first part of its push southwards. Leaving its east–west main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the "Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At that time, it was divided into the new British Railways' Eastern Region, North Eastern Region, and partially the Scottish Region. History The company was the second largest created by the Railways Act 1921. The principal constituents of the LNER were: * Great Eastern Railway * Great Central Railway * Great Northern Railway * Great North of Scotland Railway * Hull and Barnsley Railway * North British Railway * North Eastern Railway The total route mileage was . The North Eastern Railway had the largest route mileage of , whilst the Hull and Barnsley Railway was . It covered the area north and east of London. It included the East Coast Main Line from London to Edinburgh via York and Newcastle upon Tyne and the routes from Edinburgh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Midland Region
The London Midland Region (LMR) was one of the six regions created on the formation of the nationalised British Railways (BR), and initially consisted of ex- London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) lines in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The region was managed first from buildings adjacent to Euston station, and later from Stanier House in Birmingham. It existed from the creation of BR in 1948, ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s, and was wound up at the end of 1992. Territory At its inception, the LMR's territory consisted of ex-LMS lines in England and Wales. The Mersey Railway, which had avoided being "Grouped" with the LMS in 1923, also joined the LMR. The LMR's territory principally consisted of the West Coast Main Line (WCML), the Midland Main Line (MML) south of Carlisle, and the ex-Midland Cross Country route from Bristol to Leeds. During the LMR's existence there were a number of transfers of territory to and from other regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the north-west, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the north-east, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the west and south-west and Cheshire to the west. Kinder Scout, at , is the highest point and Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, the lowest at . The north–south River Derwent is the longest river at . In 2003, the Ordnance Survey named Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms, near Swadlincote, as Britain's furthest point from the sea. Derby is a unitary authority area, but remains part of the ceremonial county. The county was a lot larger than its present coverage, it once extended to the boundaries of the City of Sheffield district in South Yorkshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staveley Central Railway Station
Staveley Central was a railway station serving the town of Staveley, Derbyshire, England. History The station was on the Great Central Main Line which ran between London Marylebone and Manchester via Sheffield Victoria. It was opened on 1 June 1892 as Staveley Town and was renamed Staveley Central on 25 September 1950 by British Railways to reduce confusion with the ex-MR station, also called Staveley Town, which was about 250 yards away on the same street. The latter station was on the Barrow Hill to Clowne and Barrow Hill to Pleasley West lines. The renaming also reduced the likelihood of people confusing the station with that at Barrow Hill and Staveley Works, which was officially renamed Barrow Hill on 18 June 1951 to further differentiate the stations. Staveley Central closed on 4 March 1963, but continued to serve summer weekend excursion traffic until the end of the 1964 season. The station was the northern junction for the loop line to and so had four platform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heath Railway Station
Heath railway station was a railway station in the village of Holmewood, Derbyshire. The station name of Heath was named after the neighbouring village of Heath although the station was in Holmewood instead. The station was just before the Great Central Chesterfield Loop which ran between Staveley Central and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station) on the Great Central Main Line The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railw .... References Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Great Central Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1893 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1963 {{EastMidlands-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
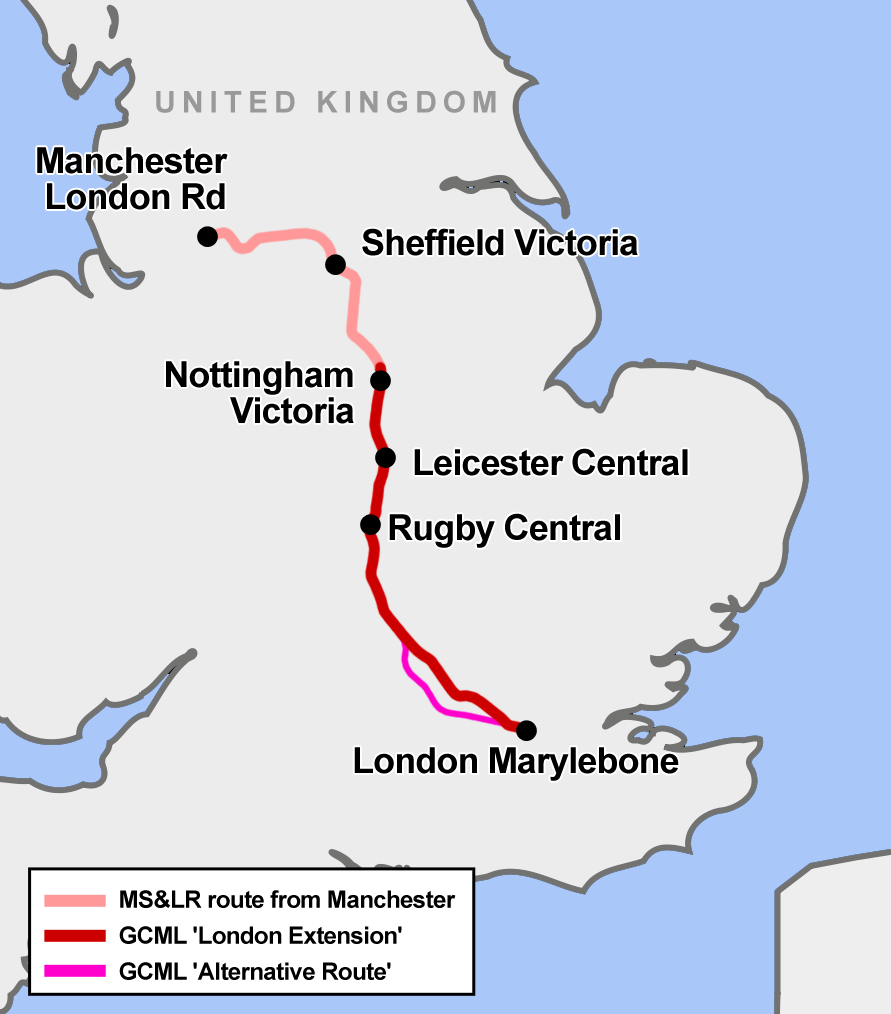
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield Victoria railway station, Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham Victoria railway station, Nottingham and Leicester Central railway station, Leicester to Marylebone station, Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian era, Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheepbridge And Brimington Railway Station
Sheepbridge and Brimington railway station was on the outskirts of the town of Chesterfield, Derbyshire. The station was on the Great Central Chesterfield Loop which ran between Staveley Central and Heath Junction (just north of Heath railway station) on the Great Central Main Line The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railw .... The station opened on 4 June 1892, was renamed to Brimington on 18 June 1951 and closed on 2 January 1956. References Disused railway stations in Derbyshire Former Great Central Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1892 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1956 Buildings and structures in Chesterfield, Derbyshire {{EastMidlands-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |