|
Sogdian Whirl Dance
The Sogdian Whirl dance or Sogdian Whirl (胡旋, ''Húxuăn'', "Whirling Barbarian", also 胡旋舞, ''Húxuănwǔ'', "Dance of the Whirling Barbarian", sometimes rendered as "Whirling barbarian" but known as "Sogdian Whirl dance" or simply "Sogdian whirl" to Western scholars) was a Sogdian dance imported into China in the first half of the first millennium AD. The dance was imitated by the Chinese and became popular in China, where it went on to be performed at court. History The Sogdian Whirl and other similar, imported dances were popular in China during the Tang dynasty, especially in Chang'an and Luoyang. The Sogdian merchant-dancers, who performed different dances but were especially renowned for this dance, were very famed in China. In the Sogdian Whirl, a young woman was spinning inside a circle. The Sogdian Whirl became popular in China. It was performed both in the Chinese court and in China itself. Sources from the Tang dynasty such as the Old Book of Tang attest to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim Flask With Central Asian Dancers, China, 6th Century CE
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). An asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in print and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten, though more complex forms exist. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk was already in use as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two-thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is known to have also used the asteriskos to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogdian Art
Sogdian art refers to art produced by the Sogdians, an Iranian peoples, Iranian people living mainly in ancient Sogdia, present-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, who also had a large diaspora living in China. Its apex was between the 5th and 9th centuries, and it consists of a rich body of pre-Muslim Central Asian visual arts. New finds recovered in the past decades allowed scholars to achieve a better understanding of Sogdian art. Sogdians are best known for their painting, although they excelled also in other fields, such as metalworking and music. Their metalworking, which influenced the Chinese, is sometimes confused with Sasanian metalwork. However, characteristics of Sogdian metalwork, differentiating it from Sasanian metalwork, have been established; for example, with respect to Sasanian metalwork, the designs of Sogdian vessels are more dynamic, and their productions less massive. They differ in technique and shape, as well as iconography. The Sogdia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogdians ...
:''This category lists articles related to historical Iranian peoples'' Historical Peoples Iranian Iranian Iranian Iranian () may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Iran ** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran ** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia ** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang China
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranians In China
Iranian people, such as Persians and Sogdians, have lived in China throughout various periods in history. History The Parthian Iranian An Shigao introduced Hinayana Buddhism to China, while the Kushan Lokaksema introduced Mahayana Buddhism. Chorasmians Shams al-Din was an Iranian of Khwarezmian origin from Bukhara, and was appointed by the Mongols to serve as the first provincial governor of Yunnan, in southwestern China. He was allegedly descended from 'Alī bin Abī Tālib and the Prophet, Sayyid Ajall's father was Kamāl al-Dīn and his grandfather was Shams al-Dīn 'Umar al-Bukhārī. He served the court of the Yuan dynasty at Yanjing (modern day Beijing). Later, he was in charge of Imperial finances in 1259, sent to Yunnan by Kublai Khan after conquering the Kingdom of Dali in 1274. After his death, Sayyid was given the posthumous name Zhongyi (忠懿). Later, the imperial court conferred the title "Prince of Xianyang" (咸陽王) and the posthumous name Zhonghui (� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyang
Anyang ( zh, s=安阳, t=安陽; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan, China. Geographical coordinates are 35° 41'~ 36° 21' north latitude and 113° 38'~ 114° 59' east longitude. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively. Anyang had a total population of 5,477,614 as of the 2020 Chinese census, 2020 census, 2,675,523 of whom lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of four urban districts and Anyang and Tangyin counties, now largely agglomerated with the city proper. Anyang is the location of the ancient city of Yinxu, Yin, which was the capital of the Shang dynasty and the first stable capital of China. As the ancient capital of the Seven Dynasties and one of the birthplaces of Chinese civilization, Anyang is rich in historical and cultural resources and has a number of world-class and national historical sites. At the end of 1986, it was recogniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
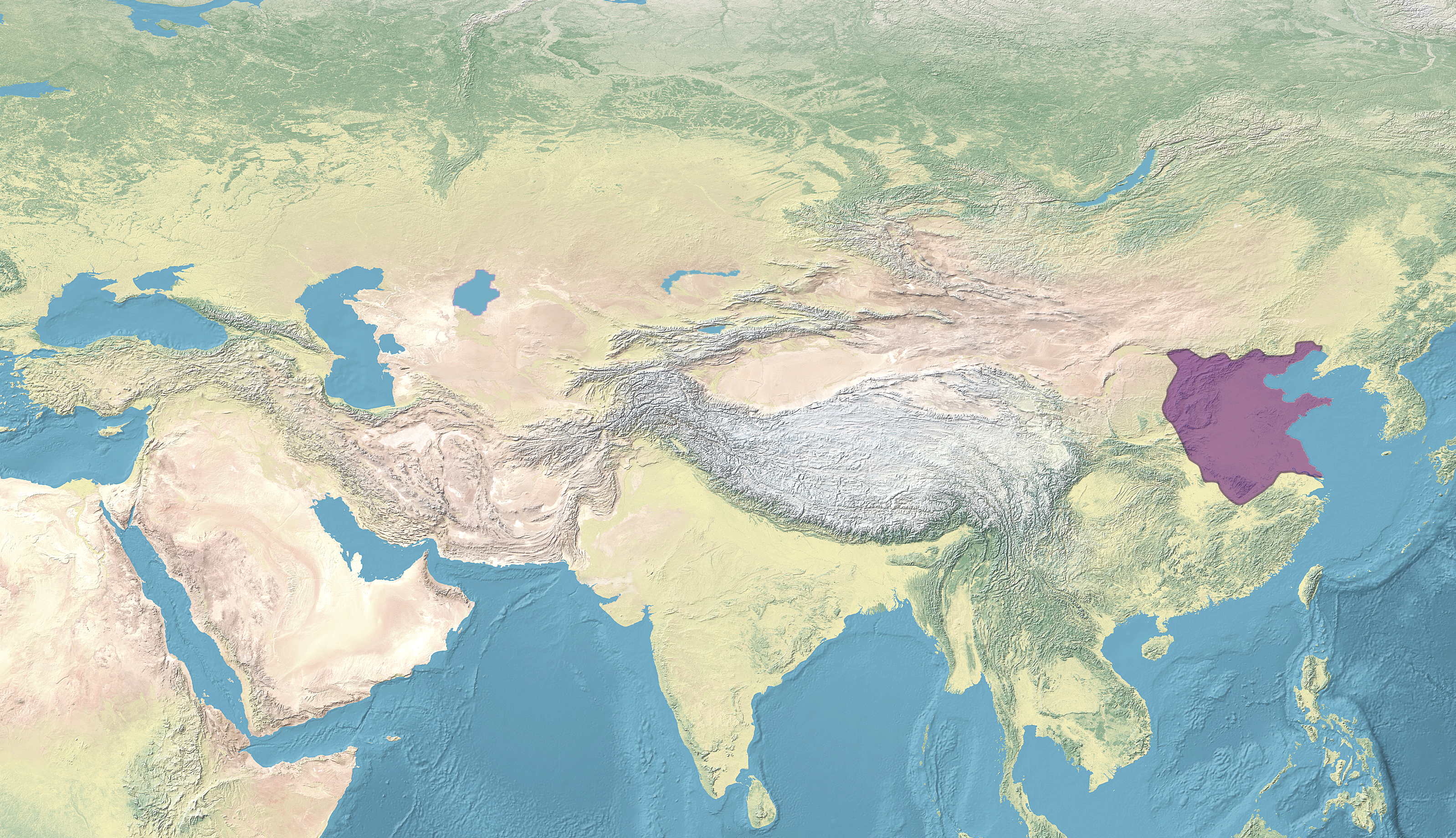
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Qi
Qi, known as the Northern Qi (), Later Qi (後齊) or Gao Qi (高齊) in historiography, was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty and one of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It ruled the eastern part of northern China from 550 to 577. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wenxuan of Northern Qi, Gao Yang (Emperor Wenxuan), and was eventually conquered by the Xianbei-led Northern Zhou, Northern Zhou dynasty in 577. History Northern Qi was the successor state of the Chinese Xianbei state of Eastern Wei and was founded by Emperor Wenxuan of Northern Qi, Emperor Wenxuan. Emperor Wenxuan had a Han Chinese, Han father of largely Xianbei culture, Gao Huan, and a Xianbei mother, Lou Zhaojun. As Eastern Wei's powerful minister Gao Huan was succeeded by his sons Gao Cheng and Gao Yang, who took the throne from Emperor Xiaojing of Eastern Wei in 550 and established Northern Qi as Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huteng
Huteng ( zh, s=胡腾, t=胡騰, p=Húténg, l=Nomadic leap, also 胡腾舞, ''Húténgwǔ'', "Dance of the Nomadic leap") was the Chinese term for a type of dance that originated in Central Asia, especially among the Sogdians and the region of Tashkent (石國, Shíguó). The dance was well known during the Tang dynasty, and there are numerous depictions of it in works of art. The dance was characterized by spinning, leaps and backflips. The dancers would particularly make summersaults, first planting their feet firmly on the carpet, tilting their face upward and arching their body, then lift their arms and jump backward to the sound of flutes and the pipa. Another famous dance from Central Asia was the Sogdian Whirl (胡旋, ''Húxuăn'', "Whirling Nomads", also 胡旋舞, ''Húxuănwǔ'', "Dance of the Whirling Nomads", sometimes rendered as "Whirling Nomads" but known as "Sogdian Whirl dance" or simply "Sogdian whirl" to Western scholars), in which a young woman was spinning i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged period of political division since the War of the Eight Princes. The Sui endeavoured to rebuild the country, re-establishing and reforming many imperial institutions; in so doing, the Sui laid much of the foundation for the subsequent Tang dynasty, who after toppling the Sui would ultimately preside over golden ages of China, a new golden age in Chinese history. Often compared to the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), the Sui likewise unified China after a prolonged period of division, undertook wide-ranging reforms and construction projects to consolidate state power, and collapsed after a brief period. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, Yang Jian (Emperor Wen), who had been a member of the military aristocracy that had developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Guifei
Yang Yuhuan (; 719 – 15 July 756Volume 218 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' recorded that Yang was killed on the ''bing'shen'' day of the 6th month of the 1st year of the ''Zhi'de'' era of Tang Suzong's reign. This date corresponds to 15 Jul 756 on the Gregorian calendar.), often known as Yang Guifei (, with ''Guifei'' being the highest rank for Imperial Chinese harem system, imperial consorts during her time), and known briefly by the Taoist nun name Taizhen (), was the beloved consort of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang during his later years. She is known as one of the Four Beauties, Four Beauties of ancient China. During the An Lushan Rebellion, as Emperor Xuanzong and his cortege were fleeing from the capital Chang'an to Chengdu, the emperor's guards demanded that he put Yang to death because they blamed the rebellion on her cousin Yang Guozhong and the rest of her family. The emperor capitulated and reluctantly ordered his attendant Gao Lishi to supervise her forced suicide. Background Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hawaiʻi Press
The University of Hawaiʻi Press is a university press that is part of the University of Hawaiʻi. The University of Hawaiʻi Press was founded in 1947, publishing research in all disciplines of the humanities and natural and social sciences in the regions of Asia and the Pacific. In addition to scholarly monographs, the press publishes educational materials and reference works such as dictionaries, language texts, classroom readers, atlases, and encyclopedias. The press is currently a member of the Association of University Presses. History The press was established in 1947 at the initiative of University of Hawaiʻi president Gregg M. Sinclair. Its first publications included a reprint of '' The Hawaiian Kingdom'' by Ralph Kuykendall and ''Insects of Hawaii,'' by Elwood C. Zimmerman, both of which have become classics. Other enduring classics from its early years include the ''Hawaiian-English Dictionary,'' by Mary Kawena Pukui and Samuel Elbert, first published in 1957, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |