|
State Of Buenos Aires
The State of Buenos Aires () was a secessionist republic resulting from the overthrow of the Argentine Confederation government in the Province of Buenos Aires on 11 September 1852. The State of Buenos Aires was never explicitly recognized by the Confederation; it remained, however, independent under its own government and constitution. Buenos Aires rejoined the Argentine Confederation after the former's victory at the Battle of Pavón in 1861. Background Regionalism had long marked the relationship among the numerous provinces of what today is Argentina, and the wars of independence did not result in national unity. Following a series of disorders and a short-lived Constitutional Republic led by Buenos Aires centralist Bernardino Rivadavia in 1826 and 1827, the Province of Buenos Aires would function as a semi-independent state amid an internecine civil war. An understanding was entered into by Buenos Aires Governor Juan Manuel de Rosas and other Federalist leaders ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolution Of 11 September 1852
The Revolution of 11 September 1852 was a conflict between the Province of Buenos Aires and the government of Justo José de Urquiza after the latter triumphed over Juan Manuel de Rosas at the Battle of Caseros. A period known as "National Organization" was initiated after the Battle of Caseros. Every political faction agreed on authorizing a national Constitution. However, in opposition to the rest of the country, the ruling upper class in Buenos Aires aspired to impose political requirements on the Argentine provinces, so as to maintain the traditional political and economic preeminence of the capital city. The result was a ten-year separation between the Argentine Confederation and the State of Buenos Aires. Both states claimed to be part of a single nation. But in reality, they behaved like separate states. Background After the Argentine Constitution of 1819, 1819 and Argentine Constitution of 1826, 1826 constitutions failed, rejected by the interior provinces due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
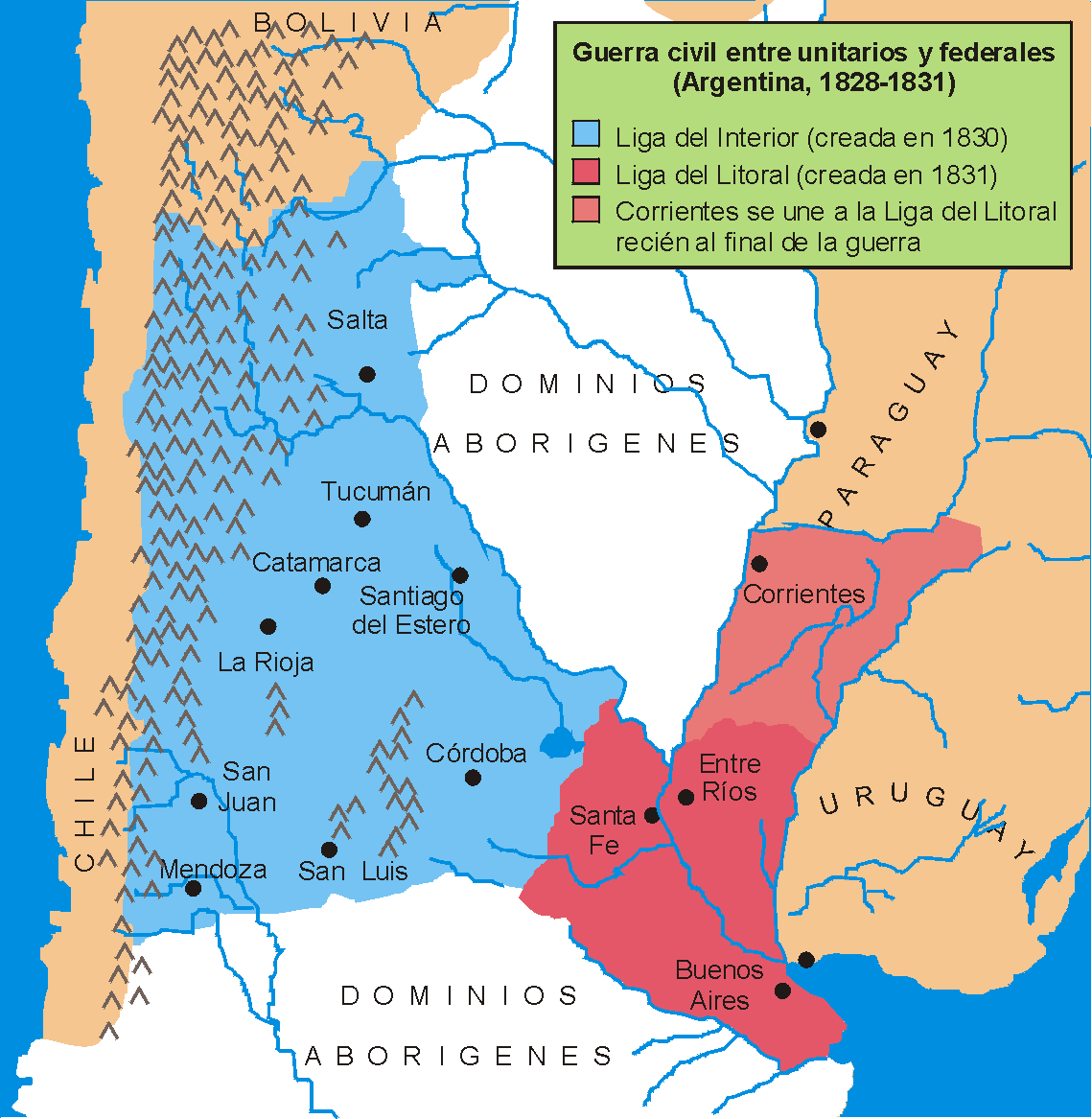
Unitarian League
The Unitarian League () also referred to as the League of the Interior () was a league of provinces of Argentina led by José María Paz, established in 1830, aiming to unite the country under Unitarian Party, unitarian principles. It comprised the provinces of San Luis Province, San Luis, La Rioja Province, Argentina, La Rioja, Catamarca Province, Catamarca, Mendoza Province, Mendoza, San Juan Province, Argentina, San Juan, Tucumán Province, Tucumán, Córdoba Province, Argentina, Córdoba, Salta Province, Salta and Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero. It was opposed and ultimately defeated by the provinces of the Pacto Federal, Federal Pact. Formation After the Cisplatine War, Argentine-Brazilian war, which brought the independence of the Banda Oriental, Banda Oriental del Uruguay, the political situation in the provinces was greatly affected by the disappearance of Bernardino Rivadavia, Rivadavia's Unitarian national government. Due to this the provinces procl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitarian Party
The Unitarian Party was the political party who had proponents the concept of a unitary state (centralized government) in Buenos Aires during the Argentine Civil Wars, civil wars that shortly followed the Declaration of Independence of Argentina in 1816. They were opposed to the Argentine Federales (Argentina), Federalists, who wanted a federation of autonomous provinces. History In the Argentine War of Independence, the forces of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata fought Spain, Spanish royalists who attempted to regain control of their Americas, American colonies after the Napoleonic Wars. After the victorious May Revolution of 1810, disagreements arose between the dominant province of Buenos Aires Province, Buenos Aires, who were known as Unitarianists, and the other provinces of Argentina, known as the Federalists. These were evident at least as early as the declaration of Argentine Declaration of Independence, Argentine independence in 1816. The Unitarianists lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federales (Argentina)
The Federalist Party was the nineteenth century Argentine political party that supported federalism. It opposed the Unitarian Party that claimed a centralised government of Buenos Aires Province, with no participation of the other provinces of Argentina, provinces of the custom taxes benefits of the Buenos Aires port. The ''federales'' supported the autonomy of the provincial governments and the distribution of external commerce taxes among the provinces. The federalists advocated a form of political organization that would ensure coexistence between autonomous provinces and a central government with limited powers. They took as a model the federalism of the United States. The view on the most prominent historical leader of the movement is controversial. Juan Manuel de Rosas is considered by his detractors as a "dictator". Among the various possible ways of characterizing him, his supporters call him a "man of order."http://biblioteca.clacso.edu.ar/clacso/otros/20130610085809/A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Manuel De Rosas
Juan Manuel José Domingo Ortiz de Rozas y López de Osornio (30 March 1793 – 14 March 1877), nicknamed "Restorer of the Laws", was an Argentine politician and army officer who ruled Buenos Aires Province and briefly the Argentine Confederation. Born into a wealthy family, Rosas independently amassed a personal fortune, acquiring large tracts of land in the process. Rosas enlisted his workers in a private army, private militia, as was common for rural proprietors, and took part in the disputes that led to numerous Argentine Civil Wars, civil wars in his country. Victorious in warfare, personally influential, and with vast landholdings and a loyal private army, Rosas became a caudillo, as provincial warlords in the region were known. He eventually reached the rank of brigadier general, the highest in the Argentine Army, and became the undisputed leader of the Federales (Argentina), Federalist Party. In December 1829, Rosas became governor of the province of Buenos Aires and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Civil War
The Argentine Civil Wars were a series of civil conflicts of varying intensity that took place in the territories of Argentina from 1814 to 1853. Beginning concurrently with the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1818), the conflict prevented the formation of a stable governing body until the signing of the Argentine Constitution of 1853, followed by low-frequency skirmishes that ended with the Federalization of Buenos Aires in 1880. The period saw heavy intervention from the Brazilian Empire, which fought against the state and provinces in multiple wars. Breakaway nations, former territories of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, Viceroyalty, such as the Banda Oriental, Paraguay and Bolivia, Upper Peru, were involved to varying degrees. Foreign powers such as the British Empire, British and Second French Empire, French empires put heavy pressure on the fledgling nations during international war. Initially, conflict arose from tensions over the organization and powers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internecine War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.James Fearon"Iraq's Civil War" in ''Foreign Affairs'', March/April 2007. For further discussion on civil war classification, see the section "Formal classification". The term is a calque of Latin which was used to refer to the various civil wars of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. Most modern civil wars involve intervention by outside powers. According to Patrick M. Regan in his book ''Civil Wars and Foreign Powers'' (2000) about two thirds of the 138 intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 saw international intervention. A civil war is often a high-intensity conflict, often involving regular armed forces, that is sustained, organized and large-scale. Civil wars may result in large numbers of casualties and the consum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino Rivadavia
Bernardino de la Trinidad González Rivadavia (May 20, 1780 – September 2, 1845) was the first President of Argentina, then called the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, from February 8, 1826 to June 27, 1827. He was educated at the Colegio Nacional de Buenos Aires, Royal College of San Carlos, but left without finishing his studies. During the British invasions of the River Plate, British Invasions he served as Third Lieutenant of the Galicia Volunteers. He participated in the Cabildo abierto del 22 de mayo de 1810, open Cabildo on May 22, 1810 voting for the deposition of the viceroy. He had a strong influence on the First Triumvirate (Argentina), First Triumvirate and shortly after he served as Minister of Government and Foreign Affairs of the Province of Buenos Aires. Although there was a General Congress intended to draft a constitution, the beginning of the Cisplatine War, War with Brazil led to the immediate establishment of the office of President of Argenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine War Of Independence
The Argentine War of Independence () was a secessionist civil war (until 1816) fought from 1810 to 1818 by Argentine patriotic forces under Manuel Belgrano, Juan José Castelli, Martín Miguel de Güemes, Martin Miguel de Guemes and José de San Martín against Royalist (Spanish American Revolution), royalist forces loyal to the Spanish Empire, Spanish crown. On July 9, 1816, an Congress of Tucumán, assembly met in San Miguel de Tucumán, Argentine Declaration of Independence, declaring independence with provisions for a Constitution of Argentina, national constitution. Background The territory of modern Argentina was part of the Spanish Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, with its capital city in Buenos Aires, seat of government of the Spanish viceroy. Modern Uruguay, Paraguay and Bolivia were also part of the viceroyalty, and began their push for autonomy during the conflict, becoming independent State (polity), states afterwards. The vast area of the territory and slow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, eighth-largest country in the world. Argentina shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a Federation, federal state subdivided into twenty-three Provinces of Argentina, provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and List of cities in Argentina by population, largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a Federalism, federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regionalism (politics)
Regionalism is a political ideology that seeks to increase the political power, influence and self-determination of the people of one or more subnational regions. It focuses on the "development of a political or social system based on one or more" regions, and/or the national, normative, or economic interests of a specific region, group of regions or another subnational entity, gaining strength from or aiming to strengthen the "consciousness of and loyalty to a distinct region with a homogeneous population", similarly to nationalism. More specifically, "regionalism refers to three distinct elements: movements demanding territorial autonomy within unitary states; the organization of the central state on a regional basis for the delivery of its policies including regional development policies; political decentralization and regional autonomy". Regions may be delineated by administrative divisions, culture, language and religion, among others. Regionalists' demands occur in "stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |