|
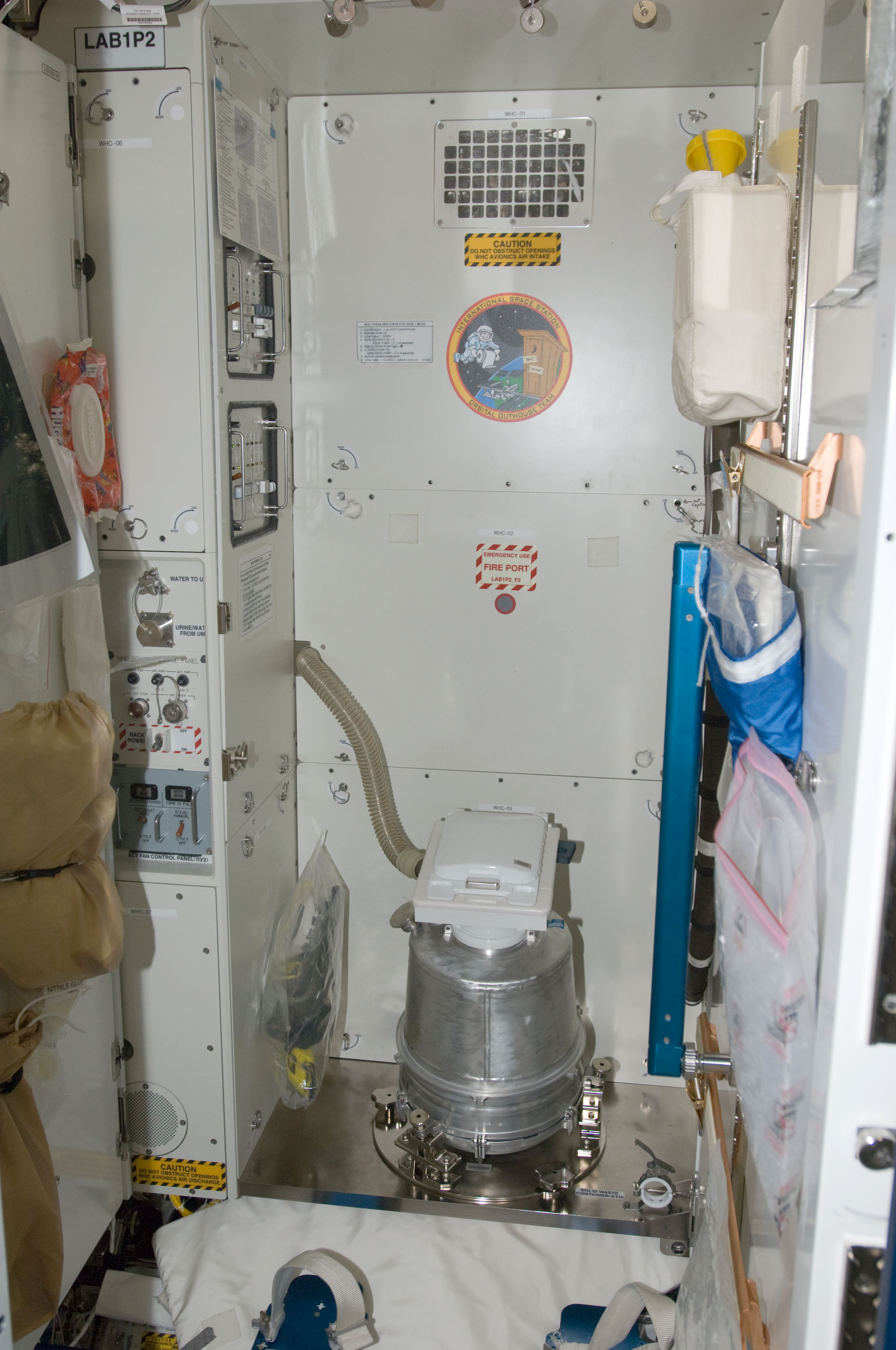
Space Toilet
A space toilet or zero-gravity toilet is a toilet that can be used in a weightless environment. In the absence of weight, the collection and retention of liquid and solid waste is directed by use of airflow. Since the air used to direct the waste is returned to the cabin, it is filtered beforehand to control odor and cleanse bacteria. In older systems, wastewater is vented into space, and any solids are compressed and stored for removal upon landing. More modern systems expose solid waste to vacuum pressures to kill bacteria, which prevents odor problems and kills pathogens. Background Astronauts say that they are most often asked how they go to the bathroom in space. In space, weightlessness causes fluids to distribute uniformly around human bodies. Kidneys detect the fluid movement and a physiological reaction causes the humans to need to relieve themselves within two hours of departure from Earth. The space toilet was thus the first device activated on shuttle flights, aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Toilet (8687080967)
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as ''spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a better model for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Nicollier
Claude Nicollier (born 2 September 1944) is the first astronaut from Switzerland. He has flown on four Space Shuttle missions. His first spaceflight ( STS-46) was in 1992, and his final spaceflight ( STS-103) was in 1999. He took part in two servicing missions to the Hubble Space Telescope (called STS-61 and STS-103). During his final spaceflight he participated in a spacewalk, becoming the first European Space Agency astronaut to do so during a Space Shuttle mission (previous ESA astronauts conducted spacewalks aboard '' Mir'', see List of spacewalks and moonwalks 1965–1999). In 2000 he was assigned to the Astronaut Office Extravehicular Activity Branch, while maintaining a position as Lead ESA Astronaut in Houston. Nicollier retired from ESA in April 2007. He was appointed full professor of Spatial Technology at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne on 28 March 2007. He was an expert board member of Swiss Space Systems, until the company's dissolution. Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
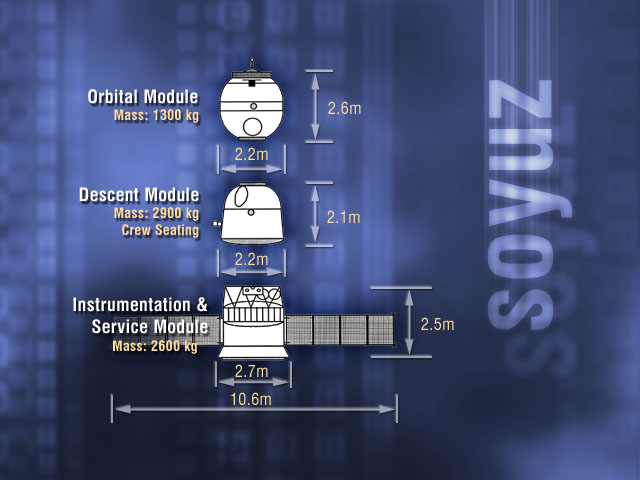
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou and Russia's Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyuz is a single-use spacecraft composed of three main sections. The descent module is where cosmonauts are seated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-124
STS-124 was the 35th mission of Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. It went to the International Space Station on this mission. ''Discovery'' launched on May 31, 2008, at 17:02 EDT, moved from an earlier scheduled launch date of May 25, 2008, and landed safely at the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, at 11:15 EDT on June 14, 2008. Its objective was to deliver the largest module of the space station – '' Kibō'', the Japanese Experiment Module pressurized section. The mission is also referred to as ISS-1J by the ISS program. Crew Crew notes * Stephen G. Bowen was originally assigned to STS-124 but was moved to STS-126 to allow this mission to rotate an ISS crew member. Bowen was scheduled to perform the EVAs on the flight along with Fossum. Garan took his place for the EVAs. Commander Kelly discusses the crew "I'm really fortunate to be given the crew members that I have on this mission. It's myself and six others. We do swap one of our crew members with the exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Discovery
Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' (Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-103) is a retired American Space Shuttle orbiter. The spaceplane was one of the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiters from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the third of five fully operational orbiters to be built. Its first mission, STS-41-D, flew from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years of service it launched and landed 39 times, aggregating more spaceflights than any other spacecraft . The Space Shuttle launch vehicle had three main components: the Space Shuttle orbiter, a single-use central fuel tank, and two reusable solid rocket boosters. Nearly 25,000 Space Shuttle thermal protection system, heat-resistant tiles cover the orbiter to protect it from high temperatures on re-entry. ''Discovery'' became the third operational orbiter to enter service, preceded by ''Space Shuttle Columbia, Columbia'' and ''Space Shuttle Challenger, Challenger''. After the Challenger and Columbia accidents, Discovery became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomatic Bag
A diplomatic bag, also known as a diplomatic pouch, is a container with certain legal protections used for carrying official correspondence or other items between a diplomatic mission and its home government or other diplomatic, consular, or otherwise official entity. The physical concept of a "diplomatic bag" is flexible and it can take many forms (e.g., a cardboard box, briefcase, duffel bag, large suitcase, crate or even a shipping container). Additionally, a diplomatic bag usually has some form of lock or tamper-evident seal attached to it to deter or detect interference by unauthorized third parties. The most important point is that as long as it is externally marked to show its status, the container has diplomatic immunity from search or seizure, as codified in article 27 of the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations., p. 8 It may only contain articles intended for official use, though there have been numerous cases where the privileges of the diplomatic bag have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia (corporation), Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle retirement, Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou (spacecraft), Shenzhou and Russia's Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress (spacecraft)
The Progress () is a Russian expendable cargo spacecraft. Originally developed for the Soviet space program and derived from the crewed Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft, Progress has been instrumental in maintaining long-duration space missions by providing consumables like food, water, and air, as well as maintenance equipment. Since its maiden flight in 1978, Progress has supported various space stations, including Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir, and remains a key resupply vehicle for the International Space Station (ISS). Each Progress mission delivers thousands of kilograms of supplies in its pressurized module. It also carries water, fuel, and gases to replenish the station's resources and sustain its onboard atmosphere. Beyond resupply duties, a docked Progress can maneuver or reboost the station, countering atmospheric drag and maintaining its operational altitude. When a Progress spacecraft nears the end of its design life, it is loaded with waste, undocked, and deorbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranquility (ISS Module)
''Tranquility'', also known as Node 3, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It contains environmental control systems, life support systems, a toilet, exercise equipment, and an observation Cupola (ISS module), cupola. The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) had ''Tranquility'' manufactured by Thales Alenia Space. A ceremony on 20 November 2009 transferred ownership of the module to NASA. On 8 February 2010, NASA launched the module on the Space Shuttle's STS-130 mission. Design and manufacturing ''Tranquility'' was built within the ESA-NASA ISS bartering system. ESA committed to build and fund both Harmony (ISS module), ''Harmony'' and ''Tranquility'' as well as the Automated Transfer Vehicle, ATV in order to use NASA ISS facilities, fly astronauts on the Shuttle and for other ISS services. ESA teamed up with the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to Manufacturing of the International Space Station, manufacture both ''Harmony'' and ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauka (ISS Module)
''Nauka'' (), also known as the ''Multipurpose Laboratory Module, Upgrade'' (MLM-U, ), is the primary laboratory of the Russian Orbital Segment of the International Space Station (ISS). Serving alongside the ''Rassvet'' and ''Poisk'' mini-research modules, Nauka conducts scientific experiments and stores research equipment. Originally built as a backup for ''Zarya'', the very first module of the ISS, ''Nauka'''s construction was halted in the late 1990s, when it was about 70% complete. After exploring various options, Roscosmos decided to convert the partially completed module into a laboratory. While the initial target launch date was set for 2007, and outfitting equipment for Nauka was delivered by Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' in 2010 attached to the ''Rassvet'' module, numerous delays and technical issues delayed the launch by 14 years. ''Nauka'' finally launched on 21 July 2021 at 14:58:25UTC from the Baikonur Cosmodrome atop a Proton-M rocket. Like most of the Russian mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |