|
Soviet National Anthem
The State Anthem of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was the national anthem of the Soviet Union and the regional anthem of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic from 1944 to 1991, replacing "The Internationale". Its original lyrics were written by Sergey Mikhalkov (1913–2009) in collaboration with El-Registan (1899–1945), and its music was composed by Alexander Alexandrov (1883–1946). For a two-decade interval following de-Stalinization, the anthem was performed without lyrics. The second set of lyrics, also written by Mikhalkov and in which Stalin's name was omitted, was adopted in 1977. A decade after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the same melody was used for the Soviet Union's successor state, as the State Anthem of the Russian Federation. History Origins The anthem's music was originally composed by Alexander Alexandrov in 1938 for the Hymn of the Bolshevik Party. Its opening bars were borrowed from one of Alexandrov's previous pieces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Ukraine. It is the first language, first (native) language of a large majority of Ukrainians. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard language is studied by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often made between Ukrainian and Russian language, Russian, another East Slavic language, yet there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian language, Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic", ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: "[The] distinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegelin. 1977. ''Classification and Index of the World's Languages'' (Elsevier). p. 311, "In terms of immediate mutual intelligibility, the East Slavic zone is a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakha Language
Sakha may refer to: * Sakha Republic, a federal subject of Russia * Sakha language, or Yakut, a Turkic language * Sakha people, also Yakuts, a Turkic people * Sakha scripts, writing systems for the Sakha language * Sakha, Egypt, a town also known as Xois * Sakha, Iran, a village in Zanjan Province, Iran * Sakha Consulting Wings, a taxi service provided by women for women in Delhi, India See also * Saha (other) * Saka (other) * Sakhi (other) * Sakhavu (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( ) is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Language
Bulgarian (; , ) is an Eastern South Slavic, Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic languages, South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of grammatical case, case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidentiality, evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official Languages of Bulgaria, language of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Language
Kurdish (, , ) is a Northwestern Iranian languages, Northwestern Iranian language or dialect continuum, group of languages spoken by Kurds in the region of Kurdistan, namely in southeast Turkish Kurdistan, Turkey, northern Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq, northwest Iranian Kurdistan, Iran, and northern Syrian Kurdistan, Syria. It is also spoken in northeast Iran, as well as in certain areas of Armenia and Azerbaijan. Kurdish Variety (linguistics), varieties constitute a dialect continuum, with some Mutual intelligibility, mutually unintelligible varieties, and collectively have 26 million native speakers. The main varieties of Kurdish are Kurmanji, Sorani, and Southern Kurdish (). The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script. A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetian Language
Ossetian ( , , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete, is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Russian-Georgian border in the Greater Caucasus region. It is the native language of the Ossetian people, and a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian, Sarmatian, and Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetian region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the '' de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the 2010 Russian census. Despite Ossetian being the official languages of both North and South Ossetia, since 2009 UNESCO has listed Ossetian as "vulnerable". In the 2010 Russian census only 36% of North Ossetians claimed to be fluent i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chechen Language
Chechen ( , ; , , ) is a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian language spoken by approximately 1.8 million people, mostly in the Chechnya, Chechen Republic and by Chechens, members of the Chechen diaspora throughout Russia and the rest of Europe, Jordan, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Ukraine, Central Asia (mainly Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan) and Georgia (country), Georgia. History Before the Caucasian War, Russian conquest, most writings in Chechnya consisted of Islamic texts and clan histories, written usually in Arabic but sometimes also in Chechen using Arabic script. The Chechen literary language was created after the October Revolution, and the Latin script began to be used instead of Arabic for Chechen writing in the mid-1920s. The Cyrillic script was adopted in 1938. Almost the entire library of Chechen medieval writing in Arabic and Georgian script about the land of Chechnya and its people was destroyed by Soviet authorities in 1944, leaving the modern Chechens and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avar Language
Avar (, , "language of the mountains" or , , "Avar language"), also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian language of the Avar–Andic languages, Avar–Andic subgroup that is spoken by Avars (Caucasus), Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately one million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia. Geographic distribution It is spoken mainly in the western and southern parts of the Russian Caucasus republic of Dagestan, and the Balaken, Zaqatala Rayon, Zaqatala regions of north-western Azerbaijan. Some Avars (Caucasus), Avars live in other regions of Russia. There are also small communities of speakers living in the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia; in Georgia (country), Georgia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Jordan, and the Marmara Sea region of Turkey. It is spoken by about 1,200,000 people worldwide. UNESCO classifies Avar as vulnerable to extinction. Status It is one of six literary languages of Dagestan, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
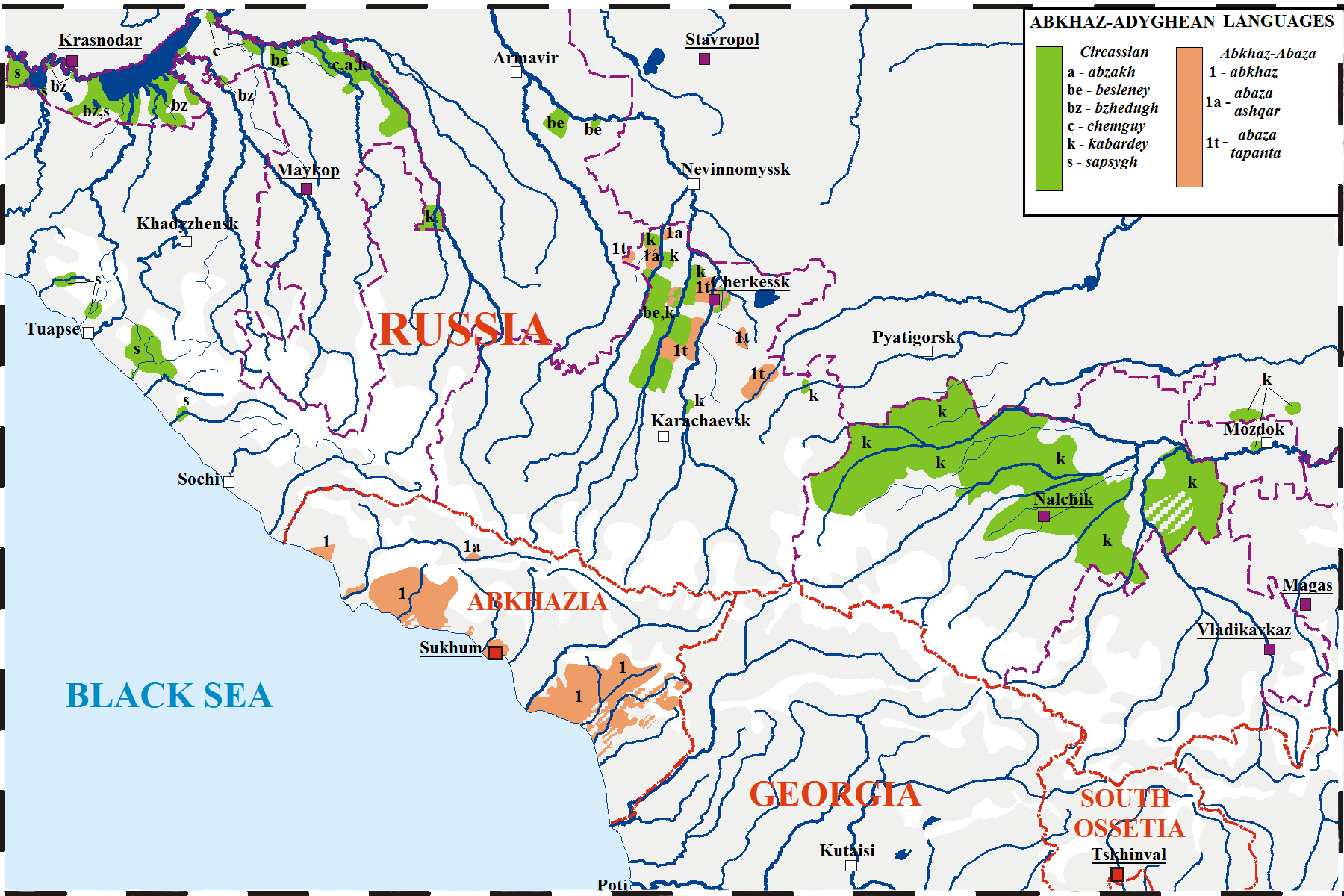
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; also known as West Circassian) is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria, Iraq and Israel, where Circassians settled after the Circassian genocide (–1870) by the Russian Empire. It is closely related to the Kabardian language, Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian languages, Circassian language. The literary standard of Adyghe is based on its Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian language, Russian are the two official languages of the Adygea, Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. In Russia, there are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the Russo-Circassian War, Russian–Circassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz, also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza language, Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhazians, Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 190,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia (country), Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia (country), Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe language, Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza language, Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Tatar Language
Crimean Tatar (), also called Crimean (), is a Turkic languages, Turkic language spoken in Crimea and the Crimean Tatar diasporas of Uzbekistan, Turkey and Bulgaria, as well as small communities in the United States and Canada. It should not be confused with Tatar language, Tatar, spoken in Tatarstan and adjacent regions in Russia; Crimean Tatar has been extensively influenced by nearby Oghuz languages and is mutually intelligible with them to varying degrees. A long-term ban on the study of the Crimean Tatar language following the deportation of the Crimean Tatars by the Soviet government has led to the fact that at the moment UNESCO ranks the Crimean Tatar language among the languages under serious threat of extinction (''severely endangered''). However, according to the A. Yu. Krymskyi Institute of Oriental Studies, Institute of Oriental Studies, due to negative situations, the real degree of the threat has elevated to critically endangered in recent years, which are highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |