|
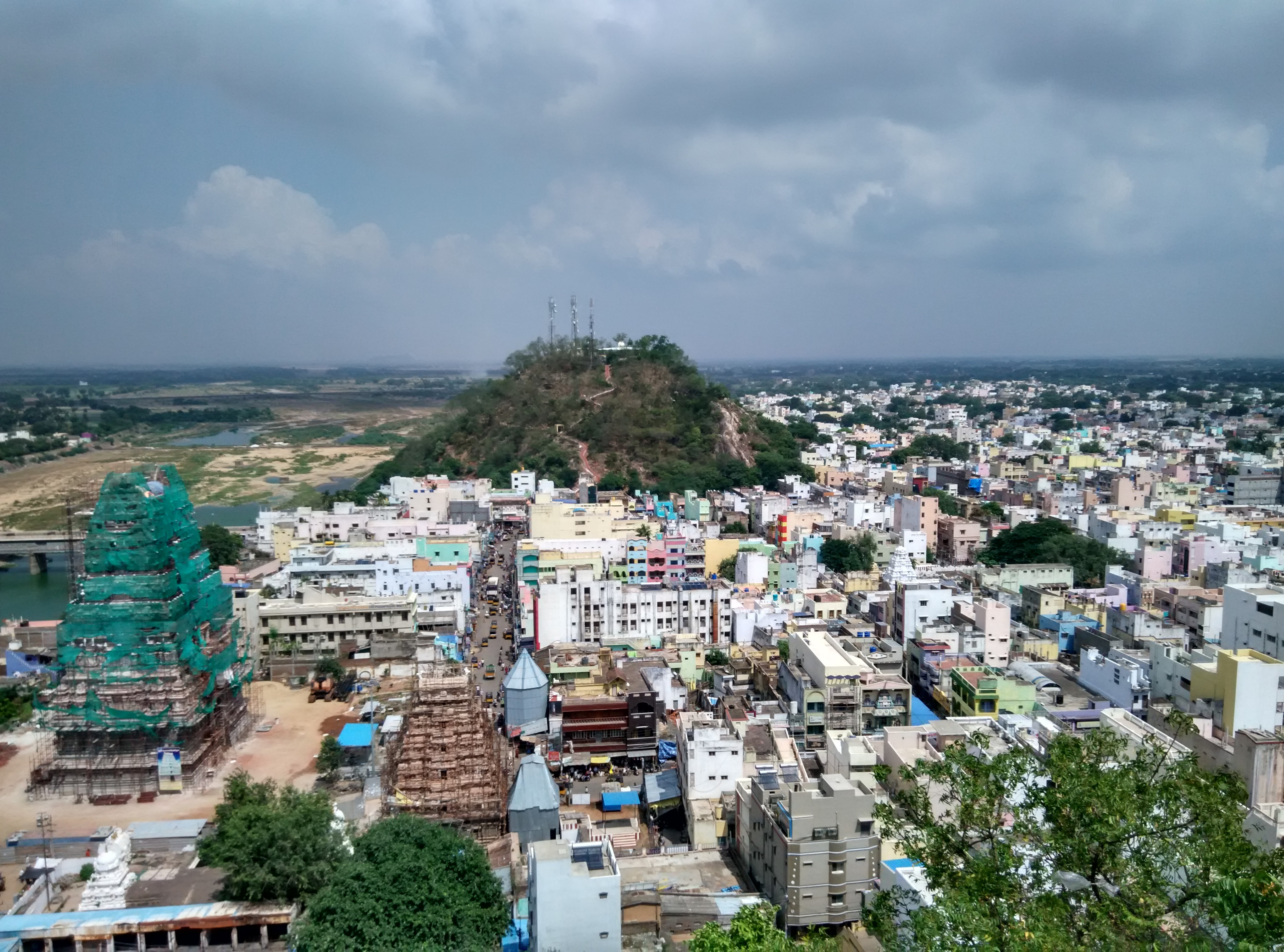
Srikalahasthi - Lord Siva Temple
The Srikalahasti Temple is located in the town of Srikalahasti in Tirupati district in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. Siva in his aspect as Vayu is worshipped as Kalahasteeswara. The temple is also regarded as ''Rahu-Ketu kshetra'' and ''Dakshina Kailasam''. According to regional tradition, it is said to be the site where Kannappa was ready to offer both his eyes to cover blood flowing from the Shivalinga before Shiva stopped him and granted him moksha. Srikalahasti temple, situated 36 km away from Tirupati, is famous for its Vayu Lingam (Wind Lingam), one of the Pancha Bhuta Sthalams, representing the wind. The temple is about 3Km from Sri Kalahasti(KHT) railway station. Legend In primordial times, the wind-god Vayu performed penance for thousands of years to the ''Karpoora Lingam'', the lingam of Shiva made of camphor. Pleased with Vayu's penance, Shiva manifested before him and bestowed him three boons. Vayu was blessed to present everywhere in the world in form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and the List of states and union territories of India by population, tenth-most populous in the country. Telugu language, Telugu is the most widely spoken language in the state, as well as its official language. Amaravati is the state capital, while the largest city is Visakhapatnam. Andhra Pradesh shares borders with Odisha to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the north, Karnataka to the southwest, Tamil Nadu to the south, Telangana to northwest and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the Coastline of Andhra Pradesh, third-longest coastline in India at about . Archaeological evidence indicates that Andhra Pradesh has been continuously inhabited for over 247,000 years, from early archaic Hominini, hominins to Neolithic settlements. The earliest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
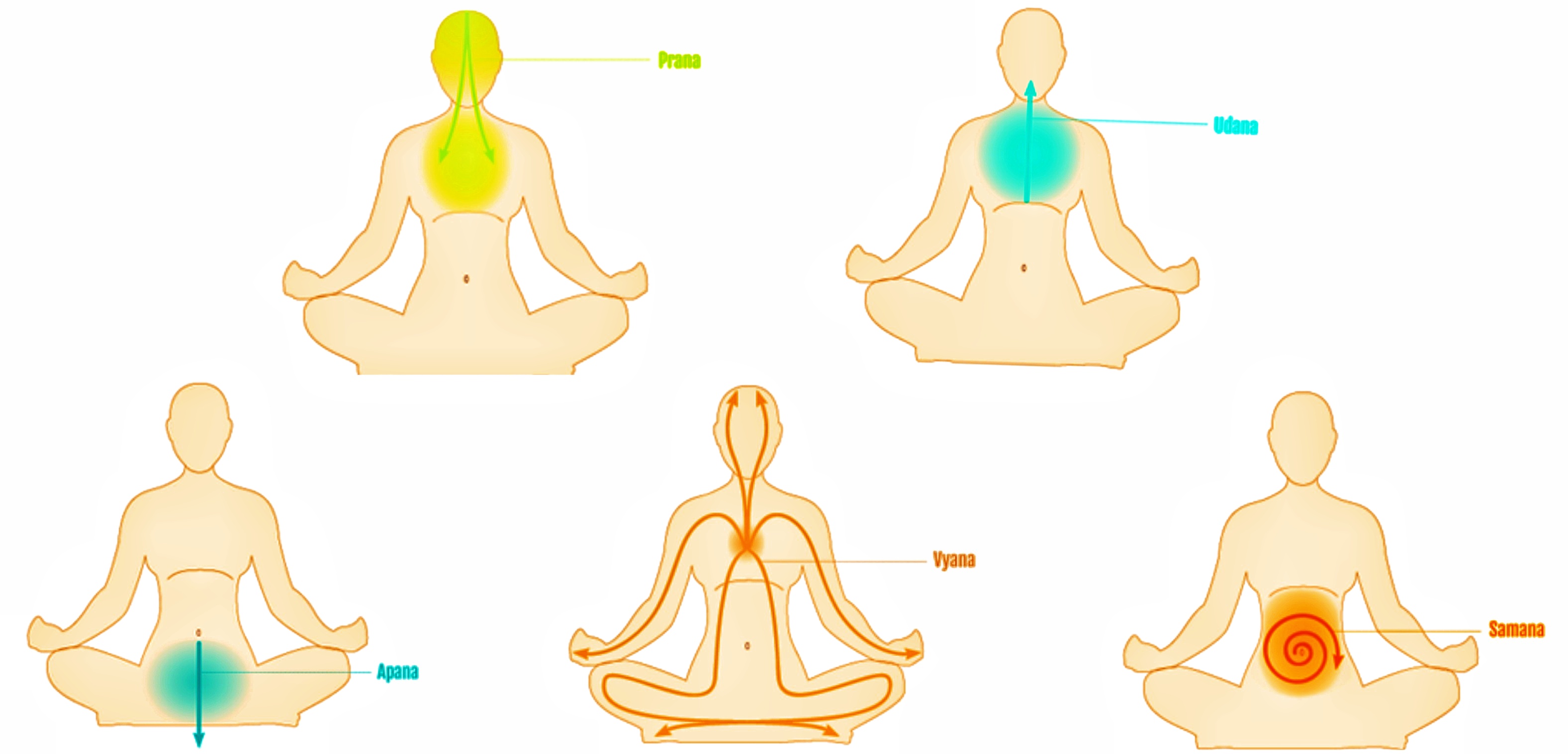
Prana
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
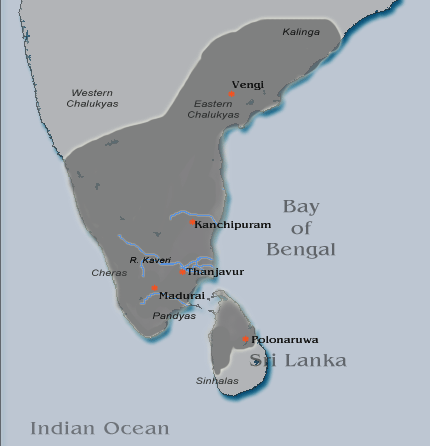
Cholas
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka of the Maurya Empire. The Chola empire was at its peak and achieved imperialism under the Medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera and Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territories until the 13th century CE. The heartland of the Cholas was the fertile valley of the Kaveri River. They ruled a significantly larger area at the height of their power from the latter half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century. They unified peninsular India south of the Tungabhadra River and held the territory as one state for three centuries between 907 and 1215 CE. K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A History of South In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulottunga Chola III
Kulothunga III was a Chola emperor who ruled from to 1218. He ascended the throne after succeeding his elder brother Rajadhiraja II. Kulothunga Chola III gained success in war against his traditional foes. He gained victories in war against the Hoysalas, Pandyas of Madurai, Cheras of Venad, the Sinhalese kings of Polonnaruwa, as well as the Telugu Cholas of Velanadu and Nellore. He also restored Chola control over Karur, which were ruled by the Adigaman chiefs as vassals of the Cholas. He drove out the Hoysalas under Veera Ballala II who had made inroads in the Gangavadi and adjoining areas of Tagadur in Kongu country in an effort expand their territory. However, during the last two years of his reign, he lost in war to the resurgent Pandyas, heralded a period of steady decline and ultimately, demise of the Cholas by 1280 CE. Kulottunga III had alliances with the Hoysalas. The Hoysala king Veera Ballala married a Chola queen called Cholamahadevi and gave his daughter Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajadhiraja Chola I
Rajadhiraja Chola I (994–28 May 1052) was a Chola emperor, as the successor of his father, Rajendra I. He was the only Chola emperor who was killed while leading his army in war, and although he had a short reign, he helped his father conquer several territories as well as to maintain the Chola authority over most of Sri Lanka, Eastern Chalukya and Kalinga, among others. He also established imperial relations with overseas allies despite a series of revolts in the territory. Rajadhiraja Chola proved capable of maintaining the vast and expansive empire with territories even outside the shores of India. Records also show that the king was a skilled commander on the battlefield, leading his soldiers from the front lines. He earned the title ''Jayamkonda Solan'' (The Victorious Cholan) after numerous victories. Towards the end of his reign, he sacked the Western Chalukyan capital Kalyanapuram and assumed the title ''Kalyanapuramkonda Chola'' and performed a Virabhisheka (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajaraja Chola I
Rajaraja I (Middle Tamil: ''Rājarāja Cōḻaṉ''; Classical Sanskrit: ''Rājarāja Śōḷa''; 3 November 947 – January/February 1014), also known as Rajaraja the Great, was a Chola Empire, Chola emperor who reigned from 985 to 1014. He was known for his conquests of South India, southern India and Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka, as well as increasing Chola influence across the Indian Ocean. Rajaraja's birth name is variously given as Arul Mozhi Varman and Arul Moli Varman. Rajaraja's empire encompassed vast territories, including regions of the Pandya dynasty, Pandya country, the Chera dynasty, Chera country, and northern Sri Lanka. He also extended his influence over strategic islands such as Lakshadweep, Thailand, Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and parts of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. His conquests weren't limited to the south; he also launched successful campaigns against the Western Ganga dynasty, Western Gangas and the Western Chalukya Empire, Western Chalukyas, ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajaditya Chola
Rajaditya Chola (''fl.'' mid-10th century AD) was a Chola prince, son of king Parantaka I (r. 907–955) and a Chera princess ( Ko Kizhan AdigalNarayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala.'' Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 96-100.), known for commanding the Chola troops in the battle of Takkolam (948–949).Ali, Daud. "The Death of a Friend: Companionship, Loyalty and Affiliation in Chola South India." ''Studies in History'', vol. 33, no. 1, Feb. 2017, pp. 36–60. The death of prince Rajaditya in the battle is unusually commemorated by the Cholas. The Chola version of the events can be found in Larger Leiden Grant (1006 AD) of Rajaraja I and Tiruvalangadu Plates (1018 AD) of Rajendra Chola. An account of the battle, which differs in some details from the Chola version, is found in the Atakur inscription issued by Krishna III and prince Butuga II (a young underlord of Krishna III) of the Western Ganga family.''Epigraphia Indica'' 6 (1900–01), no. 6c: 53–56. The Srava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulottunga Chola I
Kulottunga Chola I ('; Middle Tamil: Kulōttuṅka Cōḻaṉ; Classical Sanskrit: Kulottuṅgā Cōḷa; 1025–1122) also spelt Kulothunga (), born Rajendra Chalukya ( Telugu: Rājēndra Cāḷukyuḍu), was a Chola Emperor who reigned from 1070 to 1122 succeeding his cousin Athirajendra Chola. He also served as the Eastern Chalukya monarch from 1061 to 1118, succeeding his father Rajaraja Narendra. He is related to the Chola dynasty through his mother's side and the Eastern Chalukyas through his father's side. His mother, Ammangaidevi, was a Chola princess and the daughter of emperor Rajendra Chola I. His father was king Rajaraja Narendra of the Eastern Chalukya dynasty who was the nephew of Rajendra and maternal grandson of Rajaraja Chola I. According to historian Sailendra Nath Sen, his accession marked the beginning of a new era and ushered in a period of internal peace and benevolent administration. He was succeeded by his son Vikrama Chola. Kulottunga had diplomatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimurti
The Trimurti ( /t̪ɾimʊɾt̪iː/) is the triple deity of supreme divinity in Hinduism, in which the cosmic functions of creation, preservation, and destruction are personified as a triad of deities. Typically, the designations are that of Brahma the creator, Vishnu the preserver, and Shiva the destroyer. The Om symbol of Hinduism is considered to have an allusion to Trimurti, where the A, U, and M phonemes of the word are considered to indicate creation, preservation and destruction, adding up to represent Brahman. The Tridevi is the trinity of goddess consorts for the Trimurti. Evolution The Puranic period from the 4th to the 12th century CE saw the rise of post-Vedic religion and the evolution of what R. C. Majumdar calls "synthetic Hinduism." Following is a well-known verse from the Vishnu Purana (1.2.66) that mentions Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva together in a single verse, highlighting their roles within the cosmic functions of creation, preservation, and destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markandeya
Markandeya () is a rishi (sage) featured in Hindu literature. He is the son of the sage Mrikanda and his wife, Manasvini. The Markandeya Purana (one of the eighteen Mahāpurāṇas in Hinduism), attributed to the sage, comprises a dialogue between Markandeya and a sage called Jaimini. A number of chapters in the Bhagavata Purana are dedicated to his conversations and prayers. He is also mentioned in the Mahabharata. Markandeya is venerated within all mainstream Hindu traditions. Legend Rescue by Kalantaka-Shiva One legend relates the story of how Shiva, one of the main deities of Hinduism, protected Markandeya from the clutches of death, personified as Yama. Sage Mrikanda performed penance to propitiate Shiva for several years and sought from him the boon of begetting a son. Shiva offered him the choice of either a virtuous and pious son who would have a short life, or a dull-witted, malicious child who would have a long life. Mrikanda chose the former, and was bles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. [3 volumes] Indra is the most frequently mentioned deity in the ''Rigveda''. He is celebrated for his powers based on his status as a god of order, and as the one who killed the great evil, an Asura (Hinduism), asura named Vritra, who obstructed human prosperity and happiness. Indra destroys Vritra and his "deceiving forces", and thereby brings rain and sunshine as the saviour of mankind. Indra's significance diminishes in the post-Vedic Indian literature, but he still plays an important role in various mythological events. He is depicted as a powerful hero. According to the ''Vishnu Purana'', Indra is the title borne by the king of the gods, which changes every Manvantara – a cyclic period of time in Hindu cosmology. Each Manvantara has its own Indra and the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |