|
Socially Responsible Marketing
Socially responsible marketing is a marketing philosophy that a company should take into consideration; "What is in the best interest of society in the present and long term?"Armstrong, Gary, and Philip Kotler. ''Principles of Marketing''. 12th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc., 2008 Overview Socially responsible marketing is critical of excessive consumerism and environmental damages caused by corporations. It is based on the idea that market offerings must not be only profit-driven, but they must also reinforce social and ethical values for the benefit of citizens. The idea of socially responsible marketing is sometimes viewed as an extension of the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). CSR is promoted as a business model to help companies self-regulate, recognizing that their activities impact an assortment of stakeholders, including the general public.Ferrell, O. C., and Michael D. Hartline. Marketing strategy. Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce. Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or manufacturer. Products can be marketed to other businesses (B2B Marketing, B2B) or directly to consumers (B2C). Sometimes tasks are contracted to dedicated marketing firms, like a Media agency, media, market research, or advertising agency. Sometimes, a trade association or government agency (such as the Agricultural Marketing Service) advertises on behalf of an entire industry or locality, often a specific type of food (e.g. Got Milk?), food from a specific area, or a city or region as a tourism destination. Market orientations are philosophies concerning the factors that should go into market planning. The marketing mix, which outlines the specifics of the product and how it will be sold, including the channels that will be used to adverti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a Legal personality, legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether Natural person, natural, Juridical person, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared goals. Over time, companies have evolved to have the following features: "separate legal personality, limited liability, transferable shares, investor ownership, and a managerial hierarchy". The company, as an entity, was created by the State (polity), state which granted the privilege of incorporation. Companies take various forms, such as: * voluntary associations, which may include nonprofit organizations * List of legal entity types by country, business entities, whose aim is to generate sales, revenue, and For-profit, profit * financial entities and banks * programs or educational institutions A company can be created as a legal person so that the company itself has limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships ( social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent members. Human social structures are complex and highly cooperative, featuring the specialization of labor via social roles. Societies construct roles and other patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts acceptable or unacceptable—these expectations around behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. So far as it is collaborative, a society can enable its members to benefit in ways that would otherwise be difficult on an individual basis. Societies vary based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumerism
Consumerism is a socio-cultural and economic phenomenon that is typical of industrialized societies. It is characterized by the continuous acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing quantities. In contemporary consumer society, the purchase and the consumption of products have evolved beyond the mere satisfaction of basic human needs, Stearns, Peter (2006). ''Consumerism in World History''. 2nd ed. Routledge. p. vii–viii. transforming into an activity that is not only economic but also cultural, social, and even identity-forming. It emerged in Western Europe and the United States during the Industrial Revolution and became widespread around the 20th century. In economics, consumerism refers to policies that emphasize consumption. It is the consideration that the free choice of consumers should strongly inform the choice by manufacturers of what is produced and how, and therefore influence the economic organization of a society. Consumerism has been criticized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and Business ethics, business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to Duty, duties, like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Differentiation
In economics and marketing, product differentiation (or simply differentiation) is the process of distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market. This involves differentiating it from competitors' products as well as from a firm's other products. The concept was proposed by Edward Chamberlin in his 1933 book, '' The Theory of Monopolistic Competition''. Rationale Firms have different resource endowments that enable them to construct specific competitive advantages over competitors. Resource endowments allow firms to be different, which reduces competition and makes it possible to reach new segments of the market. Thus, differentiation is the process of distinguishing the differences of a product or offering from others, to make it more attractive to a particular target market. Although research in a niche market may result in changing a product in order to improve differentiation, the changes themselves are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
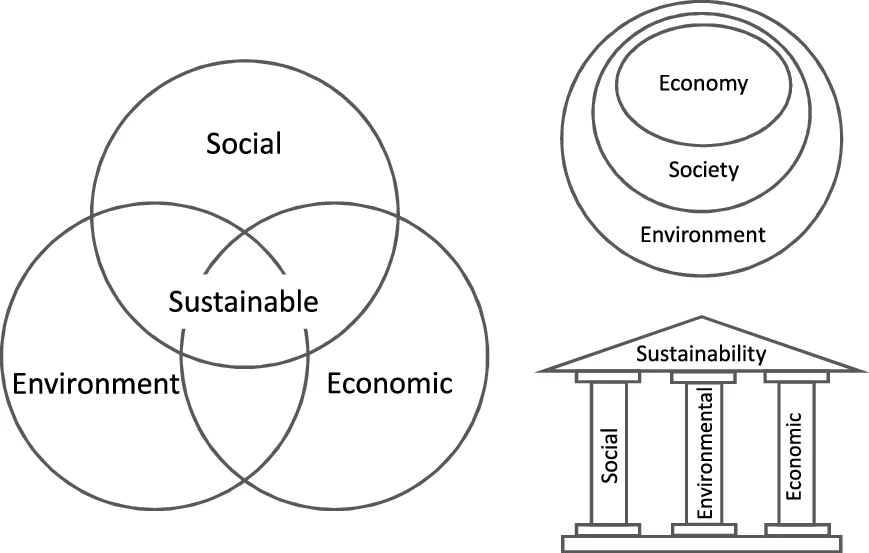
Environmental Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental issues, environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Marketing
Social marketing is a marketing approach which focuses on influencing behavior with the primary goal of achieving the "common good". It utilizes the elements of commercial marketing and applies them to social concepts. However, to see social marketing as only the use of standard commercial marketing practices to achieve non-commercial goals is an oversimplified view. Social marketing has existed for some time but has only started becoming a common term in recent decades. It was originally done using newspapers and billboards and has adapted to the modern world in many of the same ways commercial marketing has. The most common use of social marketing in today's society is through social media. Traditional commercial marketing aims are primarily financial, though they can have positive social effects as well. In the context of public health, social marketing would promote general health, raise awareness and induce changes in behavior. Social marketing is described as having " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cause Related Marketing
Cause marketing is marketing done by a for-profit business that seeks to both increase profits and to better society in accordance with corporate social responsibility, such as by including activist messages in advertising. A similar phrase, cause-related marketing, usually refers to a subset of cause marketing that involves the cooperative efforts of a for-profit business and a non-profit organization for mutual benefit. A high-profile form of cause-related marketing occurs at checkout counters when customers are asked to support a cause with a charitable donation. Cause marketing differs from corporate giving (philanthropy), as the latter generally involves a specific donation that is tax-deductible, while cause marketing is a promotional campaign not necessarily based on a donation. History The United States Congress passed the Endangered Species Act on December 14, 1973. In response, 7-Eleven sold Endangered Species Cups, and donated one cent from the sale of each cup to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Marketing
Green marketing refers to the marketing of products that are considered environmentally safe. It encompasses a broad range of activities, including product modification, changes to the production process, sustainable packaging, and modifications to advertising. However, defining ''green marketing'' is not a simple task. Other terms that are often used interchangeably are ''environmental marketing'' and ''ecological marketing''. Green, environmental and eco-marketing are part of the recent marketing approaches which do not just refocus, adjust or enhance existing marketing thinking and practice, but also seek to challenge those approaches and provide a substantially different perspective. More specifically, these approaches seek to address the lack of fit between marketing as it is currently practiced and the ecological and social realities of the wider marketing environment. The legal implications of marketing claims call for caution or overstated claims can lead to regulatory or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns". Standard indicators of the quality of life include wealth, employment, the environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, social belonging, religious beliefs, safety, security and freedom. QOL has a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, politics and employment. Health related QOL (HRQOL) is an evaluation of QOL and its relationship with health. Engaged theory One approach, called the engaged theory, outlined in the journal of ''Applied Research in the Quality of Life'', posits four domains in assessing quality of life: ecology, economics, politics and culture. In the domain of culture, for example, it includes the following subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |