|
Sonneberg
Sonneberg () in Thuringia, Germany, is the seat of the Sonneberg district. It is in the Franconian south of Thuringia, neighboring its Upper Franconian twin town Neustadt bei Coburg. Sonneberg became known as the "world toy city", and is home to the and the Sonneberg observatory, founded in 1925. The Thuringian Slate Mountains border the city, with the Franconian Forest to the east. History "The Sonneberg Castle was also called Sonneberg Castle or the Haus zu Sonneberg in old documents. In 480 Süne or Süno, Duke of Franconia, built this castle because of the Thuringian incursions ..." so it says on page 64 in the topography of the Duke of Saxe-Meiningen's share in the Duchy of Coburg from the year 1781. This not uncritical representation is based on the history of the Franks by Abbot Johannes Trithemius from 1514. The name Sonneberg was first mentioned in documents in 1207. It goes back to the noble family of the Lords of Sonneberg, which is documented in the 12th and 13t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonneberg Hauptbahnhof
Sonneberg () in Thuringia, Germany, is the seat of the Sonneberg (district), Sonneberg district. It is in the Franconian south of Thuringia, neighboring its Upper Franconian twin town Neustadt bei Coburg. Sonneberg became known as the "world toy city", and is home to the and the Sonneberg observatory, founded in 1925. The Thuringian Slate Mountains border the city, with the Franconian Forest to the east. History "The Sonneberg Castle was also called Sonneberg Castle or the Haus zu Sonneberg in old documents. In 480 Süne or Süno, Duke of Duchy of Franconia, Franconia, built this castle because of the Thuringii, Thuringian incursions ..." so it says on page 64 in the topography of the Duke of Saxe-Meiningen's share in the Saxe-Coburg, Duchy of Coburg from the year 1781. This not uncritical representation is based on the history of the Franks by Abbot Johannes Trithemius from 1514. The name Sonneberg was first mentioned in documents in 1207. It goes back to the noble family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonneberg (district)
Sonneberg is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the south of Thuringia, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from the west clockwise) the districts Hildburghausen, Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, and the Bavarian districts Kronach and Coburg. History The district was created in 1868 when districts were introduced in Saxe-Meiningen. In 1952, parts of the district were split off into a newly created district Neuhaus am Rennweg. In 1994, Neuhaus am Rennweg was dissolved and the district Sonneberg regained its original size. In 2019 the municipalities Lichte and Piesau from the district Saalfeld-Rudolstadt came as villages into the town Neuhaus am Rennweg in the district Sonneberg. Geography The district is located on the southern slopes of the mountains of the Thuringian Forest. The land descends from the more than 800m tall hills (the highest elevation is the 869m high Großer Farmdenkopf) down to the lower plains ''Sonneberger Unterland'' and ''Schalkauer Platte''. The ''Dreistromstein'' near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
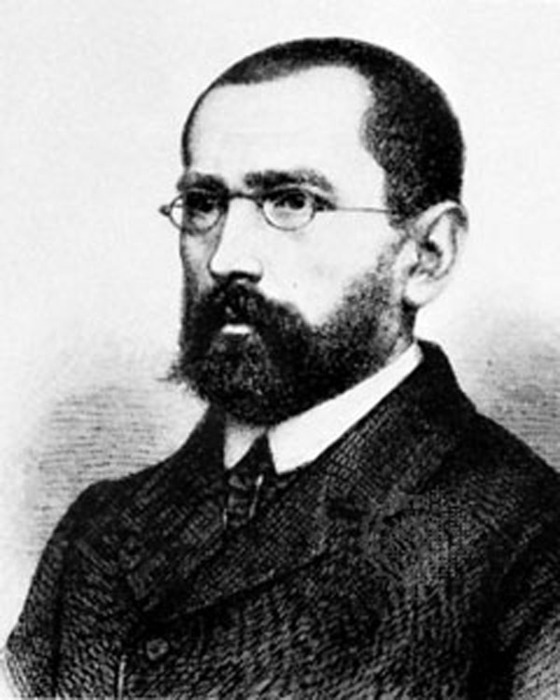
Cuno Hoffmeister
Cuno Hoffmeister (2 February 1892 – 2 January 1968) was a German astronomer, observer and discoverer of variable stars, comets and minor planets, and founder of Sonneberg Observatory. Born in Sonneberg in 1892 to Carl and Marie Hoffmeister, Cuno Hoffmeister obtained his first telescope in 1905 and became an avid Amateur astronomy, amateur astronomer. After his father lost most of his money in 1914, Hoffmeister had to leave school in 1916 to start an apprenticeship in his father's company. During this time he continued to study spherical mathematics and trigonometry. In April 1915 he had the opportunity to substitute as the assistant of Ernst Hartwig at ''Remeis Observatory'' in Bamberg while the current holder of the position was drafted, mainly working on observations of meteors and variable stars. He held this position until the end of the war and then moved back to Sonneberg, where he made his Abitur in 1920. After studying at the University of Jena, while at the same time c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberland Am Rennsteig
Oberland am Rennsteig is a former municipality in the Sonneberg district of Thuringia, Germany. Since 31 December 2013, it is part of the town Sonneberg. Statistisches Bundesamt
The Federal Statistical Office (, shortened ''Destatis'') is a federal authority of Germany. It reports to the Federal Ministry of the Interior.
The Office is responsible for collecting, processing, presenting and analysing statistical informati ...
References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
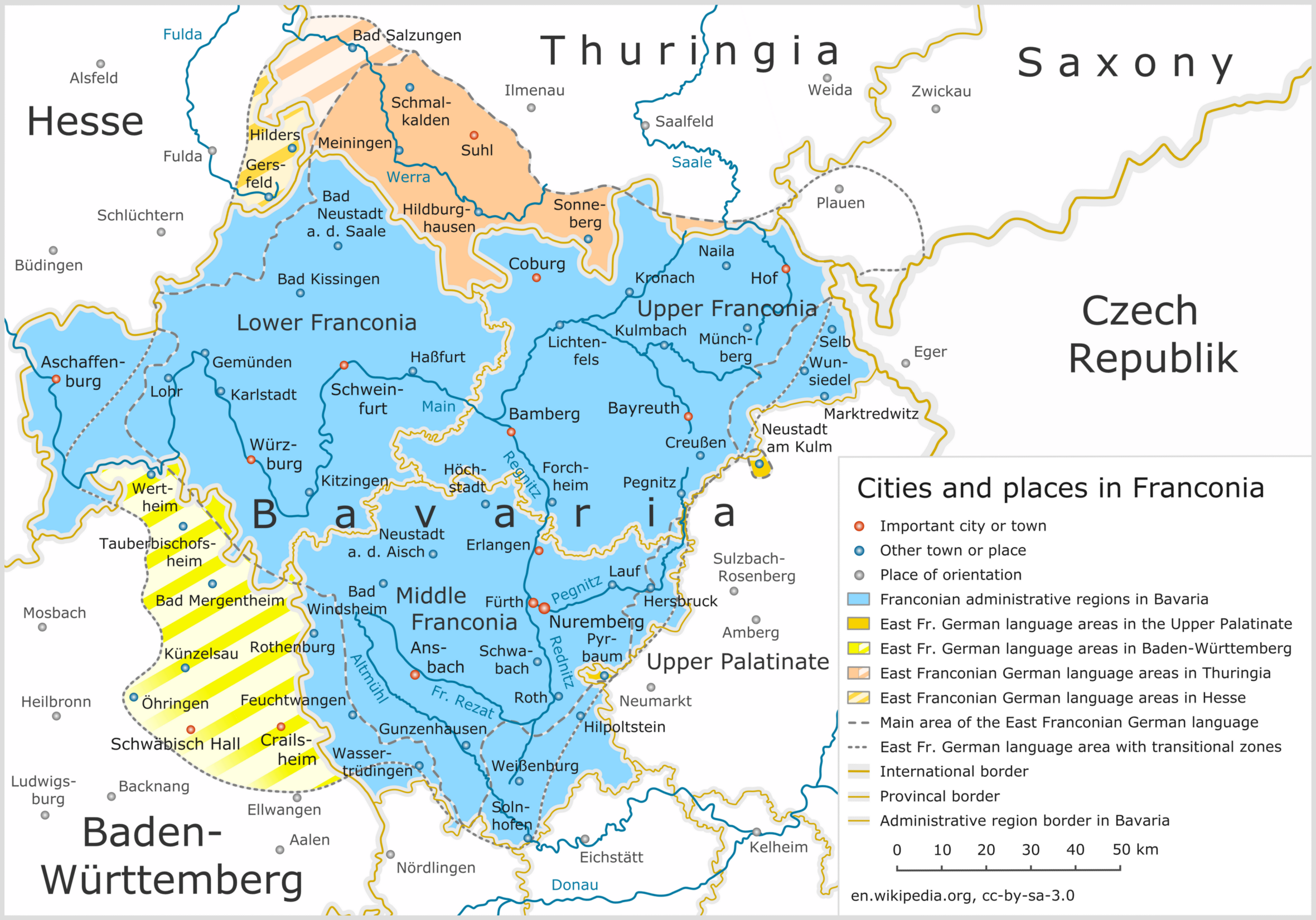
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almuth Beck
Almuth Beck (born 4 October 1940) is a German educator and politician ( SED/ PDS). After reunification she became the first member of a German parliament (''Landtag'') to be deprived of her parliamentary mandate on account of activities as an Informal collaborator for the Ministry for State Security (Stasi) in what was, at that time, East Germany. This, and successful legal challenges touching on her case, attracted attention across the nation. Biography Almuth Beck was born on 4 October 1940, in Sonneberg, a small and in some ways isolated town in the Thuringian hills to the south of Erfurt. When she was 4, World War II ended and the region found itself in the Soviet occupation zone, relaunched in October 1949 as the Soviet sponsored German Democratic Republic (East Germany). She passed her school final exams and went on to study between 1958 and 1962 at the University of Jena, during which time, in 1961, she married. She emerged qualified as a school teacher of History an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Coburg
Saxe-Coburg () was a duchy held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in today's Bavaria, Germany. History Ernestine Line When Henry IV, Count of Henneberg – Schleusingen, died in 1347, the possessions of the House of Henneberg – Schleusingen were divided between his widow, Jutta of Brandenburg-Salzwedel, and Henry's younger brother, John, and Jutta was given the so-called “''neues Herrschaft''” ("new lordship"), with Coburg among other properties. The death of Jutta six years later was followed by the division of the new ''Herrschaft'' amongst three of her daughters. The second daughter, Catherine of Henneberg, was awarded the southeastern part of the Coburgish land. After their wedding in 1346, Catherine's husband, Frederick III, the Margrave of Meissen from the House of Wettin, asked for his wife's dowry, the Coburgish land called the ''Pflege Coburg''; but his father-in-law resisted the devolution, and Frederick III could not touch it until after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Stötzer
Werner Stötzer (born Sonneberg 2 April 1931, died Seelow, Altlangsow 22 July 2010) was a German artist and Sculpture, sculptor. For the last three decades of his life he lived and worked in Altlangsow (administratively part of Seelow) in the marshy Oderbruch region of Brandenburg. Life After training as a ceramics modeller at the :de:Fachschule für angewandte Kunst, Vocational Arts Academy in Sonneberg, Stötzer moved on to study between 1949 and 1951 at the Weimar Saxon-Grand Ducal Art School, Grand Ducal Arts Academy in Weimar, where his teachers included Heinrich Domke, Hans van Breek and Siegfried Tschiersky. Because of a reorganisation at the Weimar academy he then transferred to Dresden where he continued his studies at the Dresden Academy of Fine Arts, city's Academy of Fine Arts from 1951 till 1953, taught by :de:Eugen Hoffmann, Eugen Hoffmann and Walter Arnold (German sculptor), Walter Arnold. Between 1954 and 1958 her was a "Master Schoolman" (''Meisterschüler'') wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tankred Dorst
Tankred Dorst (19 December 1925 – 1 June 2017) was a German playwright and storyteller. Dorst lived and worked in Munich. His farces, parables, one-act-plays and adaptations were inspired by the theatre of the absurd and the works of Ionesco, Giraudoux and Beckett. His monumental drama ''Merlin oder das wüste Land'', which was premiered in 1981 in Düsseldorf, has been compared to Goethe's ''Faust''. Some critics see it as the first major drama of the 1980s. In his tribute to Tankred Dorst on the occasion of the conferment of the Georg Büchner Prize in 1990, Georg Hensel remarked that Dorst's plays all have a direct connection to the present: "For 30 years Dorst's plays have responded to the great transformations. He has always been a companion to the times." Dorst first directed the '' Ring of the Nibelung'' in Bayreuth in 2006. Biography Tankred Dorst was born in Oberlind in Thuringia, Germany. Conscripted into the German army as a pupil at the age of 17, he was so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Sollmann
Friedrich Wilhelm Sollmann (1 April 1881 – 6 January 1951), later William Frederick Sollmann, was a German journalist, politician, and interior minister of the Weimar Republic. In 1919, he was on the staff of the German delegation that was to receive the Treaty of Versailles. In 1933, he emigrated and eventually moved to the United States where he became an advocate for the peaceful resolution of conflicts. Life Early life in the German Empire Wilhelm Sollmann was born on 2 April 1881 in , Saxe-Meiningen (today a part of Sonneberg, Thuringia). His father was Johan Jakob Sollmann, a brewer and farmer in Oberlind and after 1889 tenant of the ''Ratskeller'' at Coburg. His mother was Christiane Sollmann, inn keeper. After the move to Coburg, Wilhelm attended the Casimirianum gymnasium from 1891 to 1897, when he had to leave due to the family's financial difficulties. That year, his family moved to Cologne. There, he began work as an apprentice (''kaufmännische Lehre''). From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a bank (geography), left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking, hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof, Germany, Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Bernreuther
Werner Bernreuther (6 December 1941 – 17 September 2024) was a German actor, singer-songwriter, writer, poet, translator and painter. Biography Bernreuther trained as an electrician, studied 1965–1969 at the Academy of Dramatic Art in Leipzig and was then committed to the stages Freiberg and Gera. Bernreuther received Chanson lessons from Heinrich Pohle and Fania Fénelon. At the 4th Chanson days of the GDR, he was awarded the prize of the Writers' Union of the German Democratic Republic. Bernreuther sings partly in his native Itzgründisch dialect and mixed "folk song-like structure with intellectual thinking." In the 1980s, he made radio and television productions, inter alia in Rund, Liedercircus '86, Pfundgrube und Liederkarussell. Bernreuther was abroad, inter alia in Romania on tour. He studied 1979–1982 at the Literature Institute in Leipzig and had since 1981 held a lectureship for Chanson at the University of Music and Theatre Leipzig and is part of the Leip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |