|
Slavic Nationalism (other)
Below is a list of the forms of Slavic nationalism. *Pan-Slavism **Slavophile **Neo-Slavism **Austro-Slavism *East Slavic **Russian nationalism/ Greater Russia ***Russophilia **Ukrainian nationalism/ Greater Ukraine/ Little Russian identity *West Slavic, **Czech nationalism **Czechoslovakism **Slovak nationalism **Polish nationalism *South Slavic, see rise of nationalism under the Ottoman Empire **Bosniak nationalism **Croatian nationalism/ Greater Croatia/ Illyrian movement, Illyrianism **Macedonian nationalism/ United Macedonia **Montenegrin nationalism **Serbian nationalism/ Greater Serbia **Serbian–Montenegrin unionism **Slovenian nationalism/ United Slovenia/ Venetic theory **Bulgarian nationalism/ Greater Bulgaria **Yugoslavism/ Yugoslav irredentism/ Balkan Federation Pan-Slavism Nationalism in Europe Ethnic nationalism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
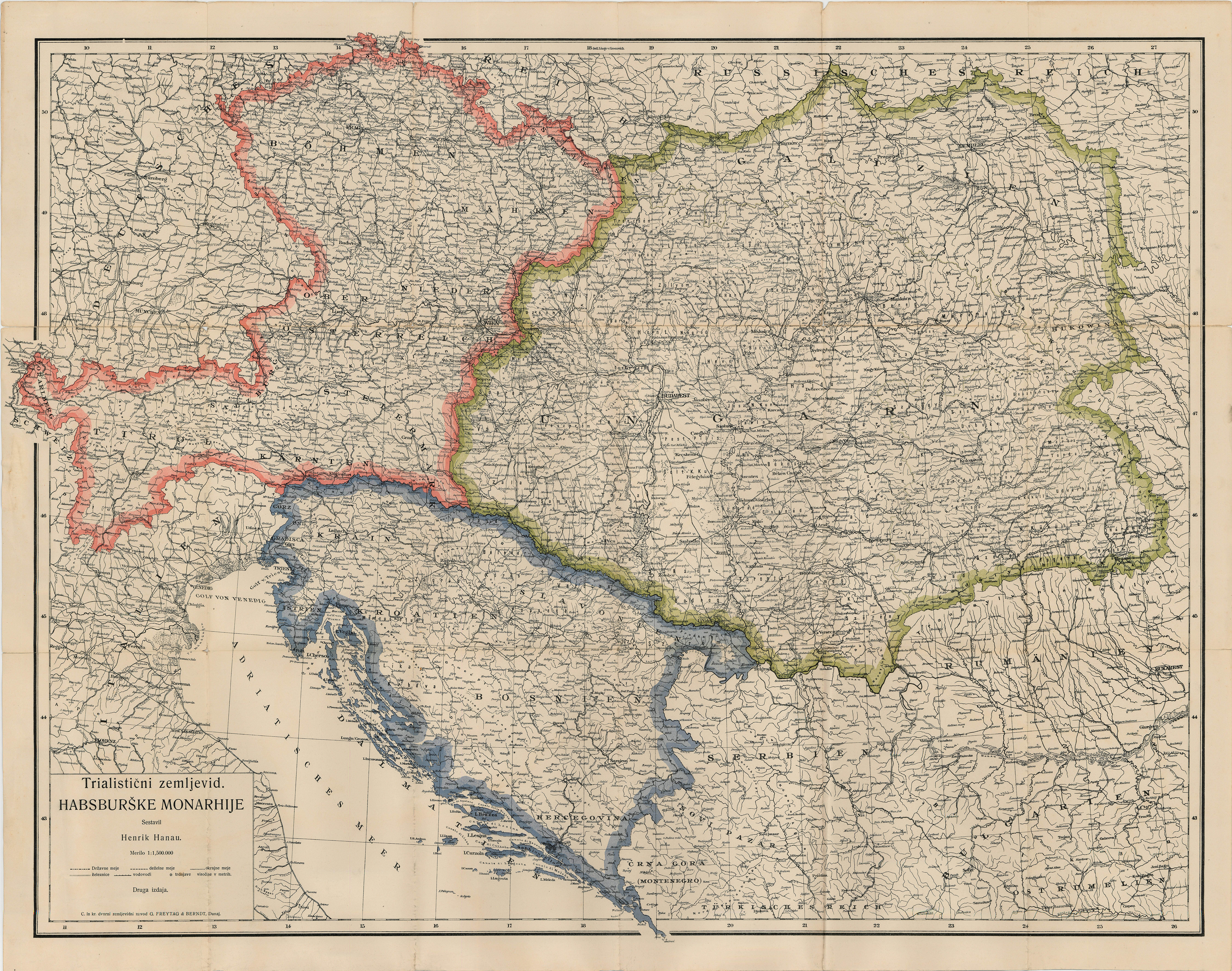
Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism, a movement that took shape in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with promoting integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice. Origins Extensive pan-Slavism began much like Pan-Germanism: both of these movements flourished from the sense of unity and nationalism experienced within ethnic groups after the French Revolution and the consequent Napoleonic Wars against traditional European monarchies. As in other Romantic nationalist movements, Slavic intellectuals and scholars in the developing fields of history, philology, and folklore actively encouraged Slavs' interest in their shared identity and ancestry. Pan-Slavism co-existed with the Southern Slavic drive towards independence. Commonly used symbols of the Pan-Slavic movement were the Pan-Slavic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
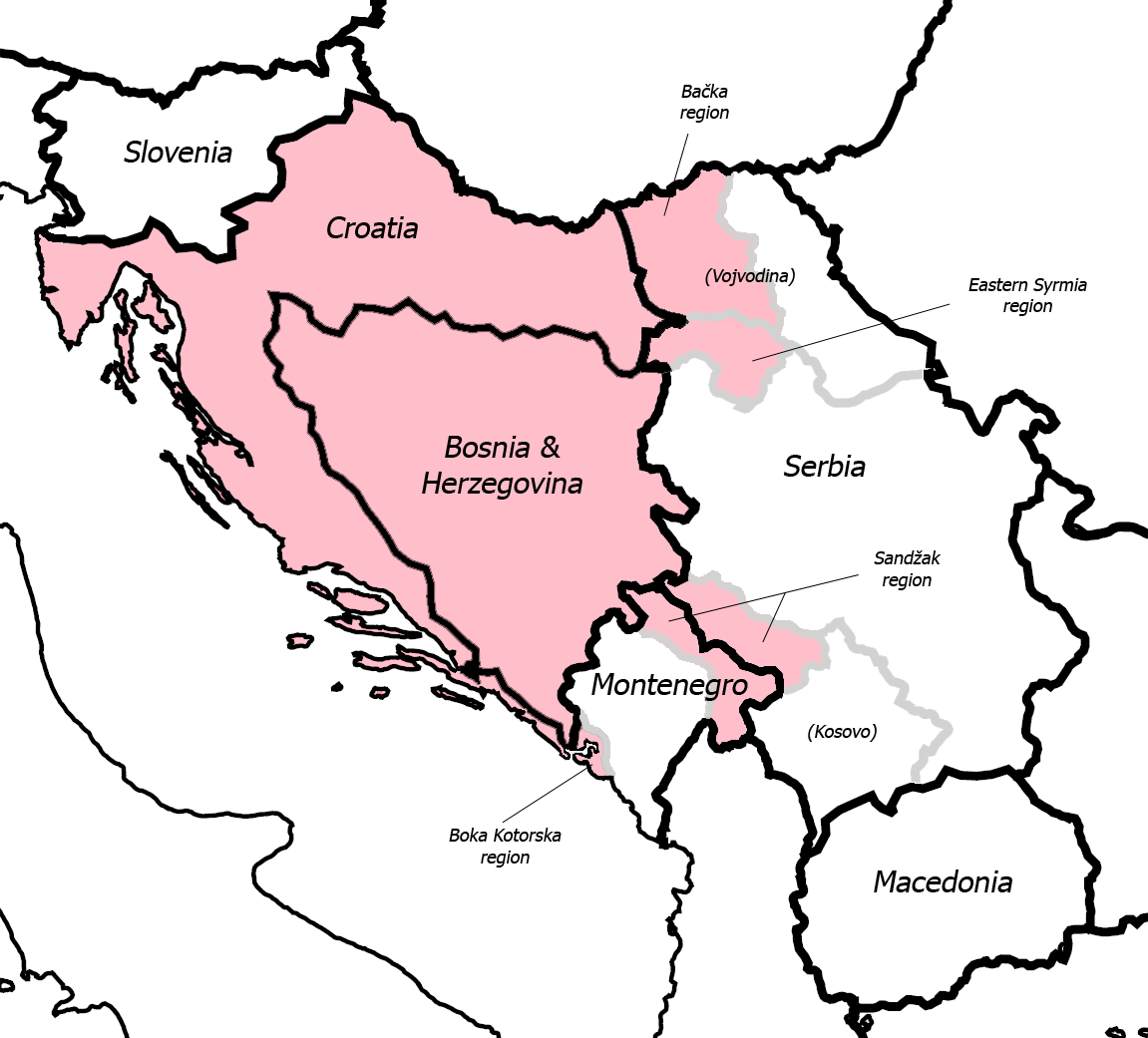
Greater Croatia
Greater Croatia () is a term applied to certain currents within Croatian nationalism. In one sense, it refers to the territorial scope of the Croatian people, emphasising the ethnicity of those Croats living outside Croatia. In the political sense, though, the term refers to an irredentist belief in the equivalence between the territorial scope of the Croatian people and that of the Croatian state. Background The concept of a Greater Croatian state has its modern origins with the Illyrian movement, a pan- South-Slavist cultural and political campaign with roots in the early modern period, and revived by a group of young Croatian intellectuals during the first half of the 19th century. Although this movement arose in the developing European nationalist context of the time, it particularly arose as a response to the more powerful nationalist stirrings in the then-Kingdom of Hungary, with whom Croatia was in a personal union. The foundations of the concept of Greater Croatia are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslavism
Yugoslavism, Yugoslavdom, or Yugoslav nationalism is an ideology supporting the notion that the South Slavs, namely the Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes belong to a single Yugoslavs, Yugoslav nation separated by diverging historical circumstances, forms of speech, and religious divides. During the interwar period, Yugoslavism became predominant in, and then the official ideology of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. There were two major forms of Yugoslavism in the period: the regime favoured integral Yugoslavism promoting Political unitarism, unitarism, Political centralization, centralisation, and unification of the country's Ethnic groups in Yugoslavia, ethnic groups into a single Yugoslav nation, by coercion if necessary. The approach was also applied to Languages of Yugoslavia, languages spoken in the Kingdom. The main alternative was Federalism, federalist Yugoslavism which advocated the autonomy of the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Bulgaria
Bulgarian irredentism is a term to identify the territory associated with a historical national state and a modern Bulgarian irredentist nationalist movement in the 19th and 20th centuries, which would include most of Macedonia, Thrace and Moesia. History The larger proposed Bulgarian state was suggested under the Treaty of San Stefano in 1878. The issue of irredentism and nationalism gained greater prominence after the Treaty of San Stefano. It established a Principality of Bulgaria, with territory including most of Moesia - the plain between the Danube and the Balkan Mountains (Stara Planina), the regions of Sofia, Pirot, and Vranje in the Morava Valley, Thrace - Northern Thrace, parts of Eastern Thrace, and nearly all of Macedonia. This treaty laid grounds for much of the later claims for a Greater Bulgaria. However, the Treaty of San Stefano was a preliminary one, and the borders of the newly created Bulgaria were established in the Treaty of Berlin. It saw the previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetic Theory
The Venetic theory () is a pseudohistorical interpretation of the origin of the Slovenes that denies the Slavic settlement of the Eastern Alps in the 6th century, claiming that proto-Slovenes (also regarded as the Veneti people by the proponents of the Venetic theory) have inhabited the region since ancient times. During the 1980s and 1990s, it gained wide attention in Slovenia and the former Yugoslavia. The Venetic theory has been rejected by scholars. A version of the Venetic theory states that most of Central Europe and portions of today's northern Turkey were originally inhabited by a single people—the Veneti—a people that were subsequently dispersed by several invasions from the North in the form of Celtic and Germanic migrations and by the push northwards of the Roman Empire. According to this variant, the Armorican Veneti, the Adriatic Veneti, the Vistula Veneti as well as portion of the Illyrians and the Veneti of northern Turkey were all related people who spoke the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Slovenia
United Slovenia ( or ) is the name originally given to an unrealized political programme of the Slovene national movement, formulated during the Spring of Nations in 1848. The programme demanded (a) unification of all the Slovene-inhabited areas into one single kingdom under the rule of the Austrian Empire, (b) equal rights of Slovene in public, and (c) strongly opposed the planned integration of the Habsburg monarchy with the German Confederation. The programme failed to meet its main objectives, but it remained the common political program of all currents within the Slovene national movement until World War I. Historical context Following the Vienna Rebellion that forced Ferdinand I to abolish feudalism and adopt a constitution, many nations of the Austrian Empire saw a chance for strengthening their ideas. After the Congress of Vienna in 1815, for the first time in centuries, all Slovenes were under the rule of one emperor. They were, however, divided between differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenian Nationalism
Slovenian nationalism is the nationalism that asserts that Slovenes are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Slovenes. Jeffrey Cole. Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, Inc., 2011. Pp. 346. Slovenian nationalism first arose in response to the influx of ideas of nationalism from the French Revolution that arrived in Slovenia when the French forces of Napoleon Bonaparte made Slovenia part of the Illyrian Provinces from 1809 to 1813. Slovenian nationalists such as Anton Korošec endorsed Yugoslav unification during World War I as a means to free Slovenia from Austro-Hungarian rule. On 8 May 1989, after the legalization of other political parties by Slovenia's reformist Communist Party-led government, new political parties published the May Declaration, demanding the formation of a sovereign, democratic, and pluralist Slovenian state. Jeffrey Cole. Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian–Montenegrin Unionism
Serbian–Montenegrin unionism () is a socio-political movement which arose in the Balkans after the Breakup of Yugoslavia, breakup of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia. It advocates Montenegro being in a political union with Serbia. The Serbia-Montenegro relations, relationship between ethnic Serbs and Montenegrins (ethnic group), Montenegrins is generally identified as being the most amicable of all the peoples of the former Yugoslavia. According to a 2023 national census which enumerated a population of 623,633, some 32.9% or 205,370 Montenegrin citizens ethnically identified as "Serb", with 2,969 (<1%) identifying as "Serbian-Montenegrin" or "Montenegrin-Serbian". History Montenegro–Serbia relations, Brotherhood between the states of Montenegro and Serbia is long-standing. In the Montenegrin–Ottoman War (1876–1878), 19th century, Montenegro and Serbia were officially Treaty of San Stefano, recogni ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
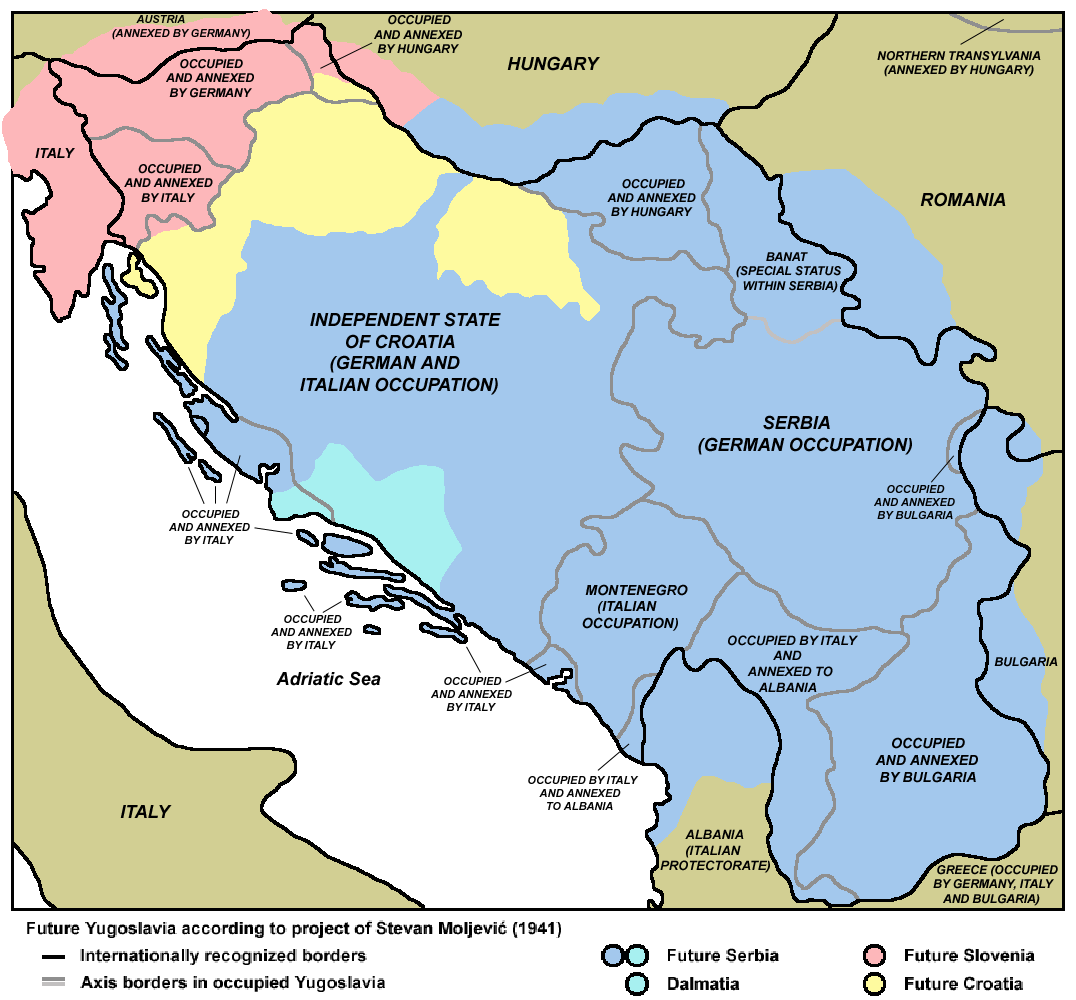
Greater Serbia
The term Greater Serbia or Great Serbia () describes the Serbian nationalist and irredentist ideology of the creation of a Serb state which would incorporate all regions of traditional significance to Serbs, a South Slavic ethnic group, including regions outside modern-day Serbia that are partly populated by Serbs. The initial movement's main ideology (Pan- Serbism) was to unite all Serbs (or all territory historically ruled, seen to be populated by, or perceived to be belonging to Serbs) into one state, claiming, depending on the version, different areas of many surrounding countries, regardless of non-Serb populations present. The Greater Serbian ideology includes claims to various territories aside from modern-day Serbia, including the whole of the former Yugoslavia except Slovenia and part of Croatia. According to Jozo Tomasevich, in some historical forms, Greater Serbian aspirations also included parts of Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania. Its inspiration comes fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Nationalism
Serbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, under the influence of Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Serbian statesman Ilija Garašanin. Serbian nationalism was an important factor during the Balkan Wars which contributed to the decline of the Ottoman Empire, during and after World War I when it contributed to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and again during the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s. After 1878, Serbian nationalists merged their goals with those of Yugoslavists, and emulated the Piedmont's leading role in the '' Risorgimento'' of Italy, by claiming that Serbia sought not only to unite all Serbs in one state, but that Serbia intended to be a South Slavic Piedmont that would unite all South Slavs in one state known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Nationalism
Montenegrin nationalism is the nationalism that asserts that Montenegrins are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Montenegrins. From the beginning of the 18th century, the population of Montenegro was torn between variants of Montenegrin and Serbian nationalism. As opposed to Serbian nationalism, which emphasizes the ethnic Serbian character of the Montenegrins, Montenegrin nationalism emphasizes the right of the Montenegrins to define themselves as a unique nation, not simply as a branch of the Serbs. Montenegrin nationalism became a major political issue in World War I when a schism arose between Tribes of Montenegro, Montenegro's tribes over plans to merge Montenegro with the Kingdom of Serbia, between the pro-independence Greens (Montenegro), Green tribes, that included the King of Montenegro amongst them, versus the pro-unification White tribes. Montenegrin ethnicity was recognized by the Communist government of Yugoslavia in the 1960s though it had been declared pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |