|
Spessart Ramp
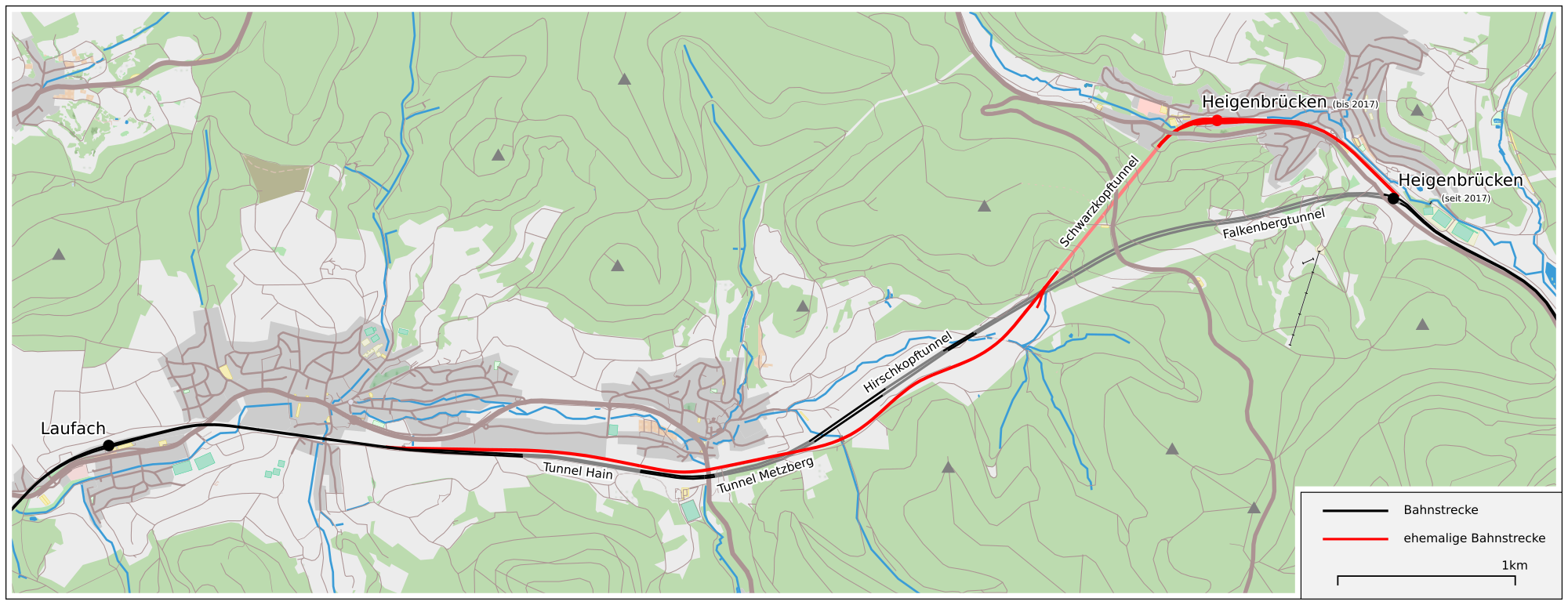
The Spessart Ramp () is a 5.4 km long incline on the Main-Spessart Railway in southern Germany between Laufach at one end and the Schwarzkopf tunnel and Heigenbrücken at the other, with an average incline of 20 ‰. The ramp is part of Ludwig's Western Railway and the section from Würzburg via Aschaffenburg to the state border at Kahl am Main was opened on 1 October 1854 by the Royal Bavarian State Railways. The ramp enabled the difference in height between the Laufach valley and the Lohr valley to be overcome as it crossed the Spessart between Kahl am Main and Aschaffenburg on the one side and Würzburg/Bamberg on the other. In keeping with the philosophy for railway construction at that time it was decided that the way to cope with large differences in height was the construction of a relatively short, steep section of line and to haul trains up the incline with the aid of banking locomotives, whilst the remaining section of the route could be made relatively level. A st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marktschorgast
Marktschorgast is a municipality in the district of Kulmbach in Bavaria in Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... City arrangement Marktschorgast is arranged in the following boroughs: References Kulmbach (district) {{Kulmbachdistrict-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisenbahn-Revue International
''Schweizer Eisenbahn-Revue (SER)'' () is a Swiss trade journal for the rail transport industry. History and profile Appearing monthly since 1978, the SER is written by correspondents (some writing anonymously) in rail transport companies, in the industry and in government. Each issue consists of four parts: reports from Switzerland, reports from other European countries, international reports and a number of articles covering current topics on one or two pages each. The editorial line is frequently critical of the Swiss state railways and its government regulators. The SER is published by ''Minirex AG'', a Lucerne-based publisher of railway books, and edited by Minirex owner Walter von Andrian. Minirex also publishes three sister publications of the SER, which share some of its content: ''Eisenbahn Österreich (EBÖ)'' and ''Schienenverkehr aktuell'', both covering Austria, ''Eisenbahn-Revue International (ERI)'', dedicated to international matters, and ''Railway Update'', a bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ÖBB
The Austrian Federal Railways ( , formally or () and formerly the or ''BBÖ'' ), now commonly known as ÖBB (), is the national railway company of Austria, and the administrator of Liechtenstein's railways. The ÖBB group is owned entirely by the Republic of Austria, and is divided into several separate businesses that manage the infrastructure and operate passenger and freight services. The Austrian Federal Railways has had two discrete periods of existence. It was first formed in 1923, using the ''Bundesbahn Österreich'' name, as a successor to the Imperial Royal Austrian State Railways (kkStB), but was incorporated into the ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' during the 1938–1945 Anschluss. It was reformed in 1947, under the slightly different name ''Österreichische Bundesbahnen'', and remains in existence in this form. Major changes currently being made to the Austrian railway network are the construction of the Koralm Railway, the Semmering Base Tunnel and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Bahn
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). DB was founded after the merger between Deutsche Bundesbahn and the East German Deutsche Reichsbahn in 1994 after the unification of Germany and has been operating ever since. is the second-largest transport company in Germany, after the German postal and logistics company / DHL. DB provides both long-distance and regional transport, serving around 132 million long distance passengers and 1.6 billion regional passengers in 2022. In 2022, DB transported 222 million tons of cargo. Company profile The group is divided into several companies, including '' DB Fernverkehr'' (long-distance passenger), '' DB Regio'' (local passenger services) and '' DB Cargo'' (rail freight). The Group subsidiary '' DB InfraGO'' also operates large parts of the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Class 151
The Class 151 is an electric heavy freight locomotive built for German Federal Railways between 1972 and 1978. They were built as a replacement for the ageing Class 150, in order to cope with the increased requirements of this type of locomotive, in particular the desire of a top speed. Locomotives of Hector Rail are designated as Class 162. Technical specifications The locomotives have a Co-Co wheel arrangement, and a weight of . History On 21 November 1972 the first locomotive, 151 001, was delivered by AEG and Krupp Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer dur .... It was followed by 11 further pilot locomotives, which were extensively tested before the main order was built. Altogether 170 locomotives were built. Originally the Class 151 locomotives were also suitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Class 150
The Class E 50 is an electric heavy freight locomotive built for Deutsche Bundesbahn, German Federal Railways between 1957 and 1973. It belongs to the ''Einheits-Elektrolokomotiven'' (standardised electric locomotives) program and was built as a heavy freight mover to be used on the increasingly electrified main lines of the DB, where they were set to replace the steam traction. In 1968 the series was redesignated as class 150 (E50). Originally the Class 150 was also suitable for passenger service; however, it did not have any steam or electric heating capability for the passenger coaches. Production In 1957 the first locomotive, 150 001, was delivered by AEG (German company), AEG and Krupp. Altogether, 194 locomotives were ordered and delivered. Performance To date, the Class 150's starting tractive effort of remains unparalleled on German rails. In fact, it was very close to the breaking force of the buffers and chain couplers used at the time of its production. Some en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class E 94
The DRG Class E94 is an electric heavy freight locomotive built for Deutsche Reichsbahn from 1940, with the bulk of deliveries taking place in that year. It was a major evolution of the DRG Class E 93. Railway aficionados still call the type "Grünes Krokodil" (Green Crocodile) because of the resemblance to the Swiss locomotive nicknamed "Crocodile". Production 146 units were built until the end of the Second World War, as it was considered important for the war effort. They were classified as KEL 2 during that time period. After World War II, a further 49 units were ordered by the Deutsche Bundesbahn and delivered as late as 1957. The final 23 units had their power rating increased to . From 1968, the top speed of these locomotives was raised to , and were reclassified as E 94.2, later Class 194.5, due to several technical differences. Transfers to ÖBB and DR After the war, 44 units were placed under the authority of the Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB). In 1952, the ÖBB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian T 20
The German DRG Class 95 are ten-coupled tank locomotives with a 2-10-2 wheel arrangement, which were procured by the Deutsche Reichsbahn (also referred to later as the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft or ''DRG'') in 1922 for hauling heavy goods trains on steep main lines. Because the development of this class was started by the Prussian state railways, it was designated as the Prussian Class T 20. History The first ten locomotives built in 1922 were ordered as ''T 20 Magdeburg 9201–9210'', and because they were at first intended to be grouped into Class 77, were supplied as numbers 77 001 to 77 010. By 1923, they had been renumbered to 95 001–010. A total of 45 locomotives were built by 1924. Their areas of operations included the Sonneberg–Probstzella line, the Spessart ramp, the Franconian Forest Railway, the Geislingen ramp (''Geislinger Steige''), the Schiefe Ebene and the Rübeland Railway, where they earned their nickname ''Bergkönigin'' ('mountain queen' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian T 16
The Prussian T16 locomotives were ten-coupled superheated freight tank locomotives of the Prussian State Railways. They were later renumbered in the 94.2–4 by Deutsche Reichsbahn History The development of the T16 locomotives was influenced by the ideas of Karl Gölsdorf. The design included three Gölsdorf axles – the first, third, and fifth – and enabled elimination of the articulated frame that had been used on the Prussian T 15. While mainly bought for banking trains up steep gradients, they were also used for freight trains and shunting. They proved to be more powerful and economical than the T 15 class. Between 1905 and 1913, 343 T 16 locomotives were built by Berliner Maschinenbau for the Prussian State Railways, and 12 by Elsässische Maschinenbau-Gesellschaft Grafenstaden for the Imperial Railways in Alsace-Lorraine. During construction, some design changes were made; for example the drive was moved from the fourth axle to the third in order to reduce the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Gt 2x4/4
Bavarian is the adjective form of the German state of Bavaria, and refers to people of ancestry from Bavaria. Bavarian may also refer to: * Bavarii, a Germanic tribe * Bavarians, a nation and ethnographic group of Germans * Bavarian, Iran, a village in Fars Province * Bavarian language, a West Germanic language See also * * Bavaria (other) Bavaria may refer to: Places Germany * Bavaria, one of the 16 federal states of Germany * Duchy of Bavaria (–1805) * Electorate of Bavaria (1623–1805) * Kingdom of Bavaria (1805–1918) * Bavarian Soviet Republic (1919), a short-lived communi ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |