|
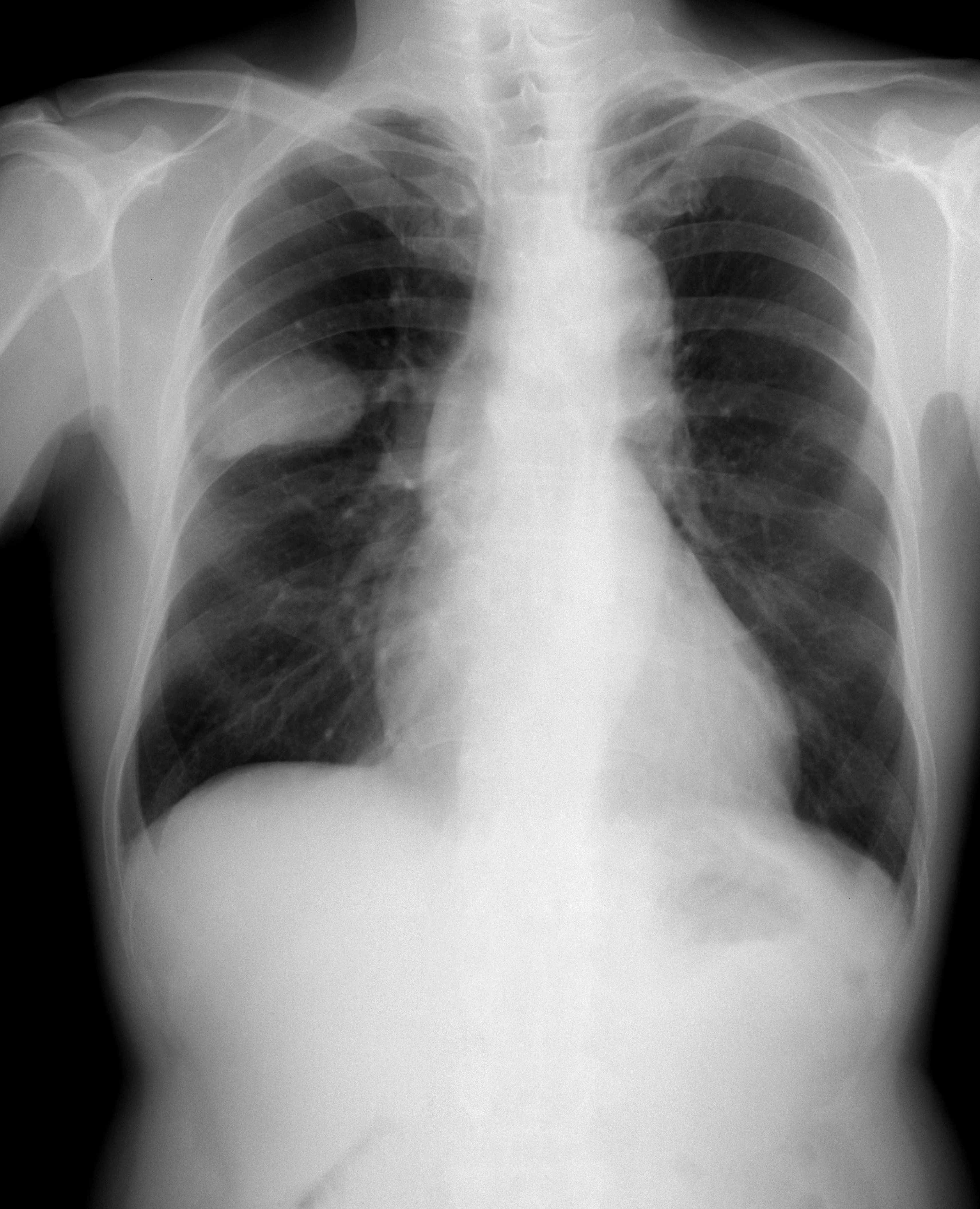
Small-cell Carcinoma
Small-cell carcinoma, also known as oat cell carcinoma, is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma is more aggressive, with a shorter doubling time, higher growth fraction, and earlier development of metastases. Extensive stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is classified as a rare disorder. Ten-year relative survival rate (combined limited and extensive SCLC) is 3.5% (4.3% for women, 2.8% for men). Survival can be higher or lower based on a combination of factors including stage, age, sex and race. While all lung cancers are associated with tobacco smoking, SCLC is very strongly associated with tobacco smoking. Types Lung cancer Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) has long been divided into two clinicopathological stages, termed limited stage (LS) and extensive stage (ES). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological stress (along with its precursor corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus). Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol and androgens by the zona fasiculata and zona reticularis, respectively. ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms. Deficiency of ACTH is an indicator of secondary adrenal insufficiency (suppressed production of ACTH due to an impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, cf. hypopituitarism) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (disease of the hypothalamus, with a decrease in the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)). Conversely, chronically e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Hormone
An ''ectopic hormone'' is a hormone produced by tumors derived from tissue that is not typically associated with its production. On the other hand, the term entopic is used to refer to hormones produced by tissue in tumors that are normally engaged in the production of that hormone. The excess hormone secretion is considered detrimental to the normal body homeostasis. This hormone production typically results in a set of signs and symptoms that are called a paraneoplastic syndrome A paraneoplastic syndrome is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) that is the consequence of a tumor in the body (usually a cancerous one). It is specifically due to the production of chemical signaling molecules (such as hormones or cytokin .... Some clinical syndromes caused by ectopic hormone production include: References {{reflist * Physiology Endocrinology Cell signaling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Cell
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bring about an integration between the nervous system and the endocrine system, a process known as neuroendocrine integration. An example of a neuroendocrine cell is a cell of the adrenal medulla (innermost part of the adrenal gland), which releases adrenaline to the blood. The adrenal medullary cells are controlled by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. These cells are modified postganglionic neurons. Autonomic nerve fibers lead directly to them from the central nervous system. The adrenal medullary hormones are kept in vesicles much in the same way neurotransmitters are kept in neuronal vesicles. Hormonal effects can last up to ten times longer than those of neurotransmitters. Sympathetic nerve fiber impulses stimulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, typically blood tests that check for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Those with high levels of PSA in their blood are at increased risk for developing prostate cancer. Diagnosis requires a prostate biopsy, biopsy of the prostate. If cancer is present, the pathologist assigns a Gleason score; a higher score represents a more dangerous tumor. Medical imaging is performed to look for cancer that has spread outside the prostate. Based on the Gleason score, PSA levels, and imaging results, a cancer case is assigned a cancer staging, stage 1 to 4. A higher stage signifies a more advanced, more dangerous disease. Most prostate tumors remain small and cause no health problems. These are managed with active surveillance of prostate cancer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkel-cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin, and trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Factors involved in the development of MCC include the Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV or MCV), a weakened immune system, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Merkel cell carcinoma usually arises on the head, neck, and extremities, as well as in the perianal region and on the eyelid. It is more common in people over sixty years old, Caucasian people, and males. MCC is less common in children. Signs and symptoms Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) usually presents as a firm nodule (up to 2 cm diameter) or mass (>2 cm diameter). These flesh-colored, red, or blue tumors typically vary in size from 0.5 cm (less than one-quarter of an inch) to more than 5 cm (2 inches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged airway cells gain the ability to multiply unchecked, causing the growth of a tumor. Without treatment, tumors spread throughout the lung, damaging lung function. Eventually lung tumors metastasize, spreading to other parts of the body. Early lung cancer often has no symptoms and can only be detected by medical imaging. As the cancer progresses, most people experience nonspecific respiratory problems: coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain. Other symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor. Those suspected of having lung cancer typically undergo a series of imaging tests to determine the location and extent of any tumors. Definitive diagnosis of lung cancer requires a biopsy of the suspected tumor be examined by a patholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Combined small cell lung carcinoma (or c-SCLC) is a form of multiphasic lung cancer that is medical diagnosis, diagnosed by a pathologist when a malignant tumor, arising from transformed cell (biology), cells originating in lung Tissue (biology), tissue, contains a component of small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) mixed with one or more components of any histological variant of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) in any relative proportion. In order to ensure that patients receive the proper treatment, it is critical that the pathologist, when making a diagnosis of lung cancer, reports the finding of small cell carcinoma, regardless of other components, because small cell carcinoma is considered the most aggressive of all the lung cancer variants, and its treatment is normally radically different than the other forms of lung cancer (see below). For epidemiological and statistical purposes, combined small cell carcinoma of the lung has been long classified as a subset of small cell c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung
Adenocarcinoma of the lung is the most common type of lung cancer, and like other forms of lung cancer, it is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. It is classified as one of several non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), to distinguish it from small cell lung cancer which has a different behavior and prognosis. Lung adenocarcinoma is further classified into several subtypes and variants. The signs and symptoms of this specific type of lung cancer are similar to other forms of lung cancer, and patients most commonly complain of persistent cough and shortness of breath. Adenocarcinoma is more common in patients with a history of cigarette smoking, and is the most common form of lung cancer in younger women and Asian populations. The pathophysiology of adenocarcinoma is complicated, but generally follows a histologic progression from cells found in healthy lungs to distinctly dysmorphic, or irregular cells. There are several distinct molecular and genetic path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous-cell Carcinoma Of The Lung
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lung is a histologic type of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It is the second most prevalent type of lung cancer after lung adenocarcinoma and it originates in the bronchi. Its tumor cells are characterized by a squamous appearance, similar to the one observed in epidermal cells. Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung is strongly associated with tobacco smoking, more than any other forms of NSCLC. Signs and symptoms Squamous-cell lung carcinoma share most of the signs and symptoms with other forms of lung cancer. These include worsening cough, including hemoptysis, chest pain, shortness of breath and weight loss. Symptoms may result from local invasion or compression of adjacent thoracic structures such as compression involving the esophagus causing dysphagia, compression involving the laryngeal nerves causing change in voice, or compression involving the superior vena cava causing facial edema. Distant metastases may also cause pain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |