|
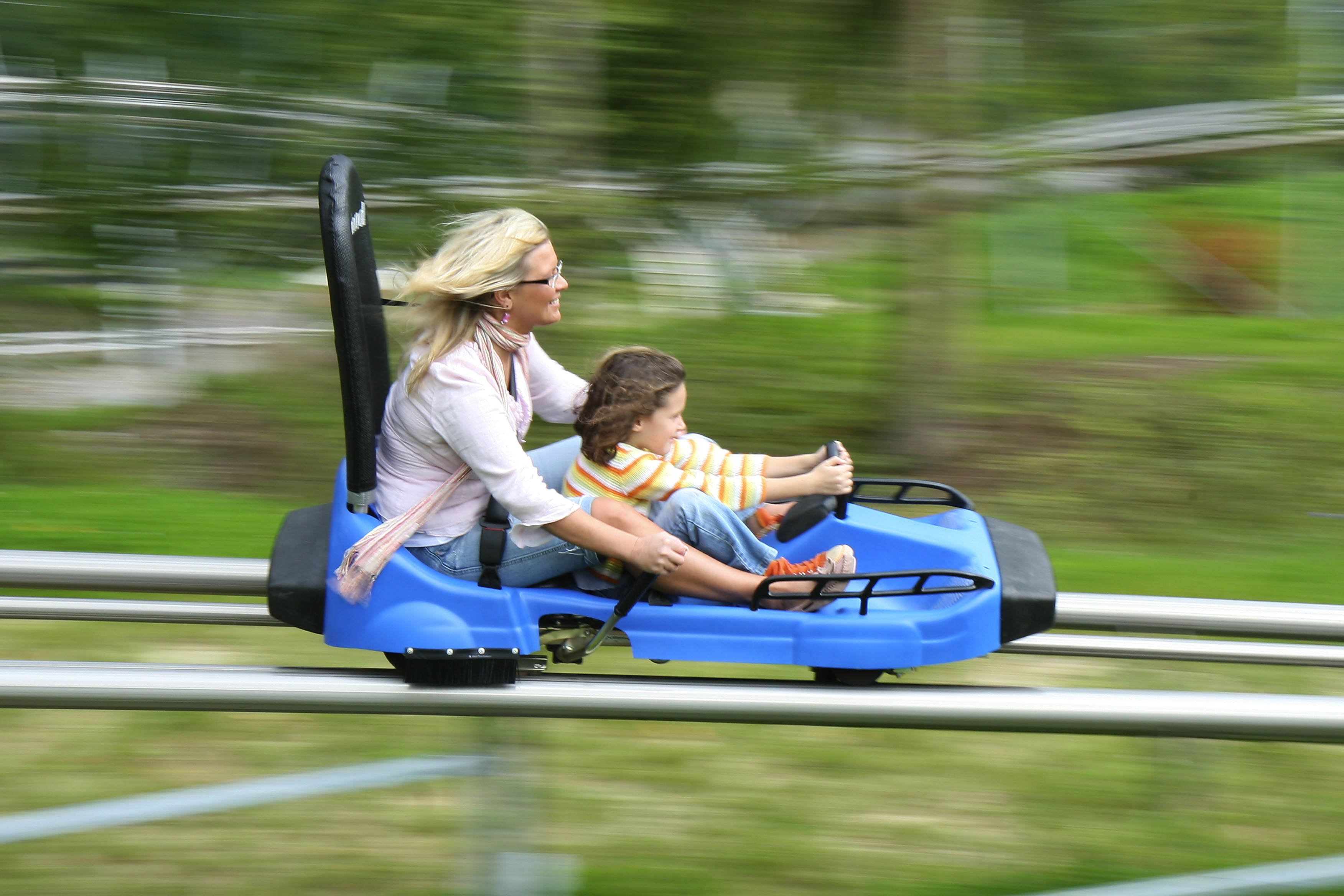
Sommerrodelbahn
A summer toboggan is an amusement or recreational ride which uses a bobsled-like sled or cart to run down a track usually built on the side of a hill. There are two main types: an alpine coaster or mountain coaster is a type of roller coaster where the cart runs on rails and is not able to leave the track, whereas with an alpine slide the cart simply runs on a smooth concave track usually made of metal, concrete or fiberglass. Both of these are sometimes denoted with the German term, ''sommerrodelbahn''. They are often built by ski resorts in order to use existing winter infrastructure and provide additional summer income, although some installations are part of amusement parks or are standalone. , the longest summer toboggan in the world is the long ''Tobotronc'' alpine coaster at ''Naturlandia'' in Andorra. The highest in the world is the long Glacier 3000 alpine coaster in Gstaad, Switzerland which starts at an elevation of . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Rides
Amusement rides, sometimes called carnival rides, are mechanical devices or structures that move people to create fun and enjoyment. Rides are often perceived by many as being scary or more dangerous than they actually are. This could be due to the design, having acrophobia, or from hearing about accidents involving rides that are similar. For some, the adrenaline associated with riding amusement rides is part of the experience. They are common at most annual events such as Fair, fairs, traveling carnivals, and Circus, circuses around the world. Sometimes music festivals and concerts also host amusement park rides. Types of rides * Flat rides are usually those that move their passengers on a plane generally parallel to the ground, such as rides that spin around a vertical axis, like carousels and twist (ride), twists; and ground-level rides such as bumper cars. The term is also used to refer to amusement rides that are not classified as dark rides, rollercoasters, transport r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifelpark Coaster
The Eifelpark is a wildlife and leisure park in Gondorf (municipality), Gondorf near Bitburg in the Eifel mountains of Germany. History In 1964 the Eifelpark was first opened under the name, ''Hochwildpark Eifel'' ("Eifel Mountain Wildlife Park"), as the first open-air wildlife enclosure in Germany. With the introduction of brown bears in 1969, Berlin took on the sponsorship of the bear gorge. In 1975 the then Minister-President of Rhineland-Palatinate, Helmut Kohl, opened the new mountain wildlife park in the Eifelpark. In the following years other attractions were added (such as the Slide Paradise, roller coaster, Eifel Express, Hüpfkissen, all weather rodelbahn, etc.). Since 2004 the Eifelpark, which had hitherto been run together with the Kurpfalz Park and the Panorama Park Sauerland Wildpark, Panorama Park, has been managed from Haan (near Düsseldorf). In early 2009, six Canadian Eastern wolf, timber wolves were introduced to the enclosure next to the renaturalised bear g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amusement Rides By Type
Amusement is the state of experiencing humorous and entertaining events or situations while the person or animal actively maintains the experience, and is associated with enjoyment, happiness, laughter and pleasure. It is an emotion with positive valence and high physiological arousal. Amusement is considered an "epistemological" emotion because humor occurs when one experiences a cognitive shift from one knowledge structure about a target to another, such as hearing the punchline of a joke. Emotions perceived overtime are focused on the daily dynamics of life as augment or blunt. The pleasant surprise that happens from learning this new information leads to a state of amusement which people often express through smiling, laughter or chuckling. Current studies have not yet reached consensus on the exact purpose of amusement, though theories have been advanced in the fields of psychology, psychiatry, and sociology. In addition, the precise mechanism that causes a given element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieders
Mieders is a municipality in the southern part of the district Innsbruck-Land in the Austrian state of Tyrol (state), Tyrol. It is located on the right side of the Stubaital 10.60 km south of Innsbruck. History Founded in 1100, the scattered village is located on a gently rising slope of the valley at the foot of the 2718 m high Serles. Inhabited from the early Middle Ages, the centre has houses decorated with baroque frescoes. Population Tourism Two seasonal tourist resorts are located directly at the bottom of the skiing and hiking area Serlesbahnen. The slopes are also known for a summer alpine coaster (monorail), which extends from the top station to the base station of the gondola, leading through the lower wooded slopes of the forest, parallel to the route of the cable car. Transportation The town of Innsbruck is connected by a bus line. Neighboring municipalities *Fulpmes *Mühlbachl *Schönberg im Stubaital *Telfes References External links Cities a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seat Belt
A seat belt, also known as a safety belt or spelled seatbelt, is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt reduces the likelihood of death or serious injury in a traffic collision by reducing the force of secondary impacts with interior strike hazards, by keeping occupants positioned correctly for maximum effectiveness of the airbag (if equipped), and by preventing occupants being ejected from the vehicle in a crash or if the vehicle rolls over. When in motion, the driver and passengers are traveling at the same speed as the vehicle. If the vehicle suddenly halts or crashes, the occupants continue at the same speed the vehicle was going before it stopped. A seat belt applies an opposing force to the driver and passengers to prevent them from falling out or making contact with the interior of the car (especially preventing contact with, or going ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braking Distance
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction. Background Most brakes commonly use friction between two surfaces pressed together to convert the kinetic energy of the moving object into heat, though other methods of energy conversion may be employed. For example, regenerative braking converts much of the energy to electrical energy, which may be stored for later use. Other methods convert kinetic energy into potential energy in such stored forms as pressurized air or pressurized oil. Eddy current brakes use magnetic fields to convert kinetic energy into electric current in the brake disc, fin, or rail, which is converted into heat. Still other braking methods even transform kinetic energy into different forms, for example by transferring the energy to a rotating flywheel. Brakes are generally a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Courtesy
Etiquette ( /ˈɛtikɛt, -kɪt/) can be defined as a set of norms of personal behavior in polite society, usually occurring in the form of an ethical code of the expected and accepted social behaviors that accord with the conventions and norms observed and practiced by a society, a social class, or a social group. In modern English usage, the French word ''étiquette'' (label and tag) dates from the year 1750 and also originates from the French word for "ticket," possibly symbolizing a person’s entry into society through proper behavior. There are many important historical figures that have helped to shape the meaning of the term as well as provide varying perspectives. History In , the Ancient Egyptian vizier Ptahhotep wrote ''The Maxims of Ptahhotep'' (), a didactic book of precepts extolling civil virtues such as truthfulness, self-control, and kindness towards other people. Recurrent thematic motifs in the maxims include learning by listening to other people, being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines. One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a physical quantity called ''rotation'' (or ''number of revolutions''), dimensionless, whose instantaneous rate of change is called ''rotational frequency'' (or ''rate of rotation''), with units of reciprocal seconds (s−1). A related but distinct quantity for describing rotation is ''angular frequency'' (or ''angular speed'', the magnitude of angular velocity), for which the SI unit is the radian per second (rad/s). Although they have the same dimensions (reciprocal time) and base unit (s−1), the hertz (Hz) and radians per second (rad/s) are special names used to express two different but proportional ISQ quantities: frequency and angular frequency, respectively. The conversions between a frequency and an angular frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Brake
Centrifugal (a key concept in rotating systems) may refer to: *Centrifugal casting (industrial), Centrifugal casting (silversmithing), and Spin casting (centrifugal rubber mold casting), forms of centrifigual casting *Centrifugal clutch *Centrifugal compressor * Centrifugal evaporator * Centrifugal extractor *Centrifugal fan *Centrifugal force *Centrifugal force (rotating reference frame) *Centrifugal governor *Centrifugal gun *Centrifugal micro-fluidic biochip *Centrifugal pump * Centrifugal railway * Centrifugal switch * Centrifugal-type supercharger * Centrifugal water–oil separator *Centrifugation * Reactive centrifugal force See also *Centrifuge *Fictitious force * History of centrifugal and centripetal forces *'' Centrifugal Funk'', a 1991 album by the Mark Varney Project *Centrifugal structure, a concept in theoretical linguistics – see Lucien Tesnière * Centripetal (other) * Centrifugal speciation - a variant model of allopatric speciation Allopatric speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toboggan Ride At Mutianyu Section Of Great Wall Of China
A toboggan is a simple sled used in snowy winter recreation. It is also a traditional form of cargo transport used by the Innu, Cree and Ojibwe of North America, sometimes part of a dog train. It is used on snow to carry one or more people (often children) down a hill or other slope for recreation, or as a rescue sled. Designs vary from simple, traditional models to modern engineered composites. A toboggan differs from most sleds or sleighs in that it has no runners or skis (or only low ones) on the underside. The bottom of a toboggan rides directly on the snow. Some parks include designated toboggan hills where ordinary sleds are not allowed and which may include toboggan runs similar to bobsleigh courses. Toboggans can vary depending on the climate and geographical region. Such examples are Tangalooma (Australia) where toboggans are made from Masonite boards and used for travelling down steep sand dunes at speeds up to . Etymology The term toboggan likely comes from an A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |