|
Slavery In Tunisia
Slavery in Tunisia was a specific manifestation of the Arab slave trade, which was abolished on 23 January 1846 by Ahmed I Bey. Tunisia was in a similar position to that of Algeria, with a geographic position which linked it with the main Trans-Saharan routes. It received caravans from Fezzan and Ghadamès, which consisted solely, in the eighteenth century, of gold powder and slaves, according to contemporary witnesses. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, slaves arrived annually in numbers ranging between 500 and 1,200. From Tunisia they were carried on to the ports of the Levant. Origins Tunisian slaves derived from two principal zones: Europe and a large area stretching from West Africa to Lake Chad. The kingdoms of Bornu Empire, Bornu and the region of Fezzan provided the majority of caravans. The greater part of the slaves were reduced to slavery in local wars between rival tribes or in abduction raids. Caravan routes from many Saharan centres terminated at Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
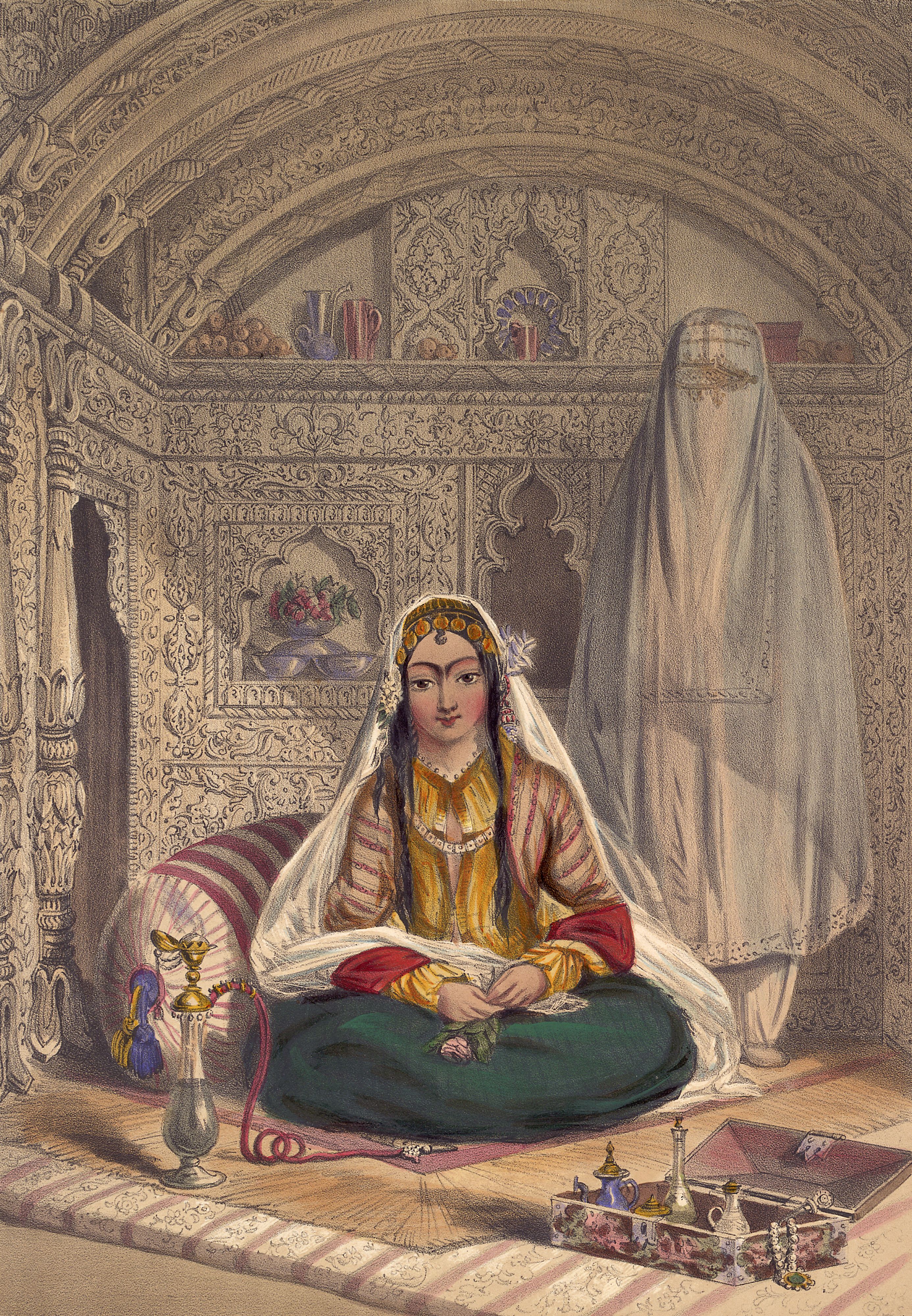
Harem
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other unmarried female relatives. In the past, during the history of slavery in the Muslim world, era of slavery in the Muslim world, harems also housed enslaved Concubinage in Islam, concubines. In former times, some harems were guarded by eunuchs who were allowed inside. The structure of the harem and the extent of monogamy or polygyny have varied depending on the family's personalities, socio-economic status, and local customs. Similar institutions have been common in other Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations, especially among royal and upper-class families, and the term is sometimes used in other contexts. In traditional Persian residential architecture, the women's quarters were known as (), and in the Indian s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maison Esclaves
Maison (French for "house") may refer to: People * Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress * Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist * Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837 * Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Marshal of France and Minister of War * René Maison (1895–1962), Belgian operatic tenor * Rudolf Maison (1854–1904), German sculptor Places in France * Maison-des-Champs, a commune in the Aube department, Grand Est * Maison-Feyne, a commune in the Creuse department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine * Maison-Maugis, a former commune in the Orne department, Normandy * Maison-Ponthieu, a commune in the Somme department, Hauts-de-France * Maison-Roland, a commune in the Somme department, Hauts-de-France * Maison-Rouge Maison-Rouge (, literally ''Red House'') is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. Demographics Inhabitants are called ''Mansyrubiens''. See also *Communes of the Seine-et-Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confraternity
A confraternity (; ) is generally a Christian voluntary association of laypeople created for the purpose of promoting special works of Christian charity or piety, and approved by the Church hierarchy. They are most common among Catholics, Lutherans, Anglicans, and the Western Orthodox. When a Catholic confraternity has received the authority to aggregate to itself groups erected in other localities, it is called an archconfraternity. Examples include the various confraternities of penitents and the confraternities of the cord, as well as the Confraternity of the Holy Guardian Angels and the Confraternity of the Rosary. Confraternities were "the most sweeping and ubiquitous movement of the central and later Middle Ages". History Pious associations of laymen existed in very ancient times at Constantinople and Alexandria. In France, in the eighth and ninth centuries, the laws of the Carolingians mention confraternities and guilds. But the first confraternity in the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium BCE. Over the millennia since, they have performed a wide variety of functions in many different cultures: courtiers or equivalent Domestic worker, domestics, for espionage or clandestine operations, ''castrato'' singers, Concubinage, concubines or sexual partners, religious specialists, soldiers, royal guards, government officials, and guardians of women or harem servants. Eunuchs would usually be servants or Slavery, slaves who had been castrated to make them less threatening servants of a royal court where physical access to the ruler could wield great influence. Seemingly lowly domestic functions—such as making the ruler's bed, bathing him, cutting his hair, carrying him in his litter (vehicle), litter, or even rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agha (Ottoman Empire)
Agha (; ; ; "chief, master, lord") is an honorific title for a civilian or officer, or often part of such title. In the Ottoman times, some court functionaries and leaders of organizations like bazaar or the janissary units were entitled to the ''agha'' title. In rural communities, this term is used for people who own considerable lands and are influential in their community. Regardless of a rural community, this title is also used for any man who is influential or respected. Etymology The word ''agha'' entered English from Turkish, and the Turkish word comes from the Old Turkic ''aqa'', meaning "elder brother". It is an equivalent of Mongolian word ''aqa'' or ''aka''. Other uses "Agha" is nowadays used as a common Persian honorific title for men, the equivalent of "mister" in English. The corresponding honorific term for women is khanum which is also of Turkic origin. However, the title is considered a baron in comparison to European nobility.Imperial, royal and noble r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisian Sahel
The Tunisian Sahel () or more precisely the Central East Tunisia is an area of central eastern Tunisia and one of the six Tunisian regions. It stretches along the eastern shore, from Bouficha in the north to Melloulèche in the south, it includes 3 governorates: Sousse, Monastir and Mahdia. Its name derives from the Arabic word ''sāḥil'' (ساحل), meaning "shore" or "coast". The region's economy is based especially on tourism and it contains the second-biggest airport in Tunisia: Monastir Habib Bourguiba International Airport. Geography The Sahel extends inland to the hills which protect the low plains of the coast and are covered in olive plantations; the region's low rainfall is compensated for by the atmospheric humidity. Since antiquity, it has formed a clear geographic unity with its own unique demographic and economic characteristics. Today it consists of the governorates of Sousse, Monastir and Mahdia. Its geographic area is quite large: about 140 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
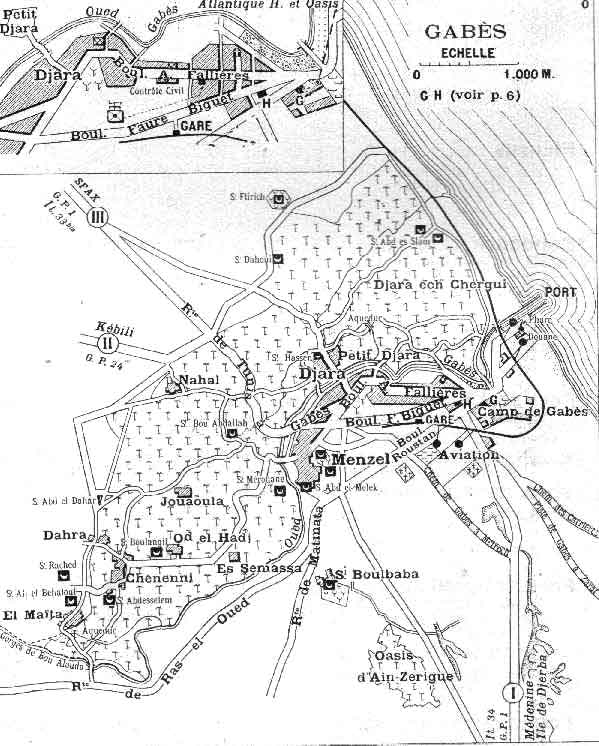
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, and Kabes, is the capital of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. Situated on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès, the city has a population of 167,863, making it the 6th largest city in Tunisia. Located 327 km southeast of Tunis and 113 km from Sfax, Gabès lies at the delta of the Wadi Qabis, which originates 10 kilometers upstream at Ras El Oued, Algeria, Ras al-Oued and serves as its primary water source. Historically, the town was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian settlement known as Tacapae before falling under Roman Empire, Roman control. It was later ruined during the 7th-century Arab invasion but was recovered by Sidi Boulbaba, a revered companion of the Muhammad, Prophet Muhammad and a patron of the town. Although it experienced decline under the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, Gabès saw significant growth under French rule from 1881 to 1955, with the development of key infrastructure, including a railway, road network, and port. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentBattesti, Vincent (2005) Jardins au désert: Évolution des pratiques et savoirs oasiens: Jérid tunisien. Paris: IRD éditions. . that sustains plant life and provides habitat for animals. Surface water may be present, or water may only be accessible from wells or underground channels created by humans. In geography, an oasis may be a current or past rest stop on a transportation route, or less-than-verdant location that nonetheless provides access to underground water through deep wells created and maintained by humans. Although they depend on a natural condition, such as the presence of water that may be stored in reservoirs and us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consul (diplomacy)
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states through antiquity and the Middle Ages, in particular in the Republics of Genoa and Pisa, then revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic. The related adjective is consular, from the Latin ''consularis''. This usage contrasts with modern terminology, where a consul is a type of diplomat. Roman consul A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic (509 to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspired). Consuls were elected to office and held power for one year. There were always two consuls in power at any time. Other uses in antiquity Private sphere It was not uncommon for an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Reade (British Army Officer)
Colonel Sir Thomas Reade (1782 – 1 August 1849) was a British Army officer during the Napoleonic Wars, known also as a collector.Sir Thomas Reade (Biographical details) - British Museum In 1799, at the age of sixteen, he ran away from home to enlist in the Army and participated in campaigns in , and America, as well as postings across Europe. Major Reade served as Deputy Quartermaster General at the 1814 Siege of Genoa. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |