|
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet (built with Persian subsidies) finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. The first phase (431–421 BC) was named the Ten Years War, or the Archidamian War, after the Spartan king Archidamus II, who invaded Attica several times with the full hoplite army of the Peloponnesian League, the alliance network dominated by Sparta (then known as Lacedaemon). The Long Walls of Athens rendered this strategy ineffective, while the superior navy of the Delian League (Athens' all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Polis, Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Graeco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the naval Battle of Artemisium: between July and September during 480 BC. The second Persians, Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion of Greece, first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius the Great, Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Classical Athens, Athenian-led Ancient Greece, Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Greece, Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nabis Of Sparta
Nabis () was the last king of independent Sparta. He was probably a member of the Heracleidae, and he ruled from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First Macedonian War, First and Second Macedonian Wars and the "War against Nabis" named for being against him. After taking the throne by executing two claimants, he began rebuilding Sparta's power. During the Second Macedonian War, Nabis sided with King Philip V of Macedon and in return he received the city of Ancient Argos, Argos. However, when the war began to turn against the Macedonians, he defected to Rome. After the war, the Romans, urged by the Achaean League, attacked Nabis and defeated him. He then was assassinated in 192 BC by the Aetolian League. He represented the last phase of Sparta's reformist period. Sources Nabis is cited by many ancient authors: Livy, Plutarch, Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias, Diodorus Siculus, Diodorus of Sicily, Justin (historian), Justin, Eutropius (historian), Eutropius and Joannes Zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
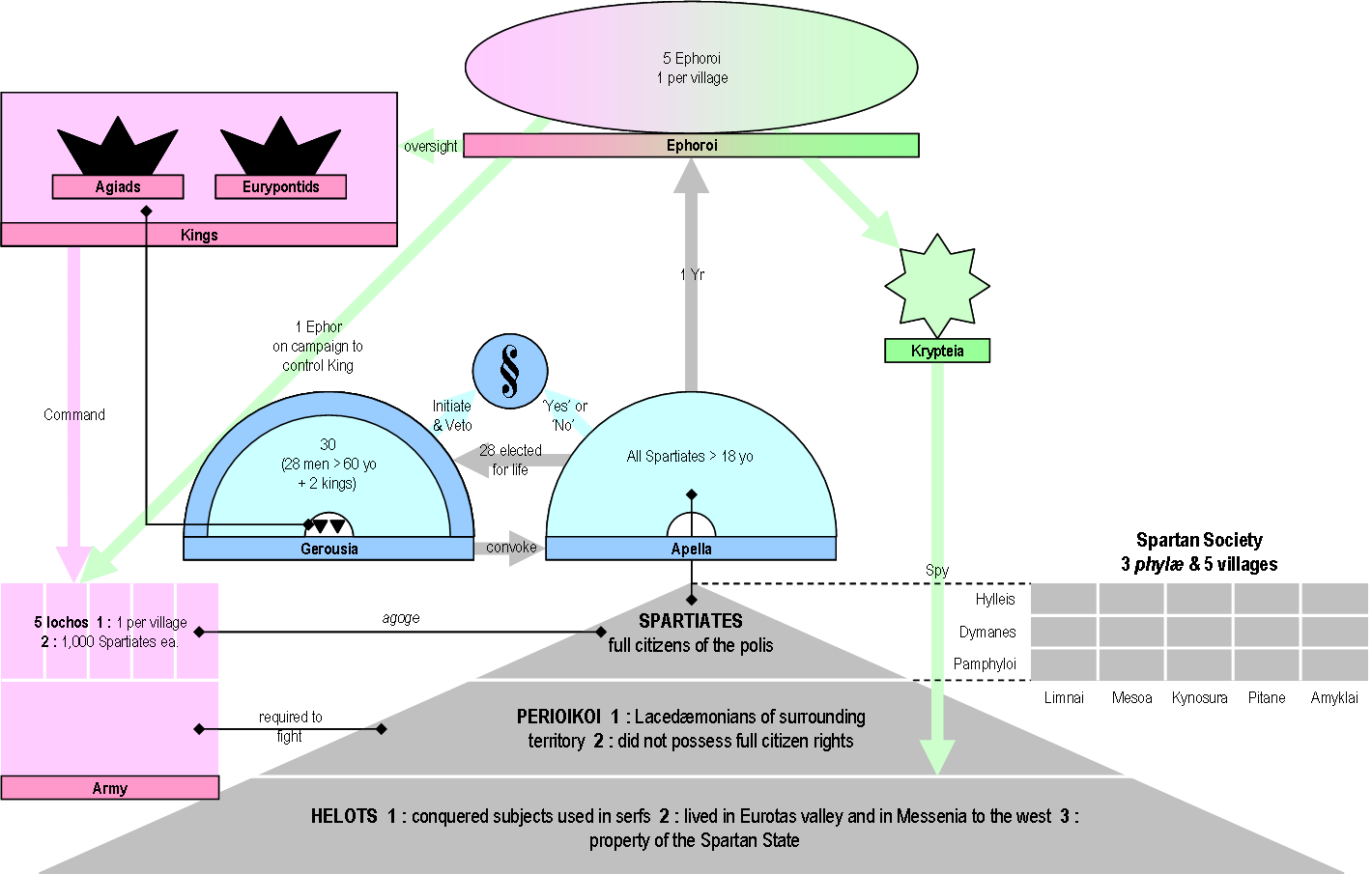
Ephors
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
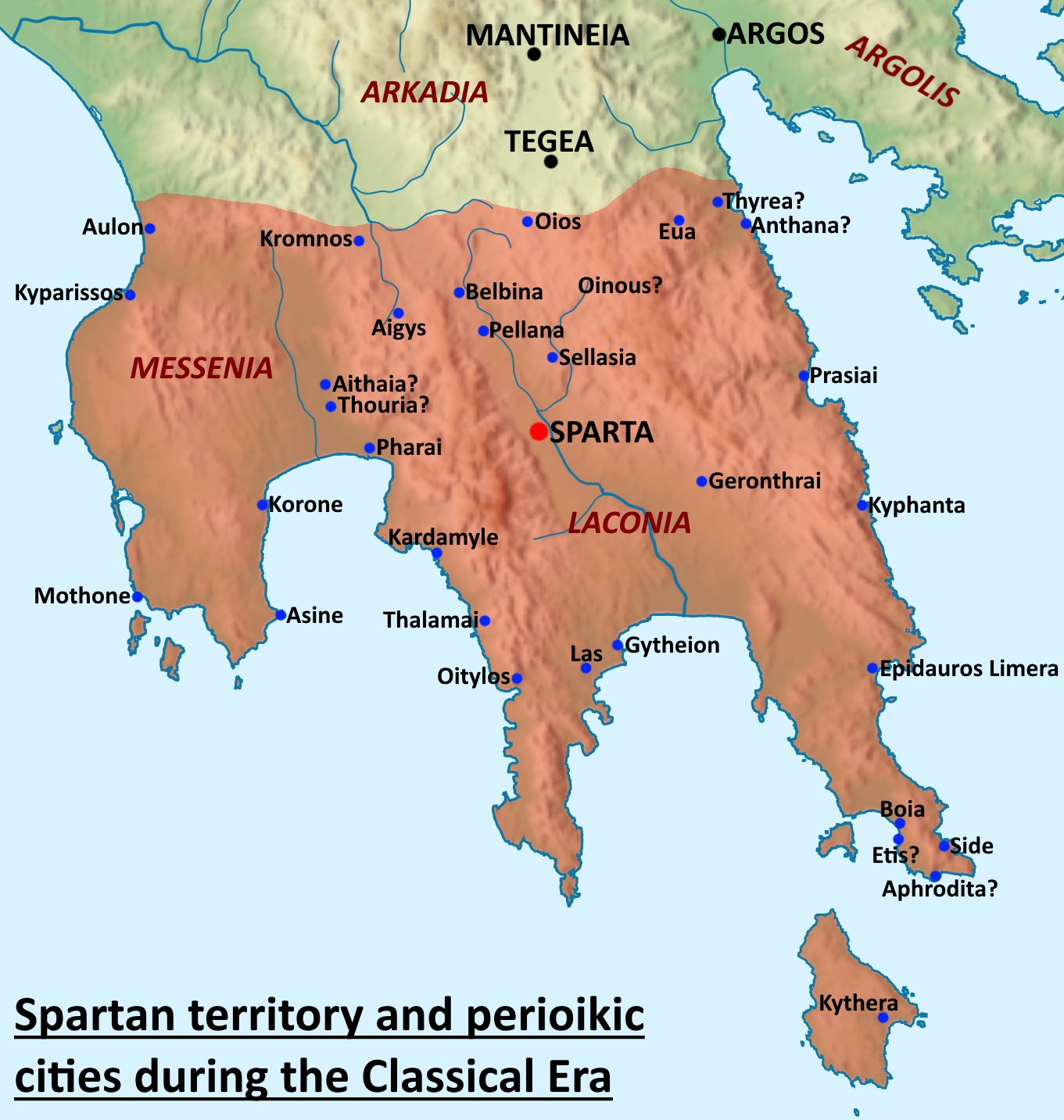
Sparta, Laconia
Sparta (, ) is a city and municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta within the Evrotas Valley. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population (as of 2021) of 32,786, of whom 17,773 lived in the city. History Beginning in the 13th century, the political and cultural center of Laconia shifted to Mystras, some 4 km to the west. The settlement at ancient Sparta, named Lacedaemonia, continued to exist, although greatly depopulated, until modern times as a town of a few thousand people who lived among the ruins, in the shadow of Mystras. The Palaiologos family (the last Byzantine Greek imperial dynasty) also lived in Mystras. The Despotate of the Morea was captured by the Ottomans under Mehmed II in 1460. In 1834, after the Greek War of Independence, King Otto of Greece decreed the town should be expanded into a city. Modern-day Sparta, the capital of the prefecture of Lakonia, lies on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spartan Hegemony
Spartan hegemony refers to the period of dominance by Sparta in Greek affairs from 404 to 371 BC. Even before this period the polis of Sparta was the greatest Spartan army, military land power of classical Ancient Greece, Greek antiquity and governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. The defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431–404 BC resulted in a short-lived Spartan dominance of the southern Greek world from 404 to 371 BC.Jones, Nicholas F. ''Politics and Society in Ancient Greece.'' Westport, CT: Prager, 2008 Due to their mistrust of others, Spartans discouraged the creation of records about their internal affairs. The only histories of Sparta are from the writings of Xenophon, Thucydides, Herodotus and Plutarch, none of whom were Spartans. Plutarch was writing several centuries after the period of Spartan hegemony had ceased. This creates difficulties in understanding the Spartan political system, which was distinctly differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Kings Of Sparta
For most of its history, the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city-state of Sparta in the Peloponnese was ruled by kings. Sparta was unusual among the Greek Polis, city-states in that it maintained its kingship past the archaic Greece, Archaic age. It was even more unusual in that it had diarchy, two kings simultaneously, who were called the ''archagetai'', coming from two separate dynasty, lines. According to tradition, the two lines, the Agiad dynasty, Agiads (, ) and Eurypontids (, ), were respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, the descendants of Heracles, who supposedly conquered Sparta two generations after the Trojan War. The dynasties themselves, however, were named after the twins' grandsons, the kings Agis I and Eurypon, respectively. The Agiad line was regarded as being senior to the Eurypontid line.Cartledge, Paul, ''The Spartans'', Vintage Books, 2003. Although there are lists of the earlier purported Kings of Sparta, there is little evidence for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perioeci
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates. The name ''perioeci'' roughly means "those dwelling around/nearby", deriving from , ''peri'', "around", and , ''oîkos'', "dwelling, house". ''Perioeci'' and Spartans were collectively called the ''Lakedaimonians''. They had a central role in the Spartan economy, controlling commerce and business, as well as being responsible for crafts and manufacturing, including producing the weapons and armour of the Spartan army, as the higher-ranking Spartan citizens considered all commercial and money-making activities to be unworthy of them. The ''perioeci'' were also the only people allowed to freely travel o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Mantinea (362 BC)
The Battle of Mantinea was fought on 4 July 362 BC between the Thebans, led by Epaminondas and supported by the Arcadians, Argives, Messenians, Thessalians, Euboeans and the Boeotian league against the Spartans, led by King Agesilaus II and supported by the Eleans, Athenians, and Mantineans. The battle was to determine which of the two alliances would dominate Greece. However, the death of Epaminondas and his intended successors would cost Thebes the military leadership and initiative to maintain Theban supremacy in the region. Similarly, the Spartans were weakened by yet another defeat and loss of troops. Epaminondas' death coupled with the impact on the Spartans of yet another defeat weakened both alliances, and paved the way for Macedonian conquest led by Philip II of Macedon. Background During the Peloponnesian War (431–404 B.C.), Thebes allied with the Spartans against Athens. After Sparta's victory against Athens, the Thebans were told that their forts were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra (, ) was fought on 6 July 371 BC between the Boeotians led by the Thebes (Greece), Thebans, and the History of Sparta, Spartans along with their allies amidst the post–Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the vicinity of Leuctra, a village in Boeotia in the territory of Thespiae. The Theban victory shattered Sparta's immense influence over the Greek peninsula, which Sparta had gained with its victory in the Peloponnesian War a generation earlier. Prelude In 371 BC, the newly established democracy of Thebes had elected four Boeotarchs, the traditional title of the generals of the Boeotia, Boeotian League, and so proclaimed their intention of reconstituting the aforementioned league that Sparta had disbanded.Tritle 1987, p. 80 During this period, Thebes had an ally in Athens, but Athens was far from happy with the treatment Plataea had received. When it came to swearing an oath to respect the treaty, Sparta swore on behalf of itself and its al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed Tyrant#Historical forms, tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, embarked on an Siege of Naxos (499 BC), expedition to conquer the island of Naxos Island, Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, preempting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt, which would last unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |