|
Soybean Mosaic Virus
Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) is a member of the plant virus genus ''Potyvirus'' (family Potyviridae). It infects mainly plants belonging to the family Fabaceae but has also been found infecting other economically important crops. SMV is the cause of soybean mosaic disease that occurs in all the soybean productions areas of the world. Soybean ('' Glycine max'') is one of the most important sources of edible oil and proteins and pathogenic infections are responsible for annual yield losses of about $4 billion in the United States. Among these pathogens, SMV is the most important and prevalent viral pathogen in soybean production worldwide. It causes yield reductions of about 8% to 35% but losses as high as 94% have been reported. The virus was first reported from Connecticut in 1915 and described in 1921. Its genome is a single stranded positive sense RNA of about 9.5kb that encodes at least 11 proteins. SMV virion is non envelope, flexuous, filamentous of about 720–800 nm lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine Max
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
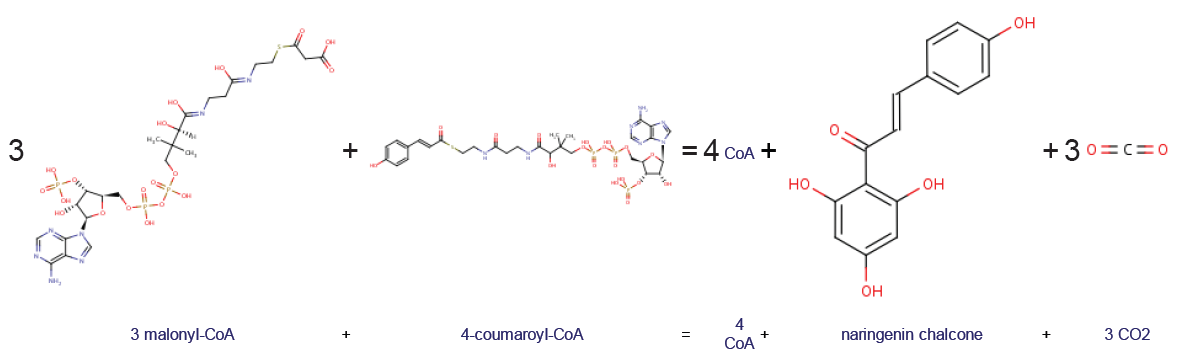
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzymes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhopalosiphum Maidis
''Rhopalosiphum maidis'', common names corn leaf aphid and corn aphid, is an insect, and a pest of maize and other crops. It has a nearly worldwide distribution and is typically found in agricultural fields, grasslands, and forest-grassland zones. Among aphids that feed on maize, it is the most commonly encountered and most economically damaging, particularly in tropical and warmer temperate areas. In addition to maize, ''R. maidis'' damages rice, sorghum, and other cultivated and wild monocots. Description The bodies of wingless parthenogenetic females are green or whitish-green. The head, antennae, legs, cornicles, tail, and transverse bands on the abdomen are black-brown. The body has sparse short hairs. The length of the antennae is less than half the length of the body. Cornicles are not longer than the finger-like tail. In winged females, the head and thoracic section are black-brown and the cornicles are shorter than in the wingless females. Most ''R. maidis'' po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myzus Persicae
''Myzus persicae'', known as the green peach aphid, greenfly, or the peach-potato aphid, is a small green aphid belonging to the order Hemiptera. It is the most significant aphid pest of peach trees, causing decreased growth, shrivelling of the leaves and the death of various tissues. It also acts as a vector for the transport of plant viruses such as cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), potato virus Y (PVY) and tobacco etch virus (TEV). Potato virus Y and potato leafroll virus can be passed to members of the nightshade/potato family (Solanaceae), and various mosaic viruses to many other food crops. Originally described by Swiss entomologist Johann Heinrich Sulzer in 1776, its specific name is derived from the Latin genitive ''persicae,'' "of the peach". The syntype specimen of this species is located in the Illinois Natural History Survey Insect Collection. Life cycle Life cycle of the green peach aphid varies depending on temperature. A fully completed generation takes approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
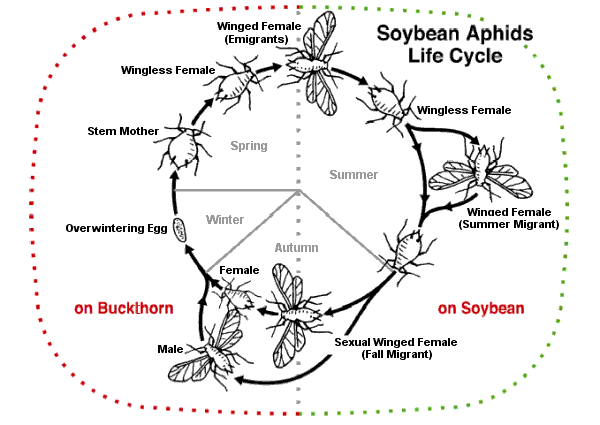
Aphis Glycines
The soybean aphid (''Aphis glycines'') is an insect pest of soybean ('' Glycine max'') that is exotic to North America. The soybean aphid is native to Asia. It has been described as a common pest of soybeans in China and as an occasional pest of soybeans in Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. The soybean aphid was first documented in North America in Wisconsin in July 2000. Ragsdale ''et al.'' (2004) noted that the soybean aphid probably arrived in North America earlier than 2000, but remained undetected for a period of time. Venette and Ragsdale (2004) suggested that Japan probably served as the point of origin for the soybean aphid's North American invasion. By 2003, the soybean aphid had been documented in Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Virginia, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. Together, these states accounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphis Fabae
The black bean aphid (''Aphis fabae'') is a small black insect in the genus ''Aphis'', with a broad, soft body, a member of the order Hemiptera. Other common names include blackfly, bean aphid, and beet leaf aphid. In the warmer months of the year, it is found in large numbers on the undersides of leaves and on the growing tips of host plants, including various agricultural crops and many wild and ornamental plants. Both winged and wingless forms exist, and at this time of year, they are all females. They suck sap from stems and leaves and cause distortion of the shoots, stunted plants, reduced yield, and spoiled crops. This aphid also acts as a vector for viruses that cause plant disease, and the honeydew it secretes may encourage the growth of sooty mould. It breeds profusely by live birth, but its numbers are kept in check, especially in the later part of the summer, by various predatory and parasitic insects. Ants feed on the honeydew it produces, and take active steps to rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyrthosiphon Pisum
''Acyrthosiphon pisum'', commonly known as the pea aphid (and colloquially known as the green dolphin, pea louse, and clover louse), is a sap-sucking insect in the family Aphididae. It feeds on several species of legumes (plant family Fabaceae) worldwide, including forage crops, such as pea, clover, alfalfa, and broad bean, and ranks among the aphid species of major agronomical importance. The pea aphid is a model organism for biological study whose genome has been sequenced and annotated. Generalities and life cycle In the autumn, female pea aphids lay fertilized eggs overwinter that hatch the following spring. The nymphs that hatch from these eggs are all females, which undergo four moults before reaching sexual maturity. They will then begin to reproduce by viviparous parthenogenesis, like most aphids. Each adult female gives birth to four to 12 female nymphs per day, around a hundred in her lifetime. These develop into mature females in about seven to ten days. The life s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ... of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving live birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs. The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and a woody plant. Some species feed on only one type of plant, while others are generalists, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phomopsis
''Phomopsis'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the family Valsaceae. Species Species include: * '' Phomopsis arnoldiae'' * '' Phomopsis asparagi'' * ''Phomopsis asparagicola'' * ''Phomopsis azadirachtae'' * '' Phomopsis cannabina'' * '' Phomopsis caricae-papayae'' * ''Phomopsis coffeae'' * '' Phomopsis durionis'' Syd. 1932 * '' Phomopsis elaeagni'' * ''Phomopsis ganjae'' * '' Phomopsis javanica'' * '' Phomopsis juniperovora'' * '' Phomopsis lokoyae'' * '' Phomopsis longicolla'' * '' Phomopsis mangiferae'' * '' Phomopsis obscurans'' * ''Phomopsis perseae'' * ''Phomopsis pittospori'' * '' Phomopsis prunorum'' * ''Phomopsis sojae'' * '' Phomopsis scabra'' * '' Phomopsis sclerotioides'' * '' Phomopsis tanakae'' * '' Phomopsis theae'' * ''Phomopsis viticola'' Formerly placed here: *''Phomopsis vaccinii'', now '' Diaporthe vaccinii'' *''Phomopsis leptostromiformis'', now ''Diaporthe toxica'' Dead-arm infection One of the species of this genus, '' P. viticola'', cause a grape diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bean Pod Mottle Virus
''Bean pod mottle virus'', or BPMV, is a species of plant pathogenic virus in the family ''Secoviridae''. It is known to infect soybean crops. Description BPMV is the viral pathogen that causes the disease Bean Pod Mottle in soybeans and other legumes such as snap peas. BPMV is a species in the plant pathogenic virus family '' Comoviridae'', and genus ''Comovirus'' characterized by icosahedral symmetry, non-enveloped, having two single stranded positive-sense RNAs (RNA-1 and RNA-2) separately encapsulated in isomeric particles, and are between 28 and 30 nm in diameter. (Bradshaw, 2007). The virus can overwinter in leaf-feeding beetle vectors (such as the bean leaf beetle), survive in perennial host species, and in virus-infected seed. In the North Central Region, the bean leaf beetle ('' Cerotoma trifurcate)'' is the most influential vector, by feeding on infected legumes and transferring virus particles to the next plant it lands on to feed. The BPMV disease has most sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |