|
Sixth Generation Of Video Game Consoles
In the history of video games, the sixth generation era (in rare occasions called the 128-bit era; see "bits and system power" below) is the era of computer and video games, video game consoles, and handheld gaming devices available at the turn of the 21st century, starting on November 27, 1998. '' Platforms'' in the sixth generation include consoles from four companies: the Sega Dreamcast (DC), Sony PlayStation 2 (PS2), Nintendo GameCube (GC), and Microsoft Xbox. This era began on November 27, 1998, with the Japanese release of the Dreamcast, which was joined by the PlayStation 2 on March 4, 2000, the GameCube on September 14, 2001 and the Xbox on November 15, 2001, respectively. The Dreamcast was among the first to be discontinued in 2001, followed by GameCube in 2007, Xbox in 2009, and PlayStation 2 in 2013. Meanwhile, the seventh generation of consoles started on November 22, 2005, with the launch of the Xbox 360. The major innovation of this generation was of full utilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Video Games
The history of video games began in the 1950s and 1960s as computer science, computer scientists began designing simple games and simulation video game, simulations on minicomputers and mainframe computer, mainframes. ''Spacewar!'' was developed by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student hobbyists in 1962 as one of the first such video games, games on a video display. The first consumer video game hardware was released in the early 1970s. The first home video game console was the Magnavox Odyssey, and the first arcade video games were ''Computer Space'' and ''Pong''. After its home console conversions, numerous companies sprang up to capture ''Pong''s success in both the arcade and the home by Video game clone, cloning the game, causing a series of boom and bust cycles due to oversaturation and lack of innovation. By the mid-1970s, low-cost programmable microprocessors replaced the discrete transistor–transistor logic circuitry of early hardware, and the first ROM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Pippin
The Pippin (stylized as PiPP!N) is a defunct open multimedia technology platform, designed by Apple Computer. According to Apple, Pippin was directed at the home market as "an integral part of the consumer audiovisual, stereo, and television environment". Pippin is based on the Macintosh platform, including the classic Mac OS architecture. Apple built a demonstration device based on Pippin called Pippin Power Player and used it to demonstrate the platform at trade shows and to the media, to attract potential software developers and hardware manufacturers. Apple licensed the Pippin technology to third-party companies. Bandai Company Ltd. developed the ATMARK and @WORLD models, and focused them on the gaming and entertainment business in Japan, Canada and the United States. Katz Media developed the KMP 2000, and focused it on vertical markets throughout Europe and Canada. __TOC__ Naming The Pippin platform was named for the Newtown Pippin, an apple cultivar, a smaller and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
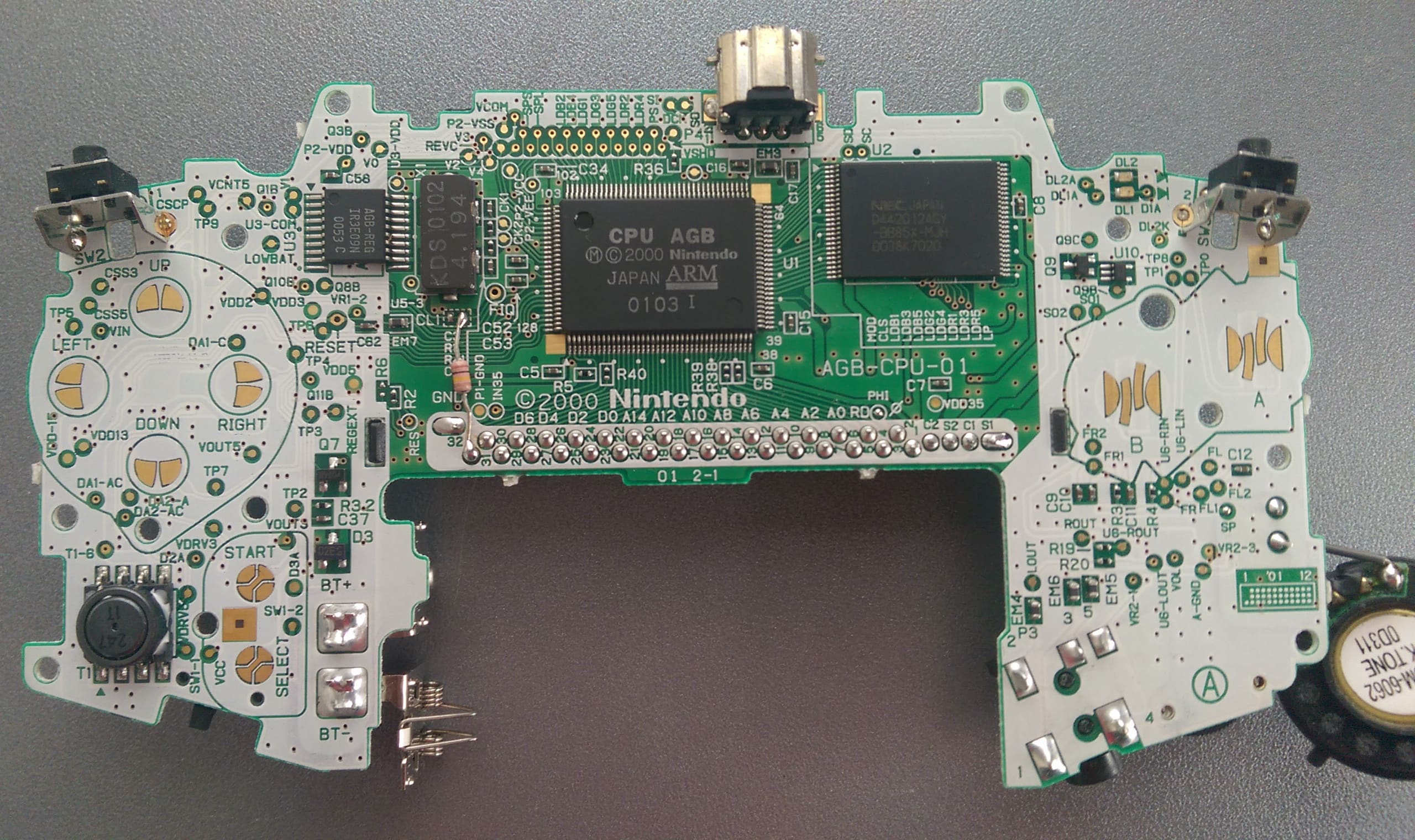
Game Boy Advance
The (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld game console, manufactured by Nintendo, which was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, and to international markets that June. It was later released in mainland China in 2004, under the name iQue Game Boy Advance''.'' Compared to the Game Boy Color it succeeded, the console offered a significantly more powerful ARM7 processor and improved graphics, while retaining backward compatibility with games initially developed for its predecessor. The GBA is part of the sixth generation of video game consoles, competing against Nokia's N-Gage and Bandai's WonderSwan. The original model was followed in 2003 by the Game Boy Advance SP, a redesigned model with a frontlight, frontlit screen and Clamshell design, clamshell form factor. Game Boy Advance SP#Backlit model (AGS-101), A newer revision of the SP with a backlight, backlit screen was released in 2005. A miniaturized redesign, the Game Boy Micro, was released in September 2005. By June 2010, the Game B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WonderSwan
The is a handheld game console released in Japan by Bandai. Developed in collaboration with Gunpei Yokoi's company Koto Laboratory, it was the final piece of hardware Yokoi worked on before his death in 1997. Launched in March 1999 during the sixth generation of video game consoles, the WonderSwan was followed by two upgraded models, the WonderSwan Color and SwanCrystal, before Bandai discontinued the line in 2003. Throughout its lifespan, no version of the WonderSwan was officially released outside Japan. Powered by a 16-bit processor, the WonderSwan was designed as both a more powerful and affordable alternative to its 8-bit competitors, Nintendo's Game Boy Color and SNK's Neo Geo Pocket Color, while offering notably long battery life from a single AA battery. Later iterations improved the handheld’s display, introducing color for enhanced visual quality. One of its distinguishing features was its dual-orientation design, allowing gameplay in both vertical and horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandai
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational toy manufacturer and distributor headquartered in Taitō, Taitō, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Toys & Collectables America and Bandai UK, are respectively headquartered in Irvine, California, and Richmond, London. Since 2005, Bandai is the toy production division of Bandai Namco Holdings, currently the world's second largest toy company measured by total revenue. Between 1981 and 2001, Bandai was a manufacturer of :Bandai consoles, video game consoles. Bandai was founded by World War II veteran Naoharu Yamashina as Bandai-Ya on July 5, 1950, as the corporate spin-off of a textile wholesaler. The company began as a distributor of metallic toys and rubber swimming rings, before moving to metal cars and aircraft models. It was renamed Bandai Co., Ltd. in 1961 and achieved considerable success with its action figures based on the anime ''Astro Boy (1963 TV series), Astro Boy''. History Origins and success wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ''core'' (for magnetic core memory) and ''store''. Main memory operates at a high speed compared to mass storage which is slower but less expensive per bit and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs and data being actively processed, computer memory serves as a Page cache, mass storage cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as it is not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern computer memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cell (com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Bandwidth
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the fetching (from memory), decoding and execution (of instructions) by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers, and other components. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Speed
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word (computer Architecture)
In computing, a word is any processor design's natural unit of data. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word size'', ''word width'', or ''word length'') is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture. The size of a word is reflected in many aspects of a computer's structure and operation; the majority of the registers in a processor are usually word-sized and the largest datum that can be transferred to and from the working memory in a single operation is a word in many (not all) architectures. The largest possible address size, used to designate a location in memory, is typically a hardware word (here, "hardware word" means the full-sized natural word of the processor, as opposed to any other definition used). Documentation for older computers with fixed word size commonly states memory sizes in words rather than bytes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Generation Of Video Game Consoles
In the history of video games, the sixth generation era (in rare occasions called the 128-bit era; see "bits and system power" below) is the era of computer and video games, video game consoles, and handheld gaming devices available at the turn of the 21st century, starting on November 27, 1998. '' Platforms'' in the sixth generation include consoles from four companies: the Sega Dreamcast (DC), Sony PlayStation 2 (PS2), Nintendo GameCube (GC), and Microsoft Xbox. This era began on November 27, 1998, with the Japanese release of the Dreamcast, which was joined by the PlayStation 2 on March 4, 2000, the GameCube on September 14, 2001 and the Xbox on November 15, 2001, respectively. The Dreamcast was among the first to be discontinued in 2001, followed by GameCube in 2007, Xbox in 2009, and PlayStation 2 in 2013. Meanwhile, the seventh generation of consoles started on November 22, 2005, with the launch of the Xbox 360. The major innovation of this generation was of full utilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |