|
Sleep In Fish
Whether fish sleep or not is an open question, to the point of having inspired the title of several popular science books. In birds and mammals, sleep is defined by eye closure and the presence of typical patterns of electrical activity in the brain, including the neocortex, but fish lack eyelids and a neocortex. Some species that always live in shoals or that swim continuously (because of a need for ram ventilation of the gills, for example) are suspected never to sleep. There is also doubt about certain blind species that live in caves. Other fish do seem to sleep, however, especially when purely behavioral criteria are used to define sleep. For example, zebrafish, tilapia, tench, brown bullhead, and swell shark become motionless and unresponsive at night (or by day, in the case of the swell shark); Spanish hogfish and blue-headed wrasse can even be lifted by hand all the way to the surface without evoking a response. On the other hand, sleep patterns are easily disrupted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
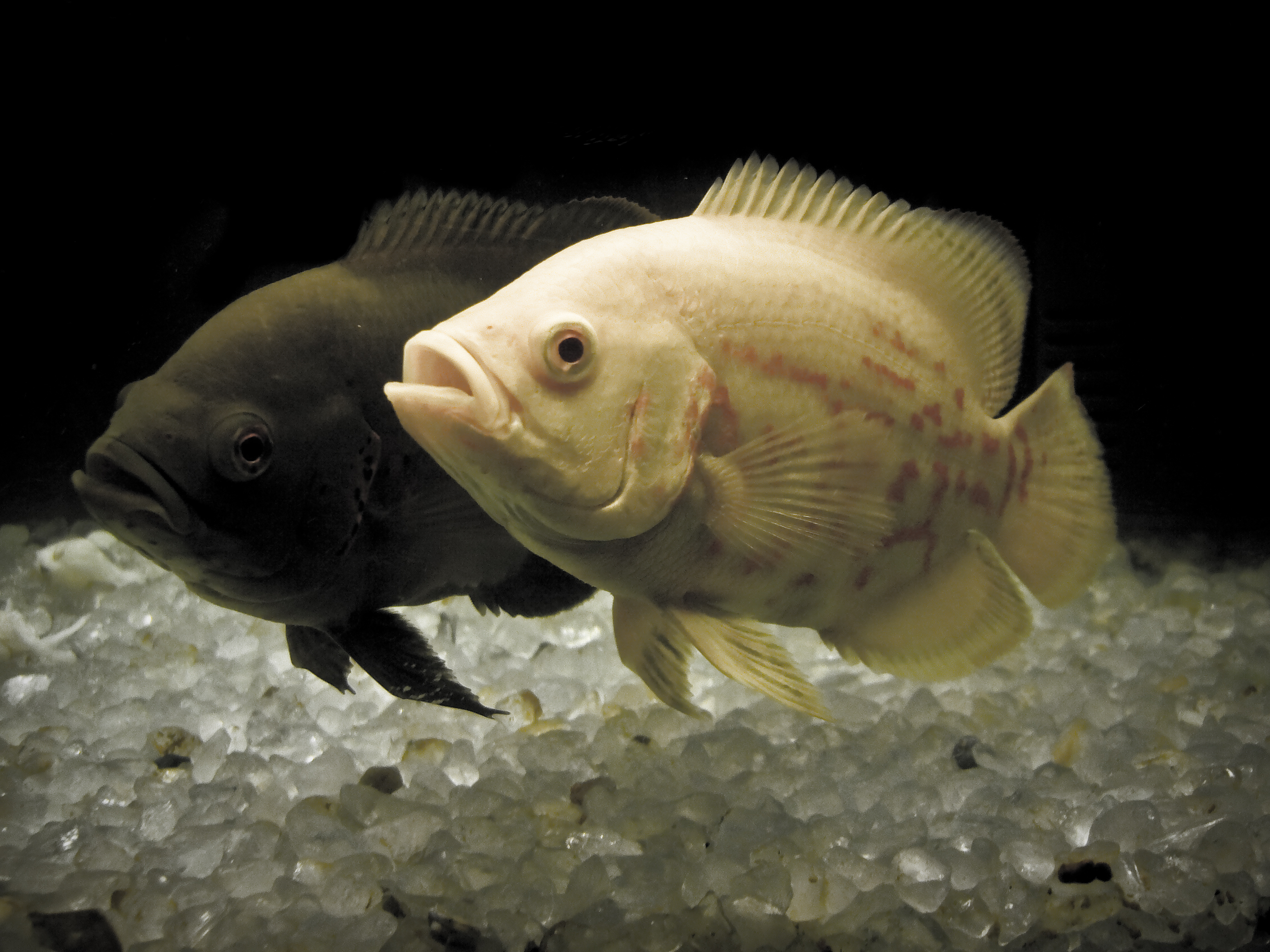
Astronotus Ocellatus
The oscar (''Astronotus ocellatus'') is a species of fish from the cichlid family known under a variety of common names, including tiger oscar, velvet cichlid, and marble cichlid. In tropical South America, where the species naturally resides, ''A. ocellatus'' specimens are often found for sale as a food fish in the local markets. The fish has been introduced to other areas, including India, China, Australia, and the United States. It is considered a popular aquarium fish in Europe and the U.S. Taxonomy The species was originally described by Louis Agassiz in 1831 as ''Lobotes ocellatus'', as he mistakenly believed the species was marine; later work assigned the species to the genus ''Astronotus''. The species also has a number of junior synonyms: ''Acara compressus'', ''Acara hyposticta'', ''Astronotus ocellatus zebra'', and ''Astronotus orbiculatus''. Description ''A. ocellatus'' examples have been reported to grow to about in length and in weight. The wild-caught forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halichoeres Bivittatus
The slippery dick (''Halichoeres bivittatus'') is a species of wrasse native to shallow, tropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean. Description The slippery dick wrasse is a small fish that can reach a maximum length of . It has a thin, elongate body with a terminal mouth, and its body coloration has three phases during its life: # The terminal phase is when the fish becomes a male, so the body coloration turns to green with two longitudinal dark stripes. The head and tail are covered with pink lines; it has a small black dot up to the pectoral fin. # The initial phase is when the juvenile becomes a female. The background body coloration is mainly whitish with pink shade, and the sides have two dark longitudinal stripes. The median one is usually black extending from the snout and via the eye to the base of the tail. The second one is a paler lateral stripe further below. The upper stripe incorporates a bicolored (green and yellow turning later to black) spot where it cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, as well as the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms; it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (''Salmo'') and North Pacific (''Oncorhynchus'') basins. ''Salmon'' is a colloquial or common name used for fish in this group, but is not a scientific name. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the shallow gravel stream bed, beds of freshwater headstreams and spend their juvenile fish, juvenile years in rivers, lakes and freshwater wetlands, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naked-back Knifefish
The naked-back knifefishes are a family, the Gymnotidae, of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Gymnotiformes. The fishes in this family are found only in fresh waters of Central America and South America. All have organs adapted to electroreception. The family has about 43 valid species in two genera. These fish are nocturnal and mostly occur in quiet waters from deep rivers to swamps. In strongly flowing waters, they may bury themselves. Physical characteristics Like the other gymnotiforms, gymnotids have classic knifefish bodies. The body is long and eel-like, the dorsal fin and pelvic fins are absent, and the anal fin is extremely long and used for movement. The electric eels of the genus ''Electrophorus'' are the largest species, and they are capable of generating both strong (up to 600 volts) and weak (<1 V) electric discharges, for use in predation and communication/navigation, respectively. The electric eel (''E. electricus'') is the largest of the gymnotiform fishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ictaluridae
The Ictaluridae, sometimes called ictalurids, are a family of catfish native to North America, where they are an important food source and sometimes fished for sport. The family includes about 51 species, some commonly known as bullheads, madtoms, channel catfish, and blue catfish. Taxonomy The family Ictaluridae is strongly supported as a monophyletic group. It is closely related to the Asian family Cranoglanididae. These two families are sister taxa in the superfamily Ictaluroidea. Though the family includes three genera of blind, subterranean, and troglobitic catfishes, '' Trogloglanis'', ''Satan'', and '' Prietella'', none of these three genera is closely related. Instead, ''Satan'' is closely related to ''Pylodictis'', ''Prietella'' to ''Noturus'', and ''Trogloglanis'' possibly to ''Ictalurus'', although it may not be closely related to any of the other ictalurids. ''Ameiurus'' is sister to a clade formed by ''Satan'', ''Pylodictis'', ''Noturus'', and ''Prietella''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family, including the carps, the true minnows, and their relatives the barbs and barbels, among others. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family, and the largest vertebrate animal family overall, with about 1,780 species divided into 166 valid genera. Cyprinids range from about in size to the giant barb (''Catlocarpio siamensis''). By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word ( 'carp'). Biology and ecology Cyprinids are stomachless, or ''agastric'', fish with toothless jaws. Even so, food can be effectively chewed by the gill rakers of the specialized last gill bow. These pharyngeal teeth allow the fish to make chewing motions against a chewing plate formed by a bony process of the skull. The pharyngeal teeth are unique to each species and are used to identify spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the Division (taxonomy), division Selachii and are the sister group to the Batoidea, Batomorphi (Batoidea, rays and skate (fish), skates). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including Extinction, extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as ''Cladoselache'' and ''Doliodus'' first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Ordovician, Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The earliest confirmed modern sharks (Selachii) are known from the Early Jurassic around , with the oldest known member being ''Agaleus'', though records of true shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
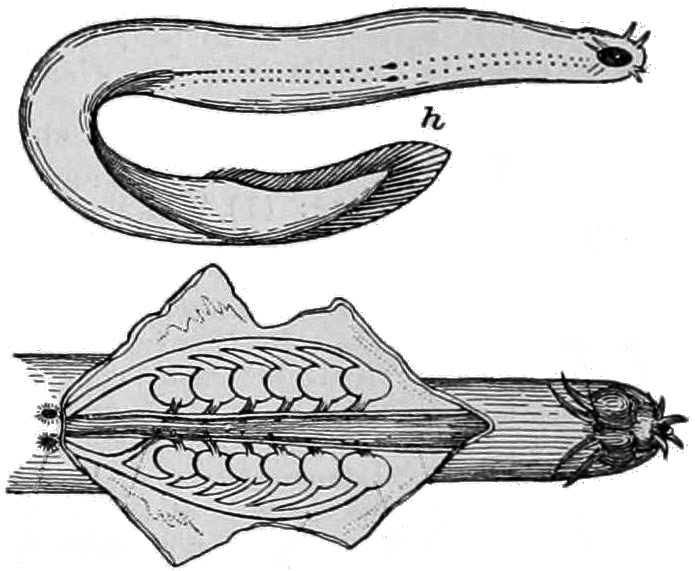
Lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. "Lamprey" is sometimes seen for the plural form. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families—two small families in the Southern Hemisphere (Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere (Petromyzontidae). Genetic evidence suggests that lampreys are more closely related to hagfish, the only other living group of jawless fish, than they are to jawed vertebrates, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossils of stem-group lampreys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although they do have rudimentary vertebrae. Hagfish are marine animal, marine predators and scavengers that can defend themselves against other larger predators by releasing copious amounts of slime coat, slime from mucous glands in their skin. Although their exact relationship to the only other extant taxon, living group of Agnatha, jawless fish, the lampreys, was long the subject of controversy, genetic evidence suggests that hagfish and lampreys are more closely related to each other than to jawed vertebrates, thus forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest-known stem group hagfish are known from the Pennsylvanian (geology), Late Carboniferous, around Moscovian (Carboniferous), 310 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythms
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment (is entrained by the environment). Circadian rhythms are regulated by a circadian clock whose primary function is to rhythmically co-ordinate biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximize the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ', meaning "around", and ', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjuste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrotfish
Parrotfish (named for their mouths, which resemble a parrot's beak) are a clade of fish placed in the tribe Scarini of the wrasse family (Labridae). Traditionally treated as their own family (Scaridae), genetic studies have found them to be deeply nested within the wrasses, and they are now treated as a subfamily (Scarinae) or tribe (Scarini) of them. With roughly 95 species, this group's largest species richness is in the Indo-Pacific. They are found in coral reefs, rocky coasts, and seagrass beds, and can play a significant role in bioerosion. Taxonomy Traditionally, the parrotfishes have been considered to be a family level taxon, Scaridae. Although phylogenetic and evolutionary analyses of parrotfishes are ongoing, they are now accepted to be a clade in the wrasses closely related to the tribe Cheilini, and are now commonly referred to as scarine labrids (tribe Scarini, family Labridae). Some authorities have preferred to maintain the parrotfishes as a family-level taxon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |