|
Sprachbund
A sprachbund (, from , 'language federation'), also known as a linguistic area, area of linguistic convergence, or diffusion area, is a group of languages that share areal features resulting from geographical proximity and language contact. The languages may be genetically unrelated, or only distantly related, but the sprachbund characteristics might give a false appearance of relatedness. A grouping of languages that share features can only be defined as a sprachbund if the features are shared for some reason other than the genetic history of the languages. Without knowledge of the history of a regional group of similar languages, it may be difficult to determine whether sharing indicates a language family or a sprachbund. History In a 1904 paper, Jan Baudouin de Courtenay emphasised the need to distinguish between language similarities arising from a genetic relationship (''rodstvo'') and those arising from convergence due to language contact (''srodstvo''). Nikolai Trub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Relatedness Of Languages
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term ''family'' is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the ''daughter languages'' within a language family as being ''genetically related''. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time. One well-known example of a language family is the Romance languages, including Spanish language, Spanish, French language, French, Italian language, Italian, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Romanian language, Romanian, Catalan language, Catalan, and many others, all of which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Convergence
Language convergence is a type of linguistic change in which languages come to resemble one another structurally as a result of prolonged language contact and mutual interference, regardless of whether those languages belong to the same language family, i.e. stem from a common genealogical proto-language. In contrast to other contact-induced language changes like Creole language, creolization or the formation of Mixed language, mixed languages, convergence refers to a mutual process that results in changes in all the languages involved. The term refers to changes in systematic linguistic patterns of the languages in contact (phonology, prosody (linguistics), prosody, syntax, morphology (linguistics), morphology) rather than alterations of individual lexical items. Contexts Language convergence occurs in geographic areas with two or more languages in contact, resulting in groups of languages with similar linguistic features that were not inherited from each language's proto-lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Language
Albanian (Endonym and exonym, endonym: , , or ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the only surviving representative of the Albanoid, Albanoid branch, which belongs to the Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan group. It is the native language of the Albanian people. Standard Albanian is the official language of Albania and Kosovo, and a co-official language in North Macedonia and Montenegro, where it is the primary language of significant Albanian minority communities. Albanian is recognized as a minority language in Italy, Croatia, Romania, and Serbia. It is also spoken in Greece and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. Albanian is estimated to have as many as 7.5 million native speakers. Albanian and other Paleo-Balkan languages had their formative core in the Balkans after the Indo-European migrations in the region. Albanian in antiquity is often thought to have been an Illyrian language for ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areal Feature
In geolinguistics, areal features are elements shared by languages or dialects in a geographic area, particularly when such features are not descended from a common ancestor or proto-language. An areal feature is contrasted with genetic relationship determined similarity within the same language family. Features may diffuse from one dominant language to neighbouring languages (see "sprachbund"). Genetic relationships are represented in the family tree model of language change, and areal relationships are represented in the wave model. Characteristics Resemblances between two or more languages (whether in typology or in vocabulary) have been observed to result from several mechanisms, including lingual genealogical relation (descent from a common ancestor language, not principally related to biological genetics); borrowing between languages; retention of features when a population adopts a new language; and chance coincidence. When little or no direct documentation of ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprachraum
In linguistics, a sprachraum (; , "language area", plural sprachräume, ) is a geographical region where a common first language (mother tongue), with dialect varieties, or group of languages is spoken. Characteristics Many sprachräume are separated by national borders, whilst others are separated by oceans or ethnolinguistic boundaries. The five major Western sprachräume (by number of speakers) are those of English, Spanish, French, Portuguese, and German. The English Sprachraum (Anglosphere) spans the globe from the United Kingdom, Ireland, United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand to the many former British and American colonies in which English has official language status alongside local languages, such as India, South Africa, and the Philippines. The Spanish Sprachraum, known as the Hispanosphere, originated in the Iberian Peninsula but today most Spanish speakers are in Hispanic America. Of all countries with a majority of Spanish speakers, only Spain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprechbund
A Sprechbund (; , "speech bond") is a "shared ayof speaking which oesbeyond language boundaries" (Romaine, 1994:23). Thus people speaking different languages can share certain linguistic characteristics. This is a particularly useful concept for describing, for example, hip-hop music. Hip-hop has a number of defining characteristics including musical style, clothing, and association with minorities. It also has a number of defining linguistic characteristics like rapping, rhyme and human beatboxing. These are essentially linguistic features, but they can be used in any language – even genetically unrelated languages. Their combined use in different languages allows a kind of universal "language of hip-hop". The sprechbund is to be contrasted with the sprachbund A sprachbund (, from , 'language federation'), also known as a linguistic area, area of linguistic convergence, or diffusion area, is a group of languages that share areal features resulting from geographical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Tibetan Languages
Sino-Tibetan (also referred to as Trans-Himalayan) is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Sinitic languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese (33 million) and the Tibetic languages (6 million). Four United Nations member states (China, Singapore, Myanmar, and Bhutan) have a Sino-Tibetan language as a main native language. Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented. Several low-level subgroups have been securely reconstructed, but reconstruction of a proto-language for the family as a whole is still at an early stage, so the higher-level structure of Sino-Tibetan re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
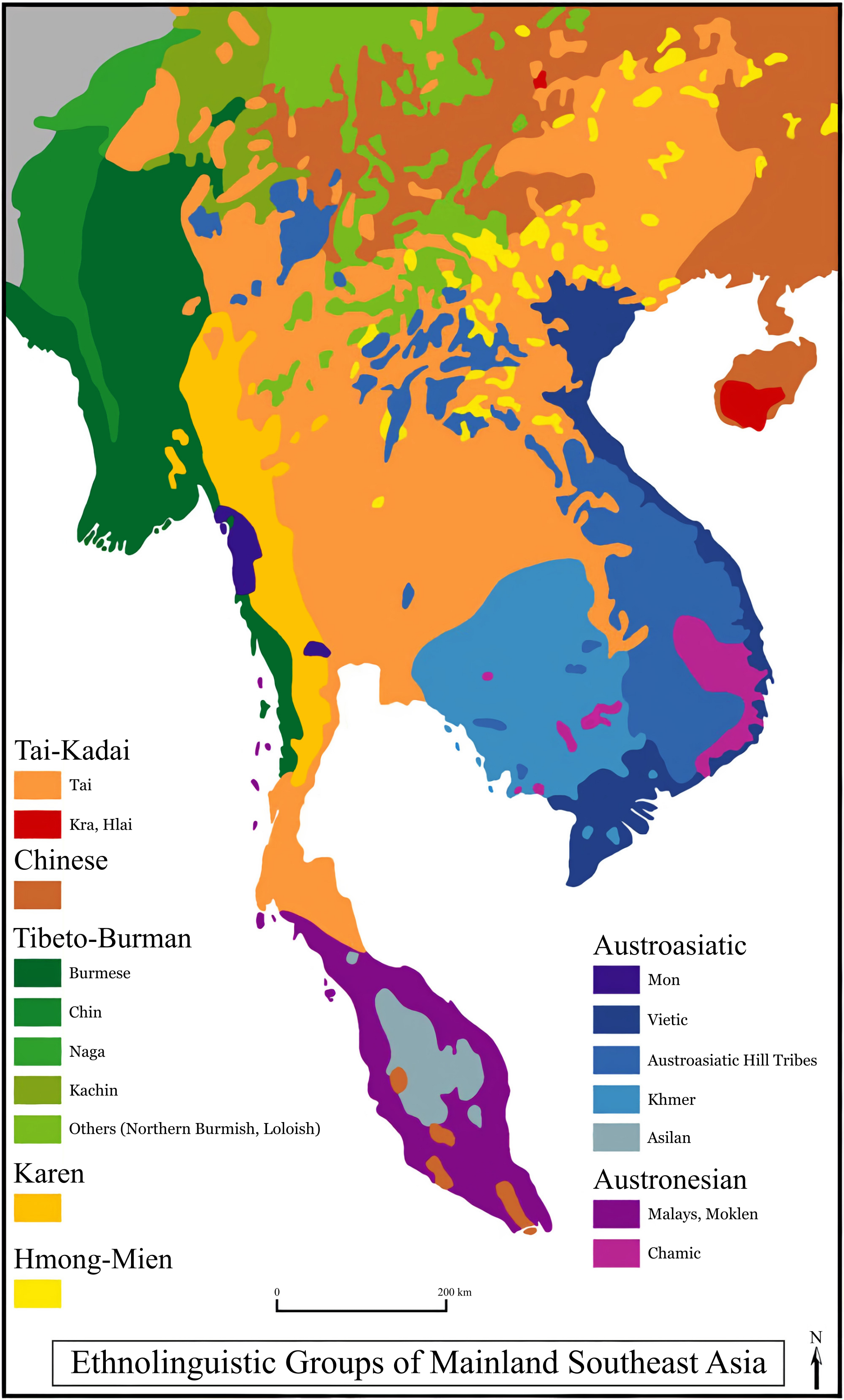
Mainland Southeast Asia Linguistic Area
The Mainland Southeast Asia linguistic area is a sprachbund including languages of the Sino-Tibetan, Hmong–Mien (or Miao–Yao), Kra–Dai, Austronesian and Austroasiatic families spoken in an area stretching from Thailand to China. Neighbouring languages across these families, though presumed unrelated, often have similar typological features, which are believed to have spread by diffusion. James Matisoff referred to this area as the "Sinosphere", contrasted with the " Indosphere", but viewed it as a zone of mutual influence in the ancient period. Language distribution The Austroasiatic languages include Vietnamese and Khmer, as well as many other languages spoken in scattered pockets as far afield as Malaya and eastern India. Most linguists believe that Austroasiatic languages once ranged continuously across southeast Asia and that their scattered distribution today is the result of the subsequent migration of speakers of other language groups from southern China. Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Language
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Italo-Western languages, Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called ''#Dialects, Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Romanians in Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Romanians in Hungary, Hungary, Romanians in Serbia, Serbia and Romanians in Ukraine, Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing system, writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Contact
Language contact occurs when speakers of two or more languages or varieties interact with and influence each other. The study of language contact is called contact linguistics. Language contact can occur at language borders, between adstratum languages, or as the result of migration, with an intrusive language acting as either a superstratum or a substratum. When speakers of different languages interact closely, it is typical for their languages to influence each other. Intensive language contact may result in language convergence or relexification. In some cases a new contact language may be created as a result of the influence, such as a pidgin, creole, or mixed language. In many other cases, contact between speakers occurs with smaller-scale lasting effects on the language; these may include the borrowing of loanwords, calques, or other types of linguistic material. Multilingualism has been common throughout much of human history, and today most people in the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |