|
Sparse Fourier Transform
The sparse Fourier transform (SFT) is a kind of discrete Fourier transform (DFT) for handling big data signals. Specifically, it is used in GPS synchronization, spectrum sensing and analog-to-digital converters.: The fast Fourier transform (FFT) plays an indispensable role on many scientific domains, especially on signal processing. It is one of the top-10 algorithms in the twentieth century. However, with the advent of big data era, the FFT still needs to be improved in order to save more computing power. Recently, the sparse Fourier transform (SFT) has gained a considerable amount of attention, for it performs well on analyzing the long sequence of data with few signal components. Definition Consider a sequence ''x''''n'' of complex numbers. By Fourier series, ''x''''n'' can be written as : x_n=(F^*X)_n=\sum_^X_k e^. Similarly, ''X''''k'' can be represented as : X_k=\frac(Fx)_k=\frac\sum_^x_n e^. Hence, from the equations above, the mapping is F:\mathbb C^N\to \mathbb C^N. Sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Fourier Transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced Sampling (signal processing), samples of a function (mathematics), function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex number, complex-valued function of frequency. The interval at which the DTFT is sampled is the reciprocal of the duration of the input sequence. An inverse DFT (IDFT) is a Fourier series, using the DTFT samples as coefficients of complex number, complex Sine wave, sinusoids at the corresponding DTFT frequencies. It has the same sample-values as the original input sequence. The DFT is therefore said to be a frequency domain representation of the original input sequence. If the original sequence spans all the non-zero values of a function, its DTFT is continuous (and periodic), and the DFT provides discrete samples of one cycle. If the original sequence is one cycle of a periodic fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
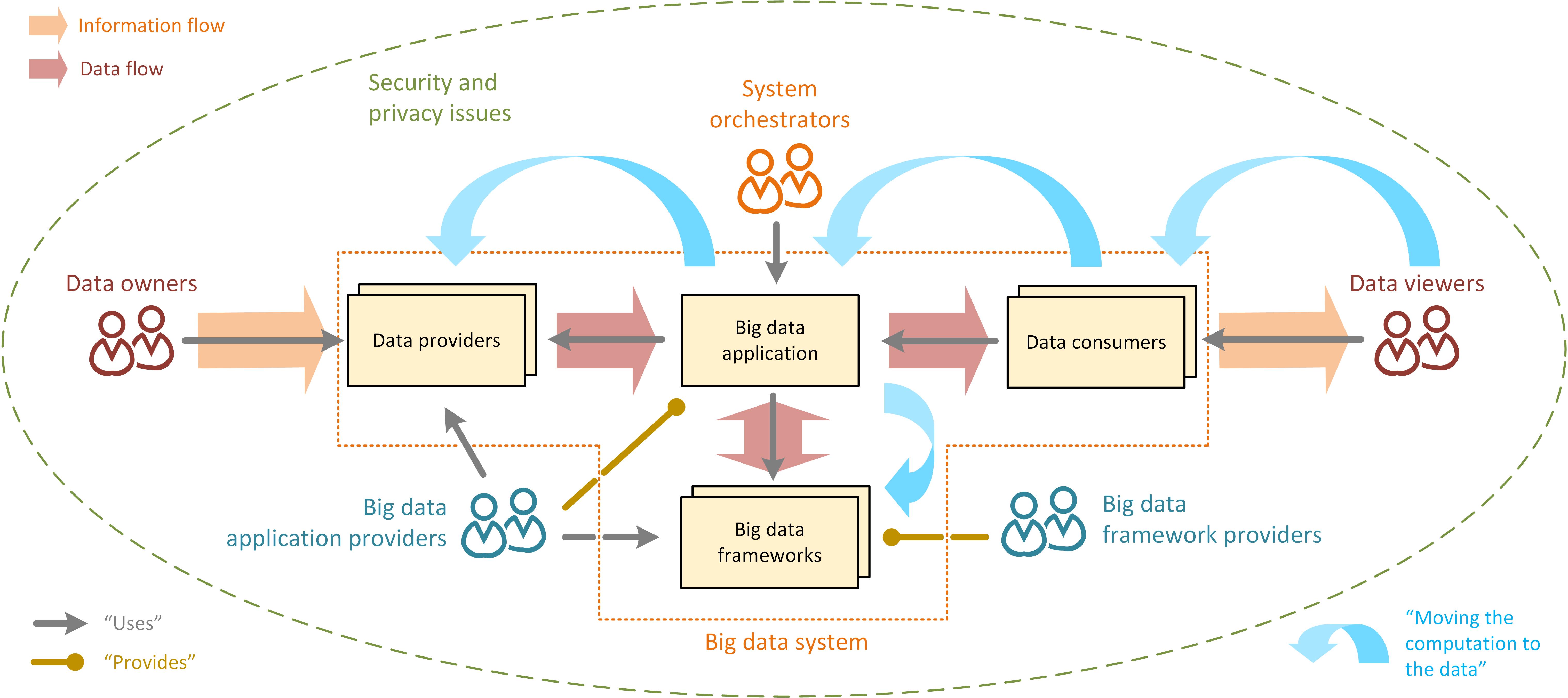
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog-to-digital Converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or Electric current, current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. There are several ADC hardware architecture, architectures. Due to the complexity and the need for precisely matched electronic component, components, all but the most specialized ADCs are implemented as integrated circuits (ICs). These typically take the form of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) mixed-signal integrated circuit chips that integrate both Analogue electronics, anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by Matrix decomposition, factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of Sparse matrix, sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the Computational complexity theory, complexity of computing the DFT from O(n^2), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(n \log n), where is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where may be in the thousands or millions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Series
A Fourier series () is an Series expansion, expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always Convergent series, converge. Well-behaved functions, for example Smoothness, smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Remainder Theorem
In mathematics, the Chinese remainder theorem states that if one knows the remainders of the Euclidean division of an integer ''n'' by several integers, then one can determine uniquely the remainder of the division of ''n'' by the product of these integers, under the condition that the divisors are pairwise coprime (no two divisors share a common factor other than 1). The theorem is sometimes called Sunzi's theorem. Both names of the theorem refer to its earliest known statement that appeared in '' Sunzi Suanjing'', a Chinese manuscript written during the 3rd to 5th century CE. This first statement was restricted to the following example: If one knows that the remainder of ''n'' divided by 3 is 2, the remainder of ''n'' divided by 5 is 3, and the remainder of ''n'' divided by 7 is 2, then with no other information, one can determine the remainder of ''n'' divided by 105 (the product of 3, 5, and 7) without knowing the value of ''n''. In this example, the remainder is 23. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the discrete uniform distribution is a symmetric probability distribution wherein each of some finite whole number ''n'' of outcome values are equally likely to be observed. Thus every one of the ''n'' outcome values has equal probability 1/''n''. Intuitively, a discrete uniform distribution is "a known, finite number of outcomes all equally likely to happen." A simple example of the discrete uniform distribution comes from throwing a fair six-sided die. The possible values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and each time the die is thrown the probability of each given value is 1/6. If two dice were thrown and their values added, the possible sums would not have equal probability and so the distribution of sums of two dice rolls is not uniform. Although it is common to consider discrete uniform distributions over a contiguous range of integers, such as in this six-sided die example, one can define discrete uniform distributions over any finite set. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filter Bank
In signal processing, a filter bank (or filterbank) is an array of bandpass filters that separates the input signal into multiple components, each one carrying a sub-band of the original signal. One application of a filter bank is a graphic equalizer, which can attenuate the components differently and recombine them into a modified version of the original signal. The process of decomposition performed by the filter bank is called ''analysis'' (meaning analysis of the signal in terms of its components in each sub-band); the output of analysis is referred to as a subband signal with as many subbands as there are filters in the filter bank. The reconstruction process is called ''synthesis'', meaning reconstitution of a complete signal resulting from the filtering process. In digital signal processing, the term ''filter bank'' is also commonly applied to a bank of receivers. The difference is that receivers also down-convert the subbands to a low center frequency that can be re-sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State or MSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan, United States. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, the first of its kind in the country. After the introduction of the Morrill Land-Grant Acts, Morrill Act in 1862, the state designated the college a land-grant institution in 1863, making it the first of the land-grant colleges in the United States. The college became coeducational in 1870. Today, Michigan State has facilities all across the state and over 634,000 alumni. Michigan State is a member of the Association of American Universities and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The university's campus houses the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, the W. J. Beal Botanical Garden, the Abrams Planetarium, the Wharton Center f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |