|
Sokolský Den
"Sokolský den" ("Sokol Day") also known as "Čtvrtého července" ("4th of July"), is a patriotic march composed by Czech music composer František Kmoch. It was composed in the period short after 1871, when he started working in local Czech Sokol movement, Sokol union in Kolín. Solely instrumental composition were later furnished by lyrics of unknown origin with origin in the United States, within the Czech Americans, Czech American diaspora. It were later written down by Young Czech Party, Young Czech politician and writer Karel Tůma (politician), Karel Tůma. An A-flat major composition later arranged by Czech composer Emil Štolc is written in ternary form. The first verse of the lyrics mentions the 4th of July, which refers to Sokol gymnastics gatherings on the date of the United States Independence Day (United States), Independence Day in Prague, promoted by Sokol organizations among the Czech diaspora in the United States. It promoted American liberal values and ideas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March (music)
A march, as a musical genre, is a piece of music with a strong regular rhythm which in origin was expressly written for marching to and most frequently performed by a military band. In mood, marches range from the moving death march in Wagner's ''Götterdämmerung'' to the brisk military marches of John Philip Sousa and the martial hymns of the late 19th century. Examples of the varied use of the march can be found in Beethoven's ''Eroica'' Symphony, in the Marches Militaires of Franz Schubert, in the Marche funèbre in Chopin's Sonata in B flat minor, the "'' Jäger March''" in the by Jean Sibelius, and in the Dead March in Handel's ''Saul''. Characteristics Marches can be written in any time signature, but the most common time signatures are , ('' alla breve'' , although this may refer to 2 time of Johannes Brahms, or ''cut time''), or . However, some modern marches are being written in or time. The modern march tempo is typically around 120 beats per minute. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
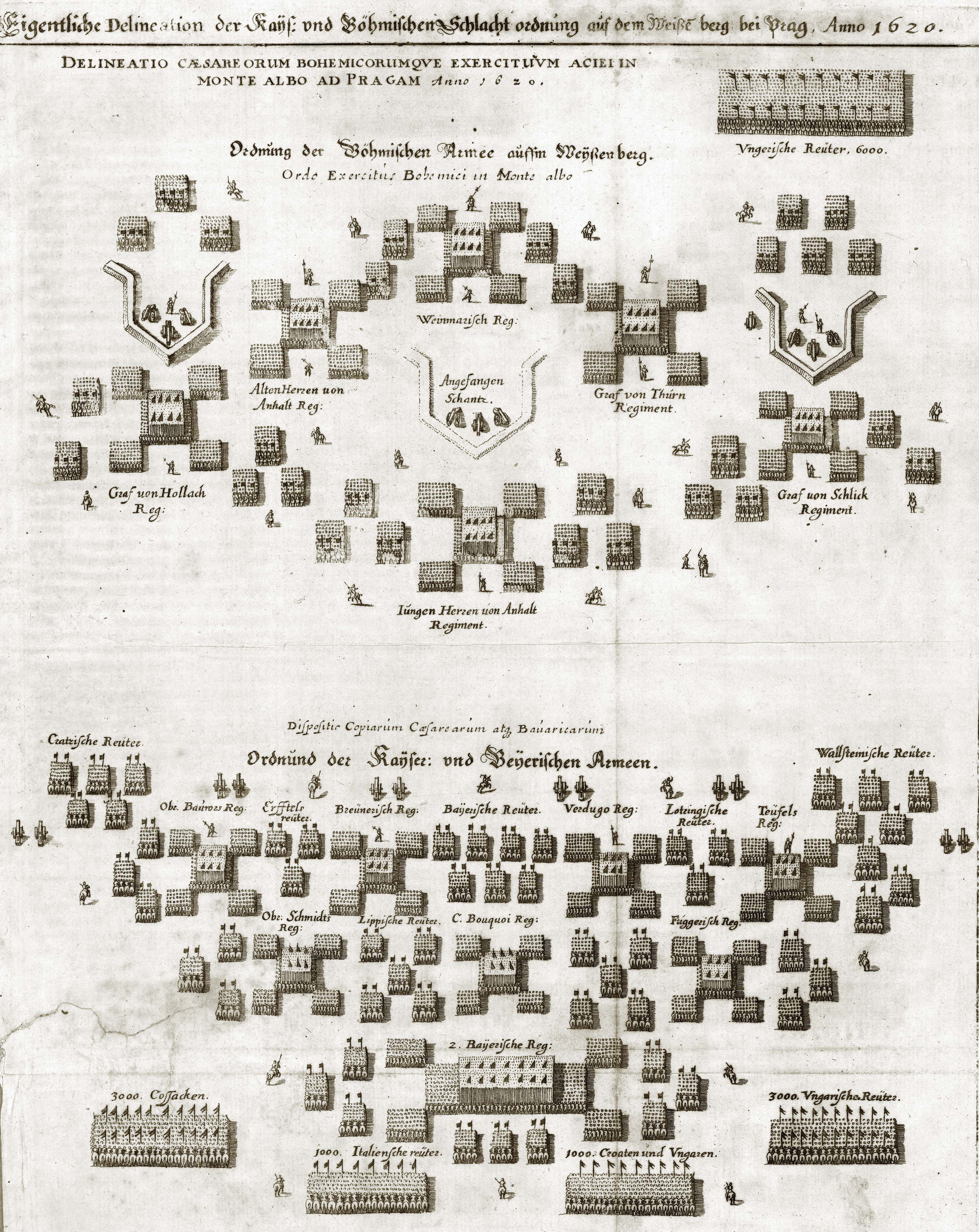
Battle Of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years. It was fought on 8 November 1620. An army of 21,000 Bohemians and mercenaries under Christian of Anhalt was defeated by 23,000 men of the combined armies of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, led by Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, Count of Bucquoy, and the German Catholic League led by Johann Tserclaes, later Count of Tilly, at Bílá Hora ("White Mountain") near Prague. Bohemian casualties were not severe but their morale collapsed and Imperial forces occupied Prague the next day. Prelude In the early 17th century most of the Bohemian estates, although under the dominion of the predominantly Catholic Holy Roman Empire, had large Protestant populations, and had been granted rights and protections allowing them varying degrees of religious and political freedom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Patriotic Songs
Czech may refer to: * Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe ** Czech language ** Czechs, the people of the area ** Czech culture ** Czech cuisine * One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus *Czech (surname) *Czech, Łódź Voivodeship, Poland *Czechville, Wisconsin, unincorporated community, United States See also * Čech, a surname * Czech lands * Czechoslovakia * List of Czechs * * * Check (other) * Czechoslovak (other) * Czech Republic (other) * Czechia (other) Czechia is the official short form name of the Czech Republic. Czechia may also refer to: * Historical Czech lands *Czechoslovakia (1918–1993) *Czech Socialist Republic (1969–1990) *Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (1939–1945) See also ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Songs
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems and confirm ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Čechie
Čechie is the personification of the Czech nation, which was used in the 19th century as reaction on personification of competing nationalism represented by Germania or Austria. See also *Flag and Coat of arms of the Czech Republic * Czech Vašek, personification of the Czechs * Deutscher Michel, personification of the German people Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ... References National personifications National symbols of the Czech Republic {{Europe-culture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Břevnov
Břevnov () is a cadastral district in the west of Prague, located in Prague 6. The district is home to the Břevnov Monastery (Czech: ''Břevnovský klášter''). On the territory of Břevnov stems Brusnice brook. Břevnov was first mentioned in the 10th century. In 1907 was promoted to the city and since 1921 then became part of the City of Prague. Apart from the Břevnov monastery, we can find other remarkable buildings on the area. The building of the Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences is located in the north-western of Břevnov. The legend of this institute was its former director Otto Wichterle Otto Wichterle (; 27 October 1913 – 18 August 1998) was a Czech chemist, best known for his invention of modern soft contact lenses. Wichterle was the author or co-author of approximately 180 patents and over 200 publications. The studie ..., to whom is devoted the monument in front of the building. Others are: Ladronka homestead, Host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strahov (Prague)
Strahov () is a district of Prague in the Czech Republic. It lies on the west bank of the Vltava, west of Petřín hill, Malá Strana and Hradčany. It is bordered by the districts of Břevnov, Smíchov, Košíře, Střešovice and Malá Strana. Description Strahov is home to the premonstratensian Strahov Monastery (), Štefánik's Observatory () and Great Strahov Stadium (), a former sports stadium that was once the largest in the world and famously hosted the spartakiáda gatherings.Scholastic Library Pub. (2006)Encyclopedia Americana vol. 30, p. 517, A smaller stadium, Stadion Evžena Rošického, currently home to football club SK Sparta Krč is in Strahov, as is a large accommodation block for the Czech Technical University in Prague. In Communist times, a radio frequency jammer was situated in the district to block the broadcasts of Radio Free Europe Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) is a media organization broadcasting news and analyses in 27 languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladislav Smoljak
Ladislav Smoljak (9 December 1931 – 6 June 2010) was a Czechs, Czech film and theater director, actor and screenwriter. Biography Smoljak was born in Prague. He tried to study at an art academy but failed the admission process. He went on to study physics and mathematics, and later worked as journalist and scriptwriter. Together with Zdeněk Svěrák he founded the ''Theater of Jára Cimrman'' (''Divadlo Járy Cimrmana'', ''DJC'') in Prague, named after a fictitious genius. Smoljak wrote scripts and directed several films; these became very successful in the Czech Republic. He died of cancer on 6 June 2010 in Kladno. Filmography Screenplay * 1974 ''Jáchyme, hoď ho do stroje!'' (with Zdeněk Svěrák and Oldřich Lipský) * 1976 ''Marečku, podejte mi pero!'' (with Zdeněk Svěrák) * 1976 ''Na samotě u lesa'' (with Zdeněk Svěrák) * 1978 ''Ball Lightning (film), Ball Lightning'' (with Zdeněk Svěrák and Zdeněk Podskalský) * 1980 ''The Hit (1981 film), Trhák'' (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zdeněk Svěrák
Zdeněk Svěrák (born 28 March 1936) is a Czech actor, humorist, playwright and scriptwriter, and one of the most well-known and popular Czech cultural personalities. Since 1968 he has appeared in 32 films. Career In 1958, he graduated in Czech language and Czech literature, literature from the Faculty of Education of Charles University in Prague. His work consists of more than 300 musical texts and plays, and he has appeared in 32 feature films. Among his film scripts are the Academy Award-winning ''Kolya (film), Kolya'' and ''The Elementary School'', both directed by his son Jan Svěrák as well as ''My Sweet Little Village''. With his close friend Ladislav Smoljak and their radio colleague Jiří Šebánek, he created the fictional polymath Jára Cimrman for the radio programme ''Vinárna U pavouka'' in 1966. Cimrman was voted Největší Čech, The Greatest Czech in 2005, but barred from winning because of being a fictional character. Zdeněk Svěrák also founded a charity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobytí Severního Pólu
''Dobytí severního pólu'' (full title: ''Dobytí severního pólu Čechem Karlem Němcem 5. dubna 1909'', in English: ''The Conquest of the North Pole by the Czech Karel Němec on 5 April 1909'') is a comedy written allegedly by fictional Czech polymath, Jára Cimrman. Its real authors are Zdeněk Svěrák and Ladislav Smoljak. The work was premiered on 25 October 1985 in ''Divadlo Jiřího Wolkera'' in Prague. The play is about a fictional Czech Arctic expedition who conquered the North Pole one day before Robert Peary. As with the other plays supposedly authored by Cimrman, it satirizes Czech national psychology and patriotic clichés, using many puns, historical hoaxes and the distancing effect. It was published as a book, CD, DVD and VHS, and was translated into English by Craig Cravens and by Emilia Machalová and Brian Stewart. The premiere of the Machalová and Stewart version of ''Conquest of The North Pole'' was premiered on April 16, 2016, at the Jára Cimrmana Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Hus
Jan Hus (; ; 1369 – 6 July 1415), sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as ''Iohannes Hus'' or ''Johannes Huss'', was a Czechs, Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and the inspiration of Hussites, Hussitism, a key predecessor to Protestantism, and a seminal figure in the Bohemian Reformation. Hus is considered to be the first Church reformer, even though some designate the theorist John Wycliffe. His teachings had a strong influence, most immediately in the approval of a reformed Bohemian religious denomination and, over a century later, on Martin Luther. After being ordained as a Catholic priest, Hus began to preach in Prague. He opposed many aspects of the Catholic Church in Bohemia, such as its views on ecclesiology, simony, the Eucharist, and other theological topics. Hus was a master, dean and rector at the Charles University in Prague between 1409 and 1410. Antipope Alexander V, Alexander V issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consisted of two sovereign states with a single monarch who was titled both the Emperor of Austria and the King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War, following wars of independence by Hungary in opposition to Habsburg rule. It was dissolved shortly after Dissolution of Austria-Hungary#Dissolution, Hungary terminated the union with Austria in 1918 at the end of World War 1. One of Europe's major powers, Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe (after Russian Empire, Russia) and the third-most populous (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |