|
Slash Distribution
In probability theory, the slash distribution is the probability distribution of a standard normal variate divided by an independent standard uniform variate. In other words, if the random variable ''Z'' has a normal distribution with zero mean and unit variance, the random variable ''U'' has a uniform distribution on ,1and ''Z'' and ''U'' are statistically independent, then the random variable ''X'' = ''Z'' / ''U'' has a slash distribution. The slash distribution is an example of a ratio distribution. The distribution was named by William H. Rogers and John Tukey in a paper published in 1972. The probability density function (pdf) is : f(x) = \frac. where \varphi(x) is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution. The quotient is undefined at ''x'' = 0, but the discontinuity is removable: : \lim_ f(x) = \frac = \frac The most common use of the slash distribution is in simulation studies. It is a useful distribution in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Density Function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a ''relative likelihood'' that the value of the random variable would be close to that sample. Probability density is the probability per unit length, in other words, while the ''absolute likelihood'' for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0 (since there is an infinite set of possible values to begin with), the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would be close to one sample compared to the other sample. In a more precise sense, the PDF is used to specify the probability of the random variable falling ''within a particular range of values'', as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Distributions
Continuity or continuous may refer to: Mathematics * Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include ** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics ** Continuous game, a generalization of games used in game theory ** Law of Continuity, a heuristic principle of Gottfried Leibniz * Continuous function, in particular: ** Continuity (topology), a generalization to functions between topological spaces ** Scott continuity, for functions between posets ** Continuity (set theory), for functions between ordinals ** Continuity (category theory), for functors ** Graph continuity, for payoff functions in game theory * Continuity theorem may refer to one of two results: ** Lévy's continuity theorem, on random variables ** Kolmogorov continuity theorem, on stochastic processes * In geometry: ** Parametric continuity, for parametrised curves ** Geometric continuity, a concept primarily applied to the coni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy Distribution
The Cauchy distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy, is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among physicists, as the Lorentz distribution (after Hendrik Lorentz), Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, Lorentz(ian) function, or Breit–Wigner distribution. The Cauchy distribution f(x; x_0,\gamma) is the distribution of the -intercept of a ray issuing from (x_0,\gamma) with a uniformly distributed angle. It is also the distribution of the ratio of two independent normally distributed random variables with mean zero. The Cauchy distribution is often used in statistics as the canonical example of a " pathological" distribution since both its expected value and its variance are undefined (but see below). The Cauchy distribution does not have finite moments of order greater than or equal to one; only fractional absolute moments exist., Chapter 16. The Cauchy distribution has no moment generating function. In mathematics, it is closely related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathological (mathematics)
In mathematics, when a mathematical phenomenon runs counter to some intuition, then the phenomenon is sometimes called pathological. On the other hand, if a phenomenon does not run counter to intuition, it is sometimes called well-behaved. These terms are sometimes useful in mathematical research and teaching, but there is no strict mathematical definition of pathological or well-behaved. In analysis A classic example of a pathology is the Weierstrass function, a function that is continuous everywhere but differentiable nowhere. The sum of a differentiable function and the Weierstrass function is again continuous but nowhere differentiable; so there are at least as many such functions as differentiable functions. In fact, using the Baire category theorem, one can show that continuous functions are generically nowhere differentiable. Such examples were deemed pathological when they were first discovered: To quote Henri Poincaré: Since Poincaré, nowhere differentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Tail
In probability theory, heavy-tailed distributions are probability distributions whose tails are not exponentially bounded: that is, they have heavier tails than the exponential distribution. In many applications it is the right tail of the distribution that is of interest, but a distribution may have a heavy left tail, or both tails may be heavy. There are three important subclasses of heavy-tailed distributions: the fat-tailed distributions, the long-tailed distributions and the subexponential distributions. In practice, all commonly used heavy-tailed distributions belong to the subexponential class. There is still some discrepancy over the use of the term heavy-tailed. There are two other definitions in use. Some authors use the term to refer to those distributions which do not have all their power moments finite; and some others to those distributions that do not have a finite variance. The definition given in this article is the most general in use, and includes all dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning, as in economics. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Removable Discontinuity
Continuous functions are of utmost importance in mathematics, functions and applications. However, not all functions are continuous. If a function is not continuous at a point in its domain, one says that it has a discontinuity there. The set of all points of discontinuity of a function may be a discrete set, a dense set, or even the entire domain of the function. This article describes the classification of discontinuities in the simplest case of functions of a single real variable taking real values. The oscillation of a function at a point quantifies these discontinuities as follows: * in a removable discontinuity, the distance that the value of the function is off by is the oscillation; * in a jump discontinuity, the size of the jump is the oscillation (assuming that the value ''at'' the point lies between these limits of the two sides); * in an essential discontinuity, oscillation measures the failure of a limit to exist; the limit is constant. A special case is if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tukey
John Wilder Tukey (; June 16, 1915 – July 26, 2000) was an American mathematician and statistician, best known for the development of the fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm and box plot. The Tukey range test, the Tukey lambda distribution, the Tukey test of additivity, and the Teichmüller–Tukey lemma all bear his name. He is also credited with coining the term 'bit' and the first published use of the word 'software'. Biography Tukey was born in New Bedford, Massachusetts in 1915, to a Latin teacher father and a private tutor. He was mainly taught by his mother and attended regular classes only for certain subjects like French. Tukey obtained a BA in 1936 and MSc in 1937 in chemistry, from Brown University, before moving to Princeton University, where in 1939 he received a PhD in mathematics after completing a doctoral dissertation titled "On denumerability in topology". During World War II, Tukey worked at the Fire Control Research Office and collaborated wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
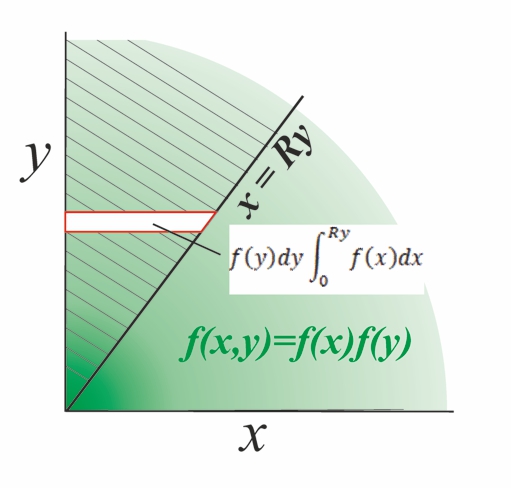
Ratio Distribution
A ratio distribution (also known as a quotient distribution) is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the ratio of random variables having two other known distributions. Given two (usually independent) random variables ''X'' and ''Y'', the distribution of the random variable ''Z'' that is formed as the ratio ''Z'' = ''X''/''Y'' is a ''ratio distribution''. An example is the Cauchy distribution (also called the ''normal ratio distribution''), which comes about as the ratio of two normally distributed variables with zero mean. Two other distributions often used in test-statistics are also ratio distributions: the ''t''-distribution arises from a Gaussian random variable divided by an independent chi-distributed random variable, while the ''F''-distribution originates from the ratio of two independent chi-squared distributed random variables. More general ratio distributions have been considered in the literature. Often the ratio distributions are heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |