 |
Slave Clock
In telecommunication and horology, a slave clock is a clock that depends on another clock, the master clock. Modern clocks are synchronized through the Internet or by radio time signals, to Coordinated Universal Time. UTC is based on a network of atomic clocks in many countries. For scientific purposes, precision clocks can be synchronized to within nanoseconds by dedicated satellite channels. Slave clock synchronization is usually achieved by phase-locking the slave clock signal to a signal received from the master clock. To adjust for the transit time of the signal from the master clock to the slave clock, the phase of the slave clocks are adjusted so that both clocks are in phase. Thus, the time markers of both clocks, at the output of the clocks, occur simultaneously. The predecessors of atomic clocks, computer clocks, and digital clocks, these electric clocks (or pneumatic clocks) were synchronized by an electrical pulse, wired to their master clock in the same facility. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Master Clock System
Master, master's or masters may refer to: Ranks or titles In education: *Master (college), head of a college *Master's degree, a postgraduate or sometimes undergraduate degree in the specified discipline *Schoolmaster or master, presiding officer of a school In military: *Master (naval), a former naval rank *Master mariner, a licensed mariner who is qualified to be a sea captain in the merchant marine *Master or shipmaster, the sea captain of a merchant vessel * Master-at-arms, a naval police officer, often addressed as "Master" in the Royal Navy In orders and organizations: *Master craftsman, in the Medieval guilds In other: *Master (form of address), an English honorific for boys and young men *Master (judiciary), a judicial official in the courts of common law jurisdictions *Master (Peerage of Scotland), the male heir-apparent or heir-presumptive to a title in the Peerage of Scotland * Master of ceremonies, or MC (emcee), the host of an official public or private staged even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Horology
Chronometry or horology () is the science studying the measurement of time and timekeeping. Chronometry enables the establishment of standard measurements of time, which have applications in a broad range of social and scientific areas. ''Horology'' usually refers specifically to the study of mechanical timekeeping devices, while ''chronometry'' is broader in scope, also including biological behaviours with respect to time (biochronometry), as well as the dating of geological material (geochronometry). Horology is commonly used specifically with reference to the mechanical instruments created to keep time: clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, Water clock, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clocks are all examples of Measuring instrument, instruments used to measure time. People interested in horology are called ''horologists''. That term is used both by people who deal professionally with timekeeping apparatuses, as well as enthus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communication, navigation, scientific research, and commerce. UTC has been widely embraced by most countries and is the effective successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) in everyday usage and common applications. In specialised domains such as scientific research, navigation, and timekeeping, other standards such as Universal Time, UT1 and International Atomic Time (TAI) are also used alongside UTC. UTC is based on TAI (International Atomic Time, abbreviated from its French name, ''temps atomique international''), which is a weighted average of hundreds of atomic clocks worldwide. UTC is within about one second of mean solar time at 0° longitude, the currently used prime meridian, and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. The coordination of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Atomic Clocks
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions between such states they interact with a very specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation. This phenomenon serves as the basis for the International System of Units' (SI) definition of a second: The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, \Delta \nu_\text, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium-133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This definition is the basis for the system of International Atomic Time (TAI), which is maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks around the world. The system of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) that is the basis of civil time implements leap seconds to allow cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Nanoseconds
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or seconds. The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and ''second'', the primary unit of time in the SI. A nanosecond is to one second, as one second is to approximately 31.69 years. A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds. Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics. Common measurements * 0.001 nanoseconds – one picosecond * 0.96 nanoseconds – 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 96 nanoseconds – Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 1.0 nanosecond – cycle time of an electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 1 GHz (). * 1.0 nan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
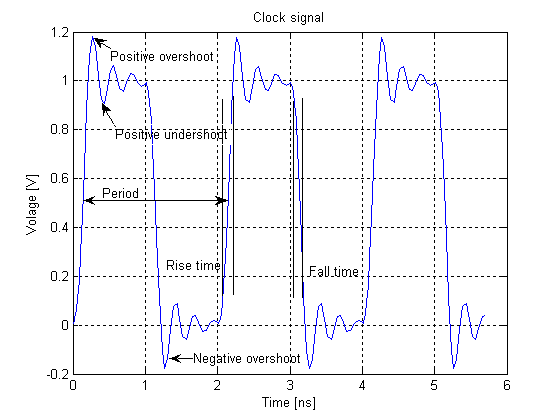 |
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Computer Clock
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices such as personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Digital Clock
A digital clock displays the time digitally (i.e. in numerals or other symbols), as opposed to an analogue clock. Digital clocks are often associated with electronic drives, but the "digital" description refers only to the display, not to the drive mechanism. (Both analogue and digital clocks can be driven either mechanically or electronically, but "clockwork" mechanisms with digital displays are rare.) History The first digital pocket watch was the invention of Austrian engineer Josef Pallweber who created his "jump-hour" mechanism in 1883. Instead of a conventional dial, the jump-hour featured two windows in an enamel dial, through which the hours and minutes are visible on rotating discs. The second hand remained conventional. By 1885, Pallweber mechanism was already on the market in pocket watches by Cortébert and IWC; arguably contributing to the subsequent rise and commercial success of IWC. The principles of Pallweber jump-hour movement had appeared in wristwatche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Electric Clocks
An electric clock is a clock that is powered by electricity, as opposed to a mechanical clock which is powered by a hanging weight or a mainspring. The term is often applied to the electrically powered mechanical clocks that were used before quartz clocks were introduced in the 1980s. The first experimental electric clocks were constructed around the 1840s, but they were not widely manufactured until mains electric power became available in the 1890s. In the 1930s, the synchronous electric clock replaced mechanical clocks as the most widely used type of clock. Types Electric clocks can operate by several different types of mechanism: ;Electromechanical clocks: These have a traditional mechanical movement, which keeps time with an oscillating pendulum or balance wheel powered through a gear train by a mainspring, but use electricity to rewind the mainspring with an electric motor or electromagnet. This mechanism is found mostly in antique clocks. ;Electric remontoire clocks: Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Pneumatic Tube
Pneumatic tubes (or capsule pipelines, also known as pneumatic tube transport or PTT) are systems that propel cylindrical containers through networks of Tubing (material), tubes by Gas compressor, compressed air or by partial vacuum. They are used for transporting solid objects, as opposed to conventional pipelines which transport fluids. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, pneumatic tube networks gained acceptance in offices that needed to transport small, urgent packages, such as mail, other paperwork, or money, over relatively short distances, within a building or, at most, within a city. Some installations became quite complex, but have mostly been superseded. However, they have been further developed in the 21st century in places such as hospitals, to send blood samples and the like to clinical laboratory, clinical laboratories for analysis. A small number of pneumatic transportation systems were built for larger cargo, to compete with train and subway systems. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
School Bell
The ringing of a school bell announces important times to a school's students and staff, such as marking the beginnings and ends of the school day, class periods, and breaks. In some schools it may take the form of a physical bell, usually electrically operated. In other schools it may be a tone, siren, electronic bell sound, a series of chimes, or music played over a PA system. In East Asian nations such as China, North Korea and South Korea, the Westminster Chimes pattern is commonly played as the bell. Schools for the hearing impaired use alternative signaling methods, for example sign language from the teacher and lights that illuminate when the public address/bell is sounding. Criticism In October 2010, Mackie Academy in Stonehaven, Kincardineshire, Scotland, took the move to turn off their school bell system, following criticism that the school bells agitated pupils. According to the headteacher, the corridors became much quieter after the system was introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |