|
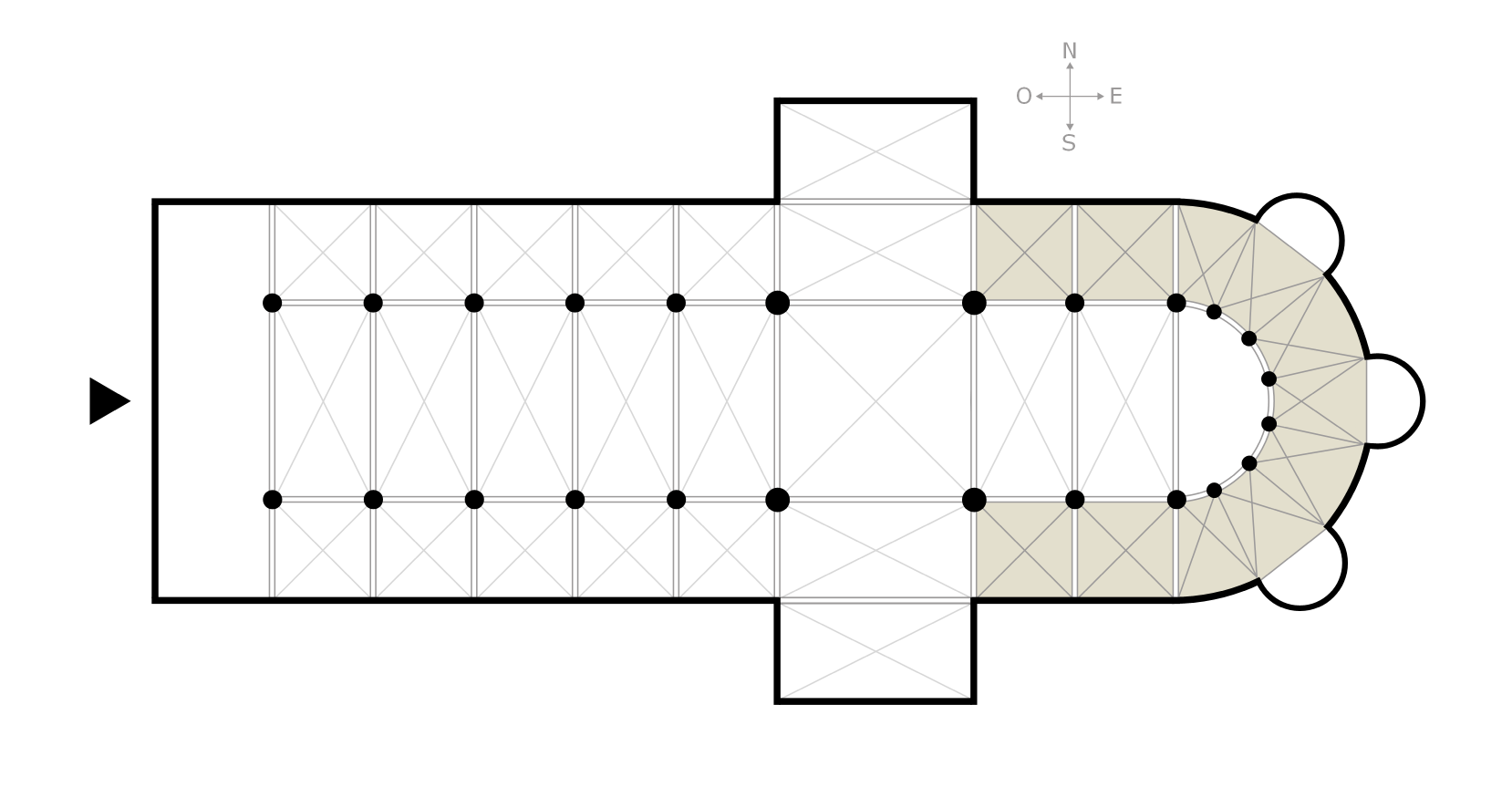
St. Michael's, Hildesheim
The Church of St. Michael (German: ''Michaeliskirche'') is an early- Romanesque church located in Hildesheim, Germany. It has been on the UNESCO World Cultural Heritage list since 1985 due to the before mentioned early-Romanesque architecture and art found within such as the Tree of Jesse and the now relocated Bernward Doors. Following the Protestant reformation, St. Michael's became a shared church, with the majority of the structure being Lutheran and the crypt Roman Catholic. History Bishop Bernward of Hildesheim (996–1022) commissioned this Benedictine monastery to be constructed on a hill linked with the archangel Michael just half a kilometer north of the city walls of his seat in Hildesheim. The structuring of the church began in 1010 and the unfinished monastery was dedicated to the Archangel Michael on archangel's feast day (29 September) in 1022 by Bernward, mere weeks before his death. Along with Bernward's significant influence on the building, layout, and physicalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
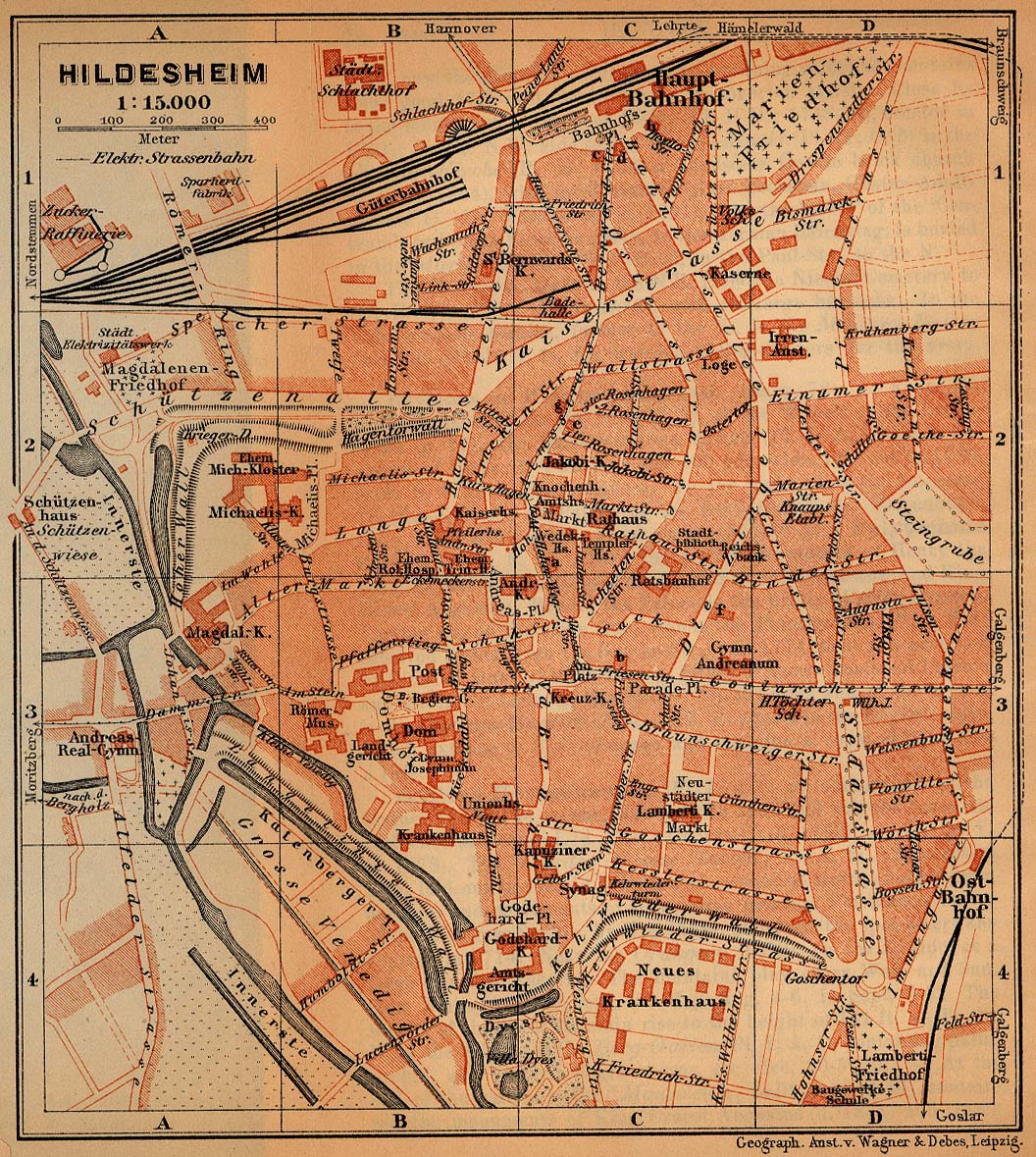
Hildesheim
Hildesheim (; or ; ) is a city in Lower Saxony, in north-central Germany with 101,693 inhabitants. It is in the district of Hildesheim (district), Hildesheim, about southeast of Hanover on the banks of the Innerste River, a small tributary of the Leine River. The Holy Roman Emperor Louis the Pious founded the Bishopric of Hildesheim in 815 and created the first settlement with a chapel on the so-called ''Domhügel''. Hildesheim is situated on the north–south Bundesautobahn 7, Autobahn 7, and hence is connected with Hamburg in the north and Austria in the south. With the Hildesheim Cathedral and the St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim, St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985. In 2015 the city and the diocese celebrated their 1200th anniversary. History Early years According to tradition, the city was named after its founder ''Hildwin''. The city is one of the oldest cities in Northern Germany, became the seat of the Bishopric of Hildes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernward Doors
The Bernward Doors () are the two leaves of a pair of Ottonian or Romanesque bronze doors, made for Hildesheim Cathedral in Germany. They were commissioned by Bishop Bernward of Hildesheim (938–1022). The doors show relief images from the Bible, scenes from the Book of Genesis on the left door and from the life of Jesus on the right door. They are considered a masterpiece of Ottonian art, and feature the oldest known monumental image cycle in German sculpture, and also the oldest cycle of images cast in metal in Germany. History Along with the Bernward Column, the doors are part of Bishop Bernward's efforts to create a cultural ascendancy for the seat of his diocese with artistic masterpieces in the context of the ''Renovatio imperii'' sought by the Ottonians. A Latin inscription on the middle crossbar produced after Bernward's death gives the year 1015 as the terminus ante quem for the creation of the doors: Creation and technical features Each leaf of the doors was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religious relics. Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a church, such as at the Abbey of Saint-Germain en Auxerre, but were later located beneath chancel, naves and transepts as well. Occasionally churches were raised high to accommodate a crypt at the ground level, such as St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim, St Michael's Church in Hildesheim, Germany. Etymology The word "crypt" developed as an alternative form of the Latin "vault" as it was carried over into Late Latin, and came to refer to the ritual rooms found underneath church buildings. It also served as a Bank vault, vault for storing important and/or sacred items. The word "crypta", however, is also the female form of ''crypto'' "hidden". The earliest known origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
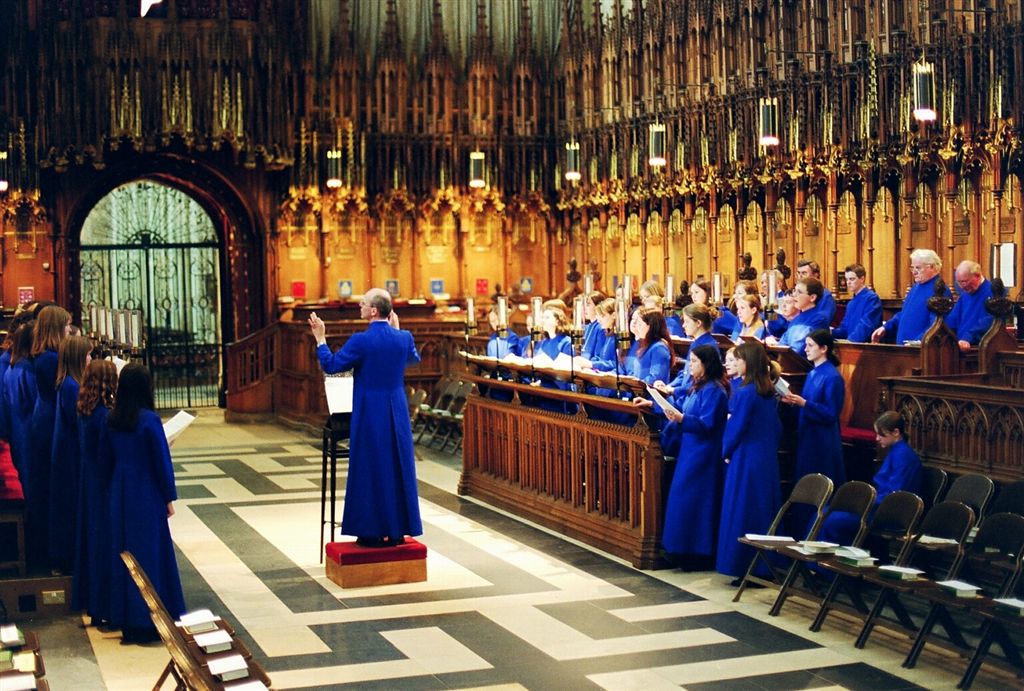
Choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words is the music performed by the ensemble. Choirs may perform music from the classical music repertoire, which spans from the Medieval music, medieval era to the present, or popular music repertoire. Most choirs are led by a conducting, conductor, who leads the performances with arm, hand, and facial gestures. The term ''choir'' is very often applied to groups affiliated with a church (whether or not they actually occupy the Choir (architecture), quire), whereas a ''chorus'' performs in theatres or concert halls, but this distinction is not rigid. Choirs may sing without instruments, or accompanied by a piano, accordion, pipe organ, a small ensemble, or an orchestra. A choir can be a subset of an ensemble; thus one speaks of the "woodwind c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossing (architecture)
A crossing, in ecclesiastical architecture, is the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church. In a typically oriented church (especially of Romanesque and Gothic styles), the crossing gives access to the nave on the west, the transept arms on the north and south, and the choir, as the first part of the chancel, on the east. The crossing is sometimes surmounted by a tower or dome. A large crossing tower is particularly common on English Gothic cathedrals. With the Renaissance, building a dome above the crossing became popular. Because the crossing is open on four sides, the weight of the tower or dome rests heavily on the corners; a stable construction thus required great skill on the part of the builders. In centuries past, it was not uncommon for overambitious crossing towers to collapse. In other cases, the supports had to be reinforced with strainer arches. Sacrist Alan of Walsingham's octagon, built between 1322 and 1328 after the collapse of Ely's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Hildesheim In World War II
The German city of Hildesheim, about south of Hanover, was the target of eight Allies of World War II, Allied Strategic bombing during World War II, air raids in 1944 and 1945 and suffered considerable bomb damage. Hildesheim during World War II In 1939 Hildesheim had about 72,000 inhabitants. For most of the war Hildesheim was regarded as a minor target by RAF Bomber Command, British Bomber Command mainly because the military potential of the industry in and around Hildesheim was underestimated and classified as "relatively small importance in the German war effort." However, a branch of the United German Metalworks (, or VDM) named in the town produced aircraft parts for constant speed propellers, landing gear and aircraft engines, others were producing fuzes and tank parts (Senking-Factory), torpedoes (Ahlborn AG) and rubber products such as Personal flotation device, lifejackets and Inflatable boat, inflatable dinghies (Wetzell Gummiwerke). In the Hildesheim forest southw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Verden
This is a list of bishops, prince-bishops, and administrators of Verden. The Catholic Diocese of Verden (), was a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Mainz. From the 12th century, the Bishop of Verden was also, ''ex officio'', a prince of the Holy Roman Empire and the ruler of a state in imperial immediacy — the Prince-Bishopric of Verden (. The Prince-Bishopric was established in 1180 and disestablished in 1648. The city of Verden upon Aller was the seat of the cathedral and the cathedral chapter. The bishop also resided there until 1195 when the residenz was moved to Rotenburg upon Wümme. Titles of the incumbents of the Verden See Not all incumbents of the Verden See were imperially invested princely power as Prince-Bishops and not all were papally confirmed as bishops. In 1180 part of the Verden diocesan territory were disentangled from the Duchy of Saxony and became an own territory of imperial immediacy called ''Prince-Bishopric of Verden'', a vassal of the Holy Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelog Of Hildesheim
Adelog von Dorstadt (died 20 September 1190) was Bishop of Hildesheim from 1171 until his death. Biography Born into a Saxon noble family, he was a relative of the Lords of Dorstadt. From about 1160 he appeared as a canon at Hildesheim Cathedral and provost of the cathedral chapter in Goslar. In the fierce Hohenstaufen– Welf dispute between Frederick Barbarossa and the Saxon duke Henry the Lion, Bishop Adelog acted cautiously and eventually sided with the emperor. When Henry was deposed in 1180, he achieved nearly independent status. Despite the tensions with the House of Welf, he also worked as diocesan bishop in the residence of Brunswick. Adelog was a builder, overseeing the reconstruction of the St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim after the fire of 1186, the completion of the basilica St. Godehard, Hildesheim, and the construction of the Neuwerk monastery in Goslar. He also sponsored construction of the ''Our Lady Altar'' in Brunswick Cathedral, which he consecrated on 8 Sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Michael
Michael, also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Archangel Michael and Saint Michael the Taxiarch is an archangel and the warrior of God in Christianity, Judaism, and Islam. The earliest surviving mentions of his name are in third- and second-century BC Jewish works, often but not always apocalyptic, where he is the chief of the angels and archangels, and he is the guardian prince of Israel and is responsible for the care of the Israelites, people of Biblical Israel, Israel. Christianity conserved nearly all the Jewish traditions concerning him, and he is mentioned explicitly in Revelation 12:7–12, where he does battle with Satan, and in the Epistle of Jude, where the archangel and the devil dispute over the body of Moses. Old Testament and Apocrypha The Book of Enoch lists him as one of seven archangels (the remaining names are Uriel, Raguel (angel), Raguel, Raphael (archangel), Raphael, Sariel, Gabriel, and Remiel), who, in the Book of Tobit, “stand ready and ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernward Of Hildesheim
Bernward (c. 960 – 20 November 1022) was the thirteenth Bishopric of Hildesheim, Bishop of Hildesheim from 993 until his death in 1022. Life Bernward came from a Saxons, Saxon noble family. His grandfather was Athelbero, Count Palatine of Saxony. Having lost his parents at an early age, he came under the care of his uncle Folcmar (bishop), Volkmar, Bishop of Utrecht, who entrusted his education to Thangmar, learned director of the cathedral school at Heidelberg. Under this master, Bernward made rapid progress in the sciences and in the liberal and even mechanical arts. He became very proficient in mathematics, painting, architecture, and particularly in the manufacture of ecclesiastical vessels and ornaments of silver and gold. He completed his studies at Mainz, where he was ordained priest by Archbishop Willigis, Chancellor of the Empire (975-1011). He declined a valuable preferment in the diocese of his uncle, Bishop Volkmar, and chose to remain with his grandfather, Athel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |