|
South Pole–Aitken Basin
The South Pole–Aitken basin (SPA Basin, ) is an immense impact crater on the far side of the Moon. At roughly in diameter and between deep, it is one of the largest known impact craters in the Solar System. It is the largest, oldest, and deepest basin recognized on the Moon. It is estimated that it was formed approximately 4.2 to 4.3 billion years ago, during the Pre-Nectarian epoch (with radiometric dating of lunar zircons proposed to originate from the basin suggesting a precise age of 4.338 billion years). It was named for two features on opposite sides of the basin: the lunar South Pole at one end and the crater Aitken on the northern end. The outer rim of this basin can be seen from Earth as a huge mountain chain located on the Moon's southern limb, sometimes informally called "Leibnitz mountains". On 3 January 2019, the Chang'e 4, a Chinese spacecraft, landed in the basin, specifically within a crater called Von Kármán. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
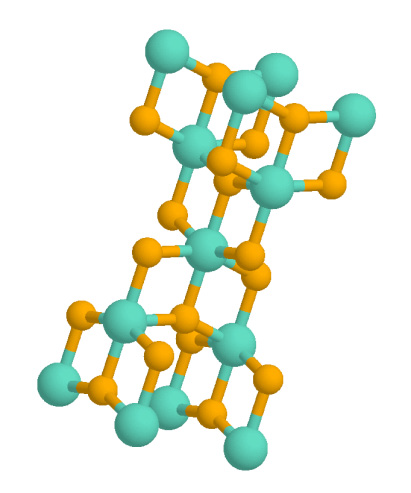
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clementine (spacecraft)
''Clementine'' (officially called the Deep Space Program Science Experiment (DSPSE)) was a joint space project between the Ballistic Missile Defense Organization (previously the Strategic Defense Initiative, Strategic Defense Initiative Organization) and NASA, launched on January 25, 1994. Its objective was to test sensors and spacecraft components in long-term exposure to space and to make scientific observations of both the Moon and the near-Earth asteroid 1620 Geographos. Its lunar observations included imaging at various wavelengths in the visible as well as in ultraviolet and infrared, laser ranging Altimeter, altimetry, gravimetry, and charged particle measurements. These observations were for the purposes of obtaining multi-spectral imaging of the entire lunar surface, assessing the surface mineralogy of the Moon, obtaining altimetry from 60°N to 60°S latitude, and obtaining gravity data for the near side. There were also plans to image and determine the size, shape, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (spacecraft)
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and Moons of Jupiter, its moons, as well as the asteroids 951 Gaspra, Gaspra and 243 Ida, Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after Gravity assist, gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the Galileo project, ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany's Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
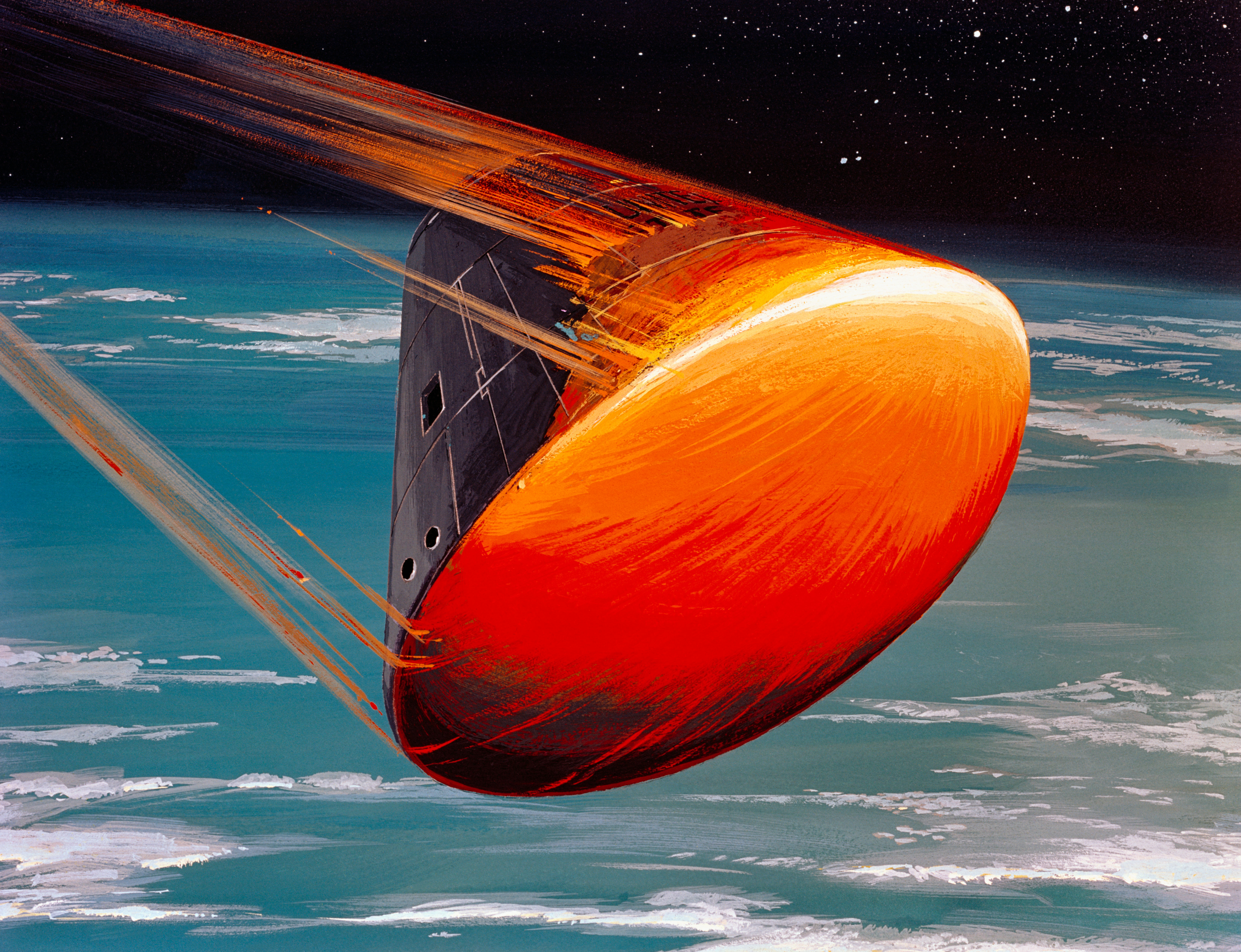
Command And Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Track
A satellite ground track or satellite ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below a satellite's trajectory. It is also known as a suborbital track or subsatellite track, and is the vertical projection of the satellite's orbit onto the surface of the Earth (or whatever body the satellite is orbiting). A satellite ground track may be thought of as a path along the Earth's surface that traces the movement of an imaginary line between the satellite and the center of the Earth. In other words, the ground track is the set of points at which the satellite will pass directly overhead, or cross the zenith, in the frame of reference of a ground observer.. The ground track of a satellite can take a number of different forms, depending on the values of the orbital elements, parameters that define the size, shape, and orientation of the satellite's orbit, although identification of the always reliant upon the recognition of the physical form that is in motion; This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbiter Program
The Lunar Orbiter program was a series of five uncrewed lunar orbiter missions launched by the United States in 1966 and 1967. Intended to help select Apollo landing sites by mapping the Moon's surface, they provided the first photographs from lunar orbit and photographed both the Moon and Earth. All five missions were successful, and 99 percent of the lunar surface was mapped from photographs taken with a resolution of or better. The first three missions were dedicated to imaging 20 potential crewed lunar landing sites, selected based on Earth-based observations. These were flown at low-inclination orbits. The fourth and fifth missions were devoted to broader scientific objectives and were flown in high-altitude polar orbits. Lunar Orbiter 4 photographed the entire nearside and nine percent of the far side, and Lunar Orbiter 5 completed the far side coverage and acquired medium () and high () resolution images of 36 preselected areas. All of the Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 3
Zond 3 was a 1965 space probe which performed a flyby of the Moon far side, taking 28 quality photographs. It was a member of the Soviet Zond program while also being part of the Mars 3MV project. It was unrelated to Zond spacecraft designed for crewed circumlunar missions (Soyuz 7K-L1). It is believed that Zond 3 was initially designed as a companion spacecraft to Zond 2 to be launched to Mars during the 1964 launch window. The opportunity to launch was missed, and the spacecraft was launched on a Mars-crossing trajectory as a spacecraft test, even though Mars was no longer attainable. Spacecraft design The spacecraft was of the 3MV-4 type, similar to Zond 2. In addition to a 106.4 mm focal length imaging system for visible light photography and ultraviolet spectrometry at 285-355 μm, it carried ultraviolet (190-275 μm) and infrared (3-4 μm) spectrophotometers, radiation sensors ( gas-discharge and scintillation counters), charged particle detector, magnetometer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna 3
Luna 3, or E-2A No.1 (), was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1959 as part of the Luna programme. It was the first mission to photograph the far side of the Moon and the third Soviet space probe to be sent to the neighborhood of the Moon. The historic, never-before-seen views of the far side of the Moon caused excitement and interest when they were published around the world, and a tentative ''Atlas of the Far Side of the Moon'' was created from the pictures. These views showed mountainous terrain, very different from the near side, and only two dark, low-lying regions, which were named Mare Moscoviense (Sea of Moscow) and Mare Desiderii (Sea of Desire). Mare Desiderii was later found to be composed of a smaller mare, Mare Ingenii (Sea of Cleverness), and several other dark craters. The reason for this difference between the two sides of the Moon is still not fully understood, but it seems that most of the dark lavas that flowed out to produce the maria formed under the Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole-Aitken Basin Rim As08-13-2319hr
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', ), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). South is sometimes abbreviated as S. Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |